|
Lotus 15
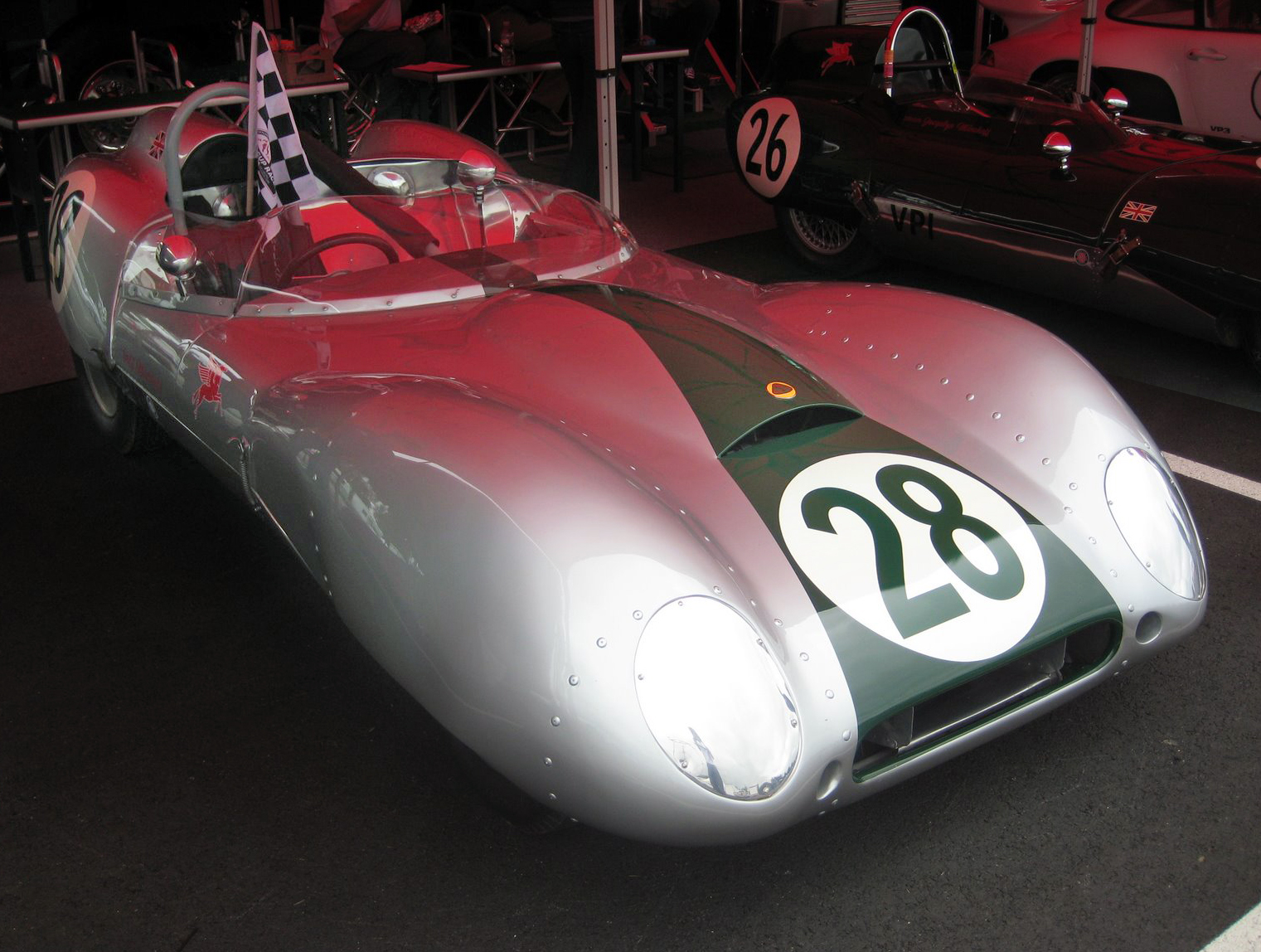
The Lotus 15 is a front-engine sports racing car designed by Colin Chapman of Lotus, built from 1958 until 1960. Series 1 The 15 is a two-seater, front-engine, rear wheel drive sports racer with an aluminium body over a space frame configuration. As opposed to the six cylinder Bristol 2L engine in its predecessor Lotus Mk.X, the Mk.15 was designed with a dry-sump, all aluminium, DOHC four cylinder Coventry Climax FPF engine of 1.5 to 2.5 Litre displacement built for Formula Two and Grand Prix racing, mated to Lotus' own 5 speed sequential transaxle nicknamed 'Queerbox'. It was designed in 1957, and the production began in late 1957. The spaceframe was similar to Lotus Eleven except for the Chapman strut rear suspension with inboard brakes and the accommodations for a larger engine, which included a slightly (7.5 degrees) tilted engine mounting space on the plan view, shifted to the right of the centerline in the front and left at the rear of the engine. This arrangement gave a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lotus Cars
Lotus Cars Limited is a British automotive company headquartered in Norfolk, England which manufactures sports cars and racing cars noted for their light weight and fine handling characteristics. Lotus was previously involved in Formula One racing, via Team Lotus, winning the Formula One World Championship seven times. Lotus Cars was founded and owned for many years by Colin Chapman. After his death and a period of financial instability, it was bought by General Motors, then Romano Artioli and DRB-HICOM through its subsidiary Proton. It is currently majority owned by Chinese multinational Geely, with Etika Automotive as a minority shareholder. The engineering consultancy firm Lotus Engineering, an offshoot of Lotus Cars, has facilities in the United Kingdom, United States, China, and Malaysia. Notable Lotus cars include the Lotus Seven, the Lotus Esprit and the Lotus Elan. History Early years The company was formed in 1952 as Lotus Engineering Ltd. by engineers Colin Ch ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chapman Strut
The Chapman strut is a design of independent rear suspension used for light cars, particularly sports and racing cars. It takes its name from, and is best known for its use by, Colin Chapman of Lotus. The characteristic feature of the Chapman strut is a long upright strut combining a coil spring and shock absorber, with a universal-jointed drive shaft itself forming the lower link of the suspension. Origins Stout Scarab The design's origin lies with William Stout's 1932 Stout Scarab. This rear-engined car used swing axle independent rear suspension, with long near-vertical coilover struts from high mounting points on the space frame chassis. Stout had also been an aircraft designer and considered that the long-travel oleo struts made, '' 'the airplane landing gear '' s' the easiest type of running gear for comfort yet devised.' '' The lower ends of the struts were attached to the swing axle casings by swivel bushes. Forward radius rods handled the longitudinal forces. