|
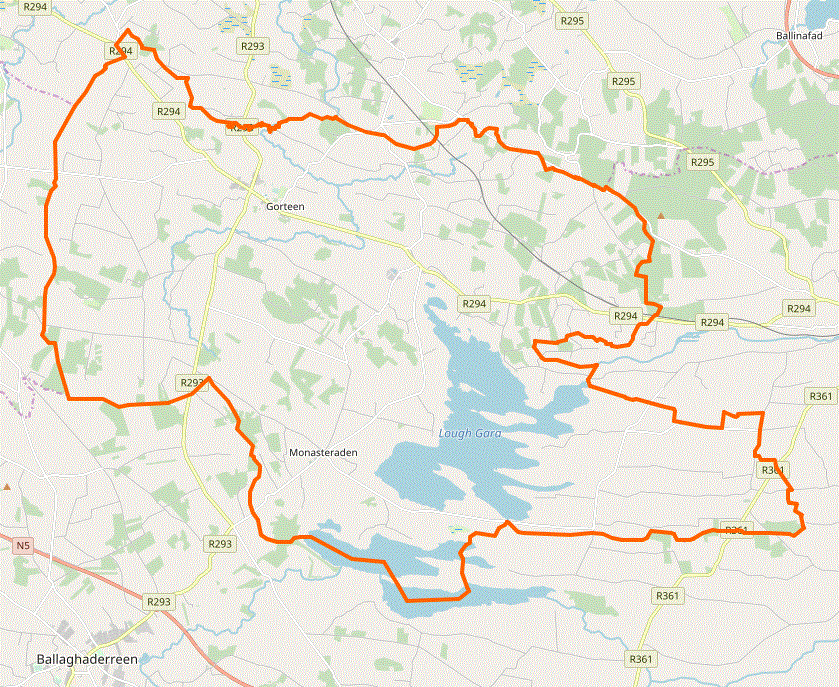
Lough Gara
Lough Gara () is a lake in Counties Sligo and Roscommon, Ireland. It is an Important Bird Area protecting 1,788 ha of which most (1,742 ha) is covered by a Ramsar Site. History Lough Gara was known in ancient times as Loch Techet, but the O’Garas, during their ownership of the Coolavin district from about the thirteenth century, renamed the lake "Loch Uí Ghadhra". The first documented reference appeared in 1285. Even though the family lost control of all their Coolavin townlands about 1650, their name has remained on the lake to the present day. The area around Lough Gara is referred to as "O'Gara heartland". Location and size Lough Gara is situated mainly in south County Sligo with a smaller part of the lake in County Roscommon. From north to south the lake spans about four miles. The widest section is a two and a half mile span. The lake lies south west of the Curlew Mountains with the town of Ballaghaderreen situated almost four miles to the southwest and the town of Boy ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
County Sligo
County Sligo ( , gle, Contae Shligigh) is a county in Ireland. It is located in the Border Region and is part of the province A province is almost always an administrative division within a country or state. The term derives from the ancient Roman '' provincia'', which was the major territorial and administrative unit of the Roman Empire's territorial possessions ou ... of Connacht. Sligo is the administrative capital and largest town in the county. Sligo County Council is the Local government in the Republic of Ireland, local authority for the county. The population of the county was 65,535 at the 2016 census. It is noted for Benbulben Mountain, one of Ireland's most distinctive natural landmarks. History The county was officially formed in 1585 by Sir Henry Sidney, Lord Deputy of Ireland, but did not come into effect until the chaos of the Nine Years' War (Ireland), Nine Years' War ended, in 1603. Its boundaries reflect the Ó Conchobhair Sligigh confederation of Lo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ballaghaderreen
Ballaghaderreen () is a town in County Roscommon, Ireland. It was part of County Mayo prior to 1898. It is located just off the N5 National primary road. The population was 1,808 in the 2016 census. History As of 1837, the town was recorded as having 1147 inhabitants in about 200 houses and as "rising in importance" as a post-town, being on the (then) new mail coach road from Ballina to Longford. As of the mid-19th century, markets were held on Fridays, with seven fairs held throughout the year. A court-house, market house and an infantry barracks to accommodate 94 persons had all been established by that time. In 1860, Ballaghaderreen Cathedral was dedicated as the cathedral for the Roman Catholic Diocese of Achonry. In March 2017, Ballaghaderreen became an Emergency Reception and Orientation Centre (EROC) for hundreds of refugees from the Syrian Civil War. In April 2018, the community was honoured with a People of the Year Award for welcoming the refugees into ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lakes Of County Sligo
A lake is an area filled with water, localized in a basin, surrounded by land, and distinct from any river or other outlet that serves to feed or drain the lake. Lakes lie on land and are not part of the ocean, although, like the much larger oceans, they do form part of the Earth's water cycle. Lakes are distinct from lagoons, which are generally coastal parts of the ocean. Lakes are typically larger and deeper than ponds, which also lie on land, though there are no official or scientific definitions. Lakes can be contrasted with rivers or streams, which usually flow in a channel on land. Most lakes are fed and drained by rivers and streams. Natural lakes are generally found in mountainous areas, rift zones, and areas with ongoing glaciation. Other lakes are found in endorheic basins or along the courses of mature rivers, where a river channel has widened into a basin. Some parts of the world have many lakes formed by the chaotic drainage patterns left over from the last ic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Important Bird Areas Of The Republic Of Ireland
