|
Lophichthyidae
''Lophichthys boschmai'', also known as Arafura frogfish or Boschma's frogfish, is a species of anglerfishes closely related to frogfish. ''L. boschmai'' is the only species in the Lophichthydae family. ''L. boschmai'' were first reported by Marinus Boseman in 1964 to the Rijksmuseum van Natuurlijke Historie, now known as National Museum of Natural History in Leiden. The species was named after Dutch zoologist, Hildbrand Boschma.Boeseman, Marinus (1964)"Notes on the fishes of western New Guinea : II. ''Lophichthys boschmai'', a new genus and species from the Arafoera Sea" ''Zoologische Mededelingen''. 39 (2): 12–18. ISSNbr>0024-0672– via Naturalis. Like the true frogfishes, it is a small fish, no more than in length, with loose skin and a lure (esca) for attracting prey. The pectoral fins are prehensile, helping the fish move along the sea bed. Unlike true frogfishes, however, it does not have an enlarged and globose head. It lives in shallow waters off the coast of New ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lophiiformes
The anglerfish are fish of the teleost order Lophiiformes (). They are bony fish named for their characteristic mode of predation, in which a modified luminescent fin ray (the esca or illicium) acts as a lure for other fish. The luminescence comes from symbiotic bacteria, which are thought to be acquired from seawater, that dwell in and around the sea. Some anglerfish are notable for extreme sexual dimorphism and sexual symbiosis of the small male with the much larger female, seen in the suborder Ceratioidei, the deep sea anglerfish. In these species, males may be several orders of magnitude smaller than females. Anglerfish occur worldwide. Some are pelagic (dwelling away from the sea floor), while others are benthic (dwelling close to the sea floor). Some live in the deep sea (such as the Ceratiidae), while others on the continental shelf, such as the frogfishes and the Lophiidae (monkfish or goosefish). Pelagic forms are most often laterally compressed, whereas the ben ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
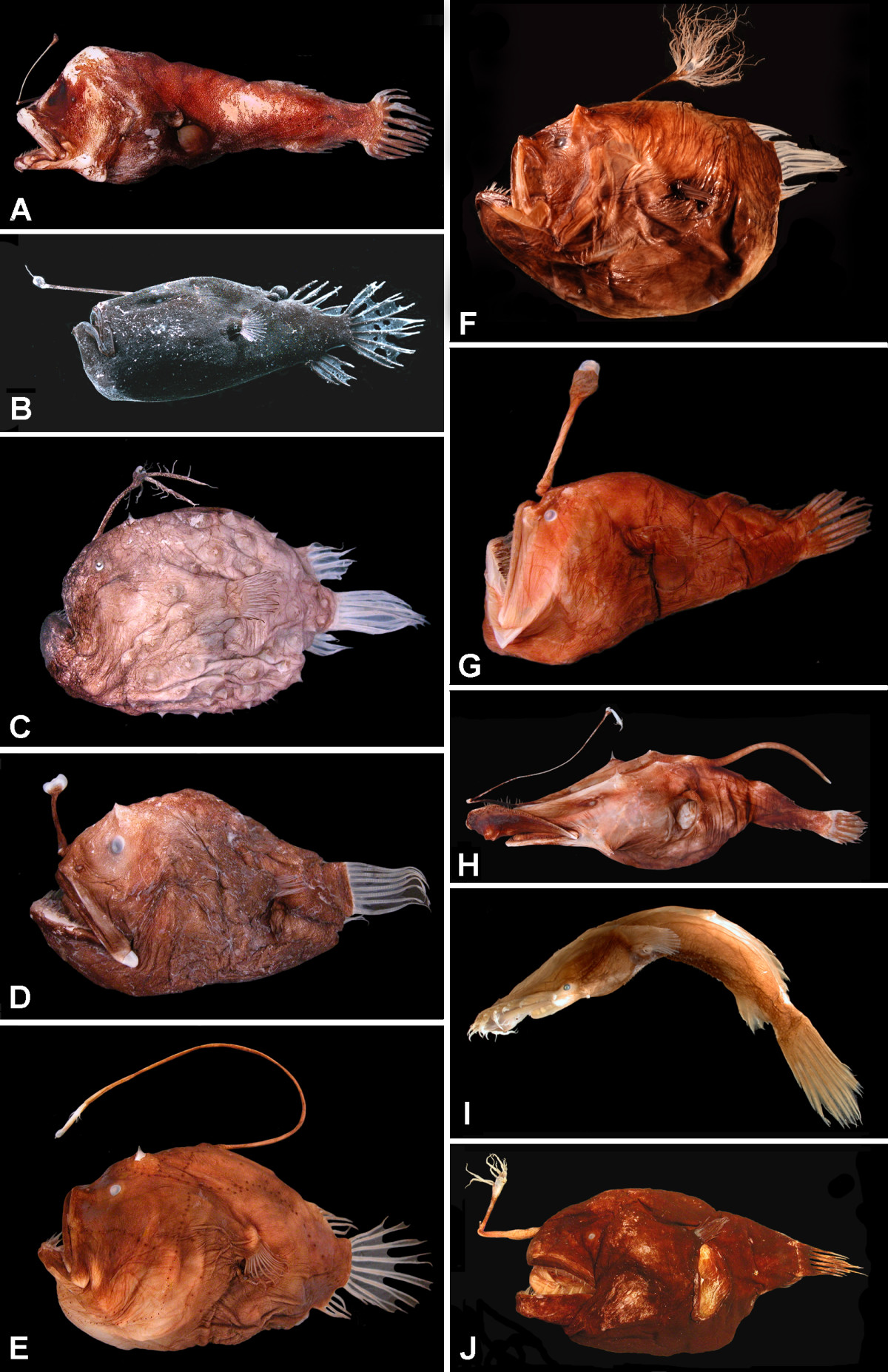
Anglerfish
The anglerfish are fish of the teleost order Lophiiformes (). They are bony fish named for their characteristic mode of predation, in which a modified luminescent fin ray (the esca or illicium) acts as a lure for other fish. The luminescence comes from symbiotic bacteria, which are thought to be acquired from seawater, that dwell in and around the sea. Some anglerfish are notable for extreme sexual dimorphism and sexual symbiosis of the small male with the much larger female, seen in the suborder Ceratioidei, the deep sea anglerfish. In these species, males may be several orders of magnitude smaller than females. Anglerfish occur worldwide. Some are pelagic (dwelling away from the sea floor), while others are benthic (dwelling close to the sea floor). Some live in the deep sea (such as the Ceratiidae), while others on the continental shelf, such as the frogfishes and the Lophiidae (monkfish or goosefish). Pelagic forms are most often laterally compressed, whereas the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Esca
The anglerfish are fish of the teleost order Lophiiformes (). They are bony fish named for their characteristic mode of predation, in which a modified luminescent fin ray (the esca or illicium) acts as a lure for other fish. The luminescence comes from symbiotic bacteria, which are thought to be acquired from seawater, that dwell in and around the sea. Some anglerfish are notable