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1959 Lotus 15 S
Events January * January 1 - Cuba: Fulgencio Batista flees Havana when the forces of Fidel Castro advance. * January 2 - Lunar probe Luna 1 was the first man-made object to attain escape velocity from Earth. It reached the vicinity of Earth's Moon, and was also the first spacecraft to be placed in heliocentric orbit. * January 3 ** The three southernmost atolls of the Maldive archipelago (Addu Atoll, Huvadhu Atoll and Fuvahmulah island) declare independence. ** Alaska is admitted as the 49th U.S. state. * January 4 ** In Cuba, rebel troops led by Che Guevara and Camilo Cienfuegos enter the city of Havana. ** Léopoldville riots: At least 49 people are killed during clashes between the police and participants of a meeting of the ABAKO Party in Léopoldville in the Belgian Congo. * January 6 ** Fidel Castro arrives in Havana. ** The International Maritime Organization is inaugurated. * January 7 – The United States recognizes the new Cuban government of Fidel Castro. * ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
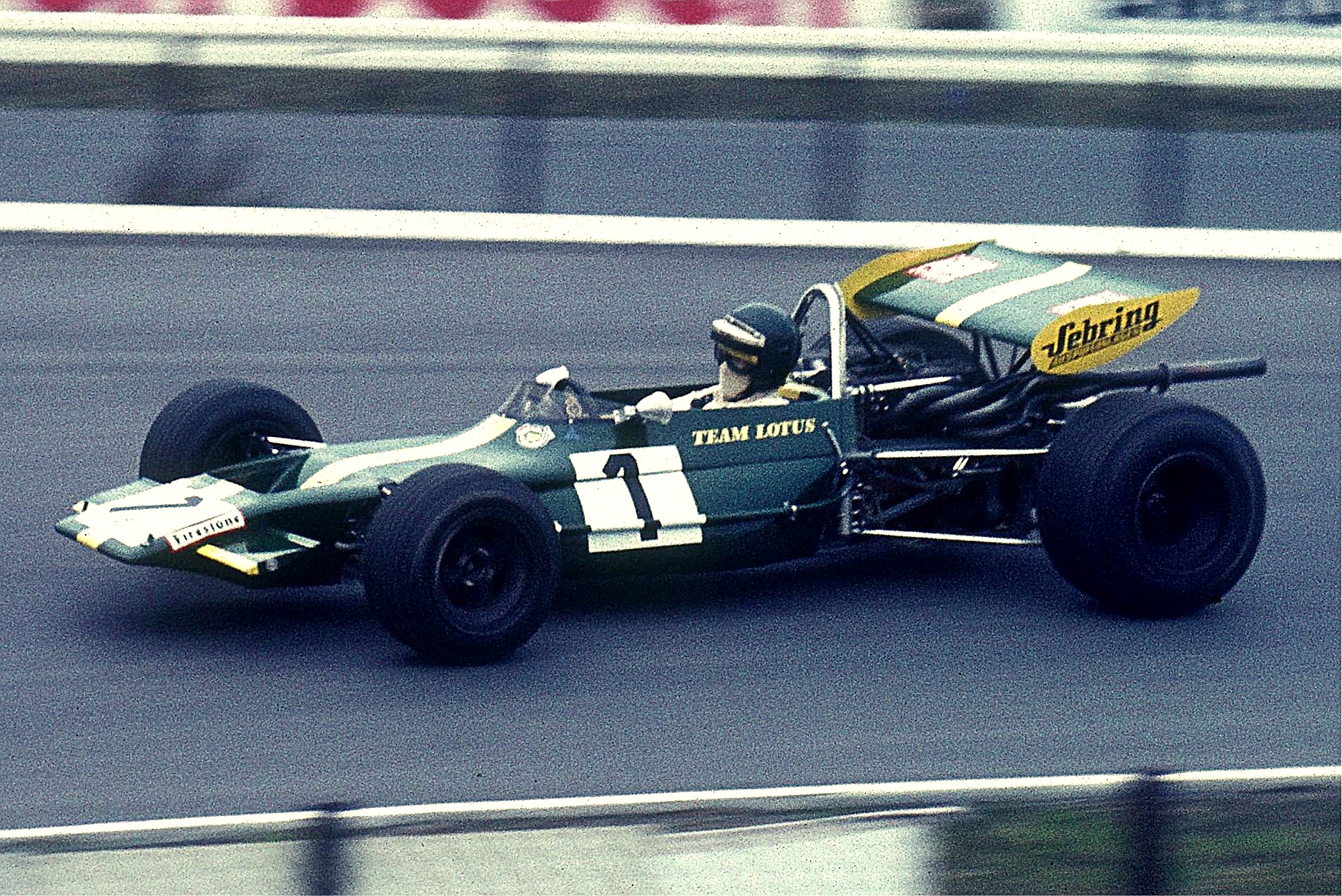
Lotus 16
The Lotus 16 was the second single-seat racing car designed by Colin Chapman, and was built by his Lotus Cars manufacturing company for the Team Lotus racing squad. The Lotus 16 was constructed to compete in both the Formula One and Formula Two categories, and was the first Lotus car to be constructed for Formula One competition. Its design carried over many technological features of the first Lotus single-seater, the Lotus 12, as well as incorporating ideas which Chapman had been developing while working on the Vanwall racing cars. Indeed, such was the visual similarity between the Vanwall and Lotus 16 designs that the Lotus was often dubbed the "''mini Vanwall''" by the contemporary motor sport press. Although the Lotus 16 only scored five Formula One World Championship points in the three seasons during which it was used, its raw pace pointed the way for its more successful successors, the Lotus 18 and 21. Design Colin Chapman had started building Ford-engined, Austin 7-ba ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Keith Duckworth