Importance is a property of entities that matter or make a difference. For example, World War II was an important event and Albert Einstein was an important person because of how they affected the world. There are disagreements in the academic literature about what type of difference is required. According to the causal impact view, something is important if it has a big causal impact on the world. This view is rejected by various theorists, who insist that an additional aspect is required: that the impact in question makes a value difference. This is often understood in terms of how the important thing affects the well-being of people. So on this view, World War II was important, not just because it brought about many wide-ranging changes but because these changes had severe negative impacts on the well-being of the people involved. The difference in question is usually understood counterfactually as the contrast between how the world actually is and how the world would have be ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
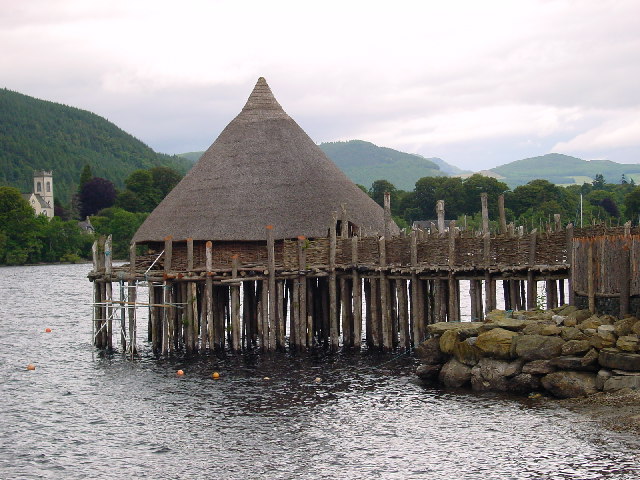
Crannóg
A crannog (; ga, crannóg ; gd, crannag ) is typically a partially or entirely artificial island, usually built in lakes and estuarine waters of Scotland, Wales, and Ireland. Unlike the prehistoric pile dwellings around the Alps, which were built on the shores and not inundated until later, crannogs were built in the water, thus forming artificial islands. Crannogs were used as dwellings over five millennia, from the European Neolithic Period to as late as the 17th/early 18th century. In Scotland there is no convincing evidence in the archaeological record of Early and Middle Bronze Age or Norse Period use. The radiocarbon dating obtained from key sites such as Oakbank and Redcastle indicates at a 95.4 per cent confidence level that they date to the Late Bronze Age to Early Iron Age. The date ranges fall ''after'' around 800 BC and so could be considered Late Bronze Age by only the narrowest of margins. Crannogs have been variously interpreted as free-standing wooden struct ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
River Shannon
The River Shannon ( ga, Abhainn na Sionainne, ', '), at in length, is the longest river in the British Isles. It drains the Shannon River Basin, which has an area of , – approximately one fifth of the area of the island of Ireland. The Shannon divides the west of Ireland (principally the province of Connacht) from the east and south ( Leinster and most of Munster). ( County Clare, being west of the Shannon but part of the province of Munster, is the major exception.) The river represents a major physical barrier between east and west, with fewer than thirty-five crossing points between Limerick city in the south and the village of Dowra in the north. The river takes its name after ''Sionna'', a Celtic goddess. Known as an important waterway since antiquity, the Shannon first appeared in maps by the Graeco-Egyptian geographer Ptolemy ( 100 – 170 AD). The river flows generally southwards from the Shannon Pot in County Cavan before turning west and emptying i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lough Key
Lough Key ( gle, Loch Cé) is a lake in Ireland. It is in the northwest of County Roscommon, northeast of the town of Boyle. The lough is believed to be named after a mythical figure named Cé. Name The name ''Lough Key'' comes from the Irish ''Loch Cé''. In Irish mythology, Cé was the druid of the god Nuada. He was wounded in the Second Battle of Mag Tuired and fled southward until he came to Carn Corrslebe, where he rested. He saw ahead of him a beautiful plain full of flowers. He sought to reach it, and when he did, he died. When his grave was dug there, a lake burst out of it, and flooded the whole plain. It was thus named Loch Cé after him. Geography The lake is in the northern part of the River Shannon drainage basin, and is fed by the Boyle River which flows from Lough Gara, through the town of Boyle, into Lough Key. From there it flows eastwards until it reaches the River Shannon just above Carrick-on-Shannon. Its area is and its average depth is . One can see ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Boyle River (Ireland)