David Keith Duckworth (10 August 1933 – 18 December 2005) was an English mechanical engineer. He is most famous for designing the Cosworth DFV (Double Four Valve) engine, an engine that revolutionised the sport of Formula One. Early life and education Duckworth was born in Blackburn, Lancashire, and was educated at Giggleswick School. Duckworth served his two years of national service with the Royal Air Force, during which time he briefly trained to become a pilot but was grounded for dangerous and incompetent flying and was reclassified as a navigator. Duckworth claimed that allergy to medication he was receiving caused his flying problem - in civilian life he became a keen light aircraft and helicopter pilot. After completing his tour of duty, which he finished as a navigator, Duckworth studied engineering at Imperial College London, earning a BSc degree in 1955. Early career After university he began working for Lotus as a gearbox engineer. Given the task of fixing t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lotus 12
The Lotus 12 was a Formula Two and Formula One racing car. Design Colin Chapman's first foray into single-seater racing, the 12 appeared in 1957. It featured a number of important innovations Chapman would use on later models. To better use the power of the Coventry Climax engine, it was designed, as usual, for low weight and low drag, relying on a space frame. It placed the driver as low as possible, reducing the height of transmission tunnel by way of a "conceptually brilliant" five-speed sequential-shift transaxle located in the back. This transaxle was designed by Richard Ansdale and Harry Mundy. The gearbox had a (long-undiagnosed) oil starvation problem, thus earned the nickname "Queerbox" for its unreliability. Although the first two examples of Lotus 12 had De Dion rear suspension, it also introduced a new suspension configuration with what came to be called "Chapman struts" in the rear, essentially a MacPherson strut with a fixed length halfshaft with universal joints ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Formula Two
Formula Two (F2 or Formula 2) is a type of open-wheel formula racing category first codified in 1948. It was replaced in 1985 by Formula 3000, but revived by the FIA from 2009–2012 in the form of the FIA Formula Two Championship. The name returned in 2017 when the former GP2 Series became known as the FIA Formula 2 Championship. History While Formula One has generally been regarded as the pinnacle of open-wheeled auto racing, the high-performance nature of the cars and the expense involved in the series has always meant a need for a path to reach this peak. For much of the history of Formula One, Formula Two has represented the penultimate step on the motorsport ladder. Pre-war Prior to the Second World War, there usually existed a division of racing for cars smaller and less powerful than Grand Prix racers. This category was usually called voiturette ("small car") racing and provided a means for amateur or less experienced drivers and smaller marques to prove themselves. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Formula One
Formula One (also known as Formula 1 or F1) is the highest class of international racing for open-wheel single-seater formula racing cars sanctioned by the Fédération Internationale de l'Automobile (FIA). The World Drivers' Championship, which became the FIA Formula One World Championship in 1981, has been one of the premier forms of racing around the world since its inaugural season in 1950. The word ''formula'' in the name refers to the set of rules to which all participants' cars must conform. A Formula One season consists of a series of races, known as ''Grands Prix'', which take place worldwide on both purpose-built circuits and closed public roads. A points system is used at Grands Prix to determine two annual World Championships: one for drivers, the other for constructors. Each driver must hold a valid Super Licence, the highest class of racing licence issued by the FIA. The races must run on tracks graded "1" (formerly "A"), the highest grade-rating issued ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
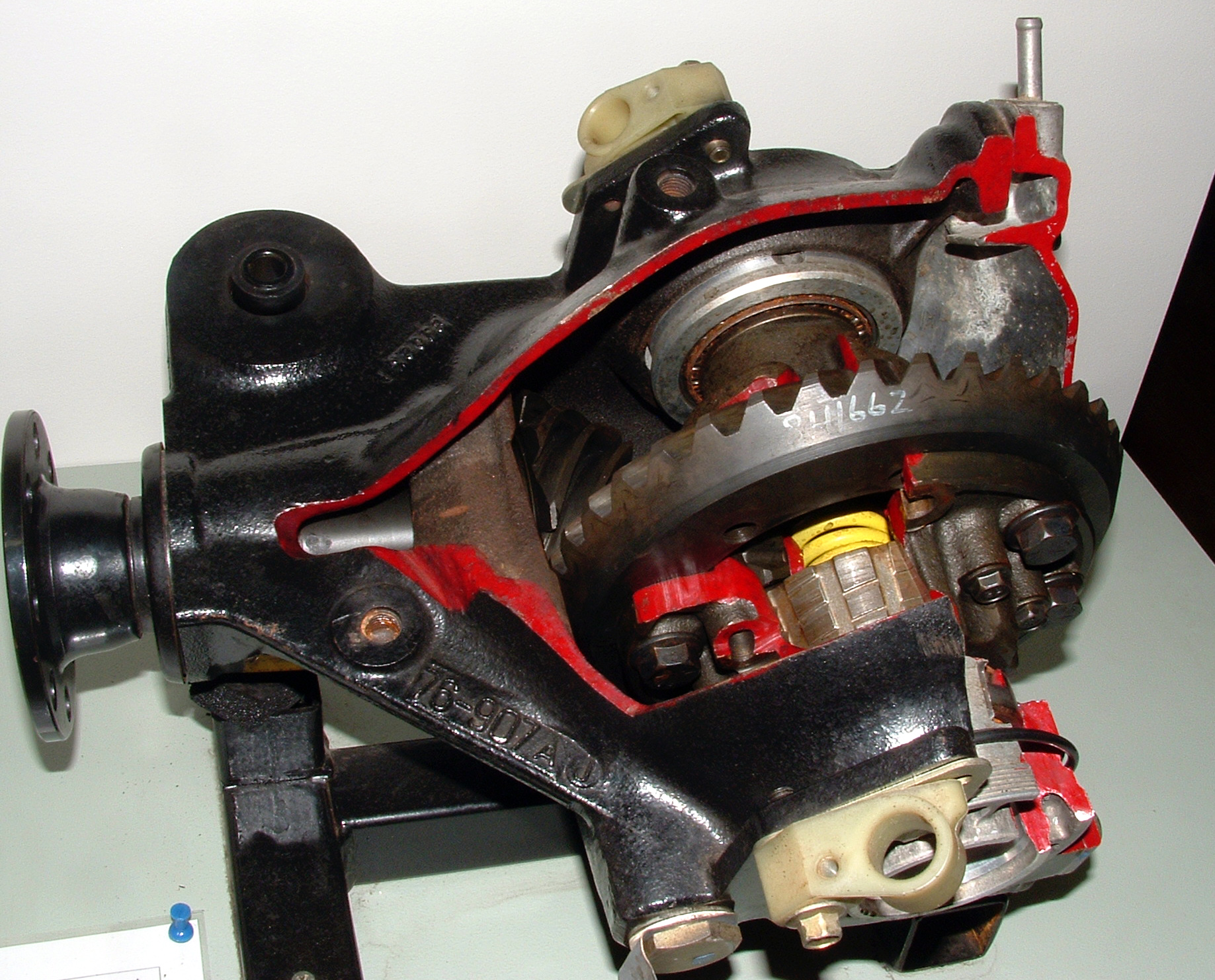
Halfshaft
An axle or axletree is a central shaft for a rotating wheel or gear. On wheeled vehicles, the axle may be fixed to the wheels, rotating with them, or fixed to the vehicle, with the wheels rotating around the axle. In the former case, bearings or bushings are provided at the mounting points where the axle is supported. In the latter case, a bearing or bushing sits inside a central hole in the wheel to allow the wheel or gear to rotate around the axle. Sometimes, especially on bicycles, the latter type axle is referred to as a ''spindle''. Terminology On cars and trucks, several senses of the word ''axle'' occur in casual usage, referring to the shaft itself, its housing, or simply any transverse pair of wheels. Strictly speaking, a shaft which rotates with the wheel, being either bolted or splined in fixed relation to it, is called an ''axle'' or ''axle shaft''. However, in looser usage, an entire assembly including the surrounding axle housing (typically a casting) is a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Limited-slip Differential