The Boyle River is a river in Ireland. Forming part of the Shannon River Basin, it flows from Lough Gara on the Sligo/Roscommon border and thence through the town of Boyle to Lough Key. From there is continues eastwards through the village of Knockvicar to the River Shannon at Lough Drumharlow, near Carrick-on-Shannon. The length of the Boyle River (from its source in Mayo to the Shannon) is 64.4 km (40mi). The area of the Boyle river basin is 725 km2 Boyle River Basin The Upper Shannon catchment, above Carrick-on-Shannon (area: 1,301 km2), has two distinct reaches, the River Shannon (basin area: 576 km2), which rises in County Cavan, and the Boyle River (basin area: 725 km2), with its source in County Mayo, which have their confluence at Lough Eidin/Drumharlow, approximately 4.7 km upstream of Carrick-On-Shannon. The Boyle River has its origins in the rivers Lung and Breedoge, which flow into Lough Gara. The 29 km (18 miLung R ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lung River
The lungs are the primary organs of the respiratory system in humans and most other animals, including some snails and a small number of fish. In mammals and most other vertebrates, two lungs are located near the backbone on either side of the heart. Their function in the respiratory system is to extract oxygen from the air and transfer it into the bloodstream, and to release carbon dioxide from the bloodstream into the atmosphere, in a process of gas exchange. Respiration is driven by different muscular systems in different species. Mammals, reptiles and birds use their different muscles to support and foster breathing. In earlier tetrapods, air was driven into the lungs by the pharyngeal muscles via buccal pumping, a mechanism still seen in amphibians. In humans, the main muscle of respiration that drives breathing is the diaphragm. The lungs also provide airflow that makes vocal sounds including human speech possible. Humans have two lungs, one on the left and one on th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Boyle, County Roscommon
Boyle (; ) is a town in County Roscommon, Ireland. It is located at the foot of the Curlew Mountains near Lough Key in the north of the county. Carrowkeel Megalithic Cemetery, the Drumanone Dolmen and the lakes of Lough Arrow and Lough Gara are also close by. , the population of the town was 2,568. History Early history On 15 August 1599, the Battle of Curlew Pass between English and Irish forces was fought in the Curlew mountains during the Nine Years' War, between an English force under Sir Conyers Clifford and a native Irish force led by Aodh Ruadh Ó Domhnaill (Red Hugh O'Donnell). The English were ambushed and routed while marching through a pass in the Curlew Mountains, with the English forces suffering heavy casualties. Losses by allied Irish forces were not recorded. The Queen's principal secretary, Sir Robert Cecil, rated this defeat (and the simultaneous defeat of Harrington in Wicklow) as the two heaviest blows suffered by the English in Ireland. Boyle suff ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Coolavin
Coolavin (Irish ''Cúl ó bhFionn'') is a barony in south County Sligo, Ireland. It was created from the ancient túath of An Corann. The O'Garas were originally Lords of Coolavin. They were succeeded by the MacDermotts, a family of the Milesian clans, who still claim their head to be the Prince of Coolavin Prince of Coolavin was a title first applied by popular usage to Charles MacDermot, 1707–1758, then head of the MacDermot family of Moylurg. Coolavin () is a barony in south County Sligo in Ireland. Up to the late 16th century the head of th ... to this day. References Baronies of County Sligo {{sligo-geo-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |




.jpg)