A limited-slip differential (LSD) is a type of differential that allows its two output shafts to rotate at different speeds but limits the maximum difference between the two shafts. Limited-slip differentials are often known by the generic trademark Positraction, a brand name owned by General Motors. In an automobile, such limited-slip differentials are sometimes used in place of a standard differential, where they convey certain dynamic advantages, at the expense of greater complexity. Early history In 1932, Ferdinand Porsche designed a Grand Prix racing car for the Auto Union company. The high power of the design caused one of the rear wheels to experience excessive wheel spin at any speed up to . In 1935, Porsche commissioned the engineering firm ZF to design a limited-slip differential to improve performance. The ZF "sliding pins and cams" became available, and one example was the Type B-70 used during the Second World War in the military VWs ( Kübelwagen and Schwimmwa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Graham Hill
Norman Graham Hill (15 February 1929 – 29 November 1975) was a British racing driver and team owner, who was the Formula One World Champion twice, winning in and as well as being runner up on three occasions (1963, 1964 and 1965). Despite not passing his driving test until 1953 when he was already 24 years of age, and only entering the world of motorsports a year later, Hill would go on to become one of the greatest drivers of his generation. Hill is most celebrated for being the only driver ever to win the Triple Crown of Motorsport, an achievement which he defined as winning the Indianapolis 500, the 24 Hours of Le Mans, and the Formula One World Drivers' Championship. While several of his peers have also espoused this definition, including fellow F1 World Champion Jacques Villeneuve, the achievement is today most commonly defined as including the Monaco Grand Prix rather than the Formula One World Championship. By this newer definition, Hill is still the only driver to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Williams & Pritchard (coachbuilders)
Williams & Pritchard Limited was a small coachbuilding business operating from First Avenue, Edmonton, London N18 which made lightweight sports and racing car bodies as well as runs of cars for small manufacturers fabricated using aluminium or composite construction or moulded fibre-glass. Start The business was founded in the late 1940s by Charlie Williams (1915-1969) from Corsica Coachworks and Len Pritchard (1919-2008) whose coachbuilding careers had been diverted by the war to building Spitfire aircraft. They began in Edmonton then worked from Hornsey with an extra workshop in Hammersmith before returning permanently to Edmonton. Clients The clients of Williams & Pritchard included: Colin Chapman, Lotus, AC (Aceca coupé), Lola, Cooper, Lister-Jaguar, Elva, John Surtees, Costin, Gordon-Keeble, BRM, John Sprinzel, Speedwell. The last coach building client of William's and Pritchard was designer David Gittens McLaren based Ikenga GT prototypes, constructed betwee ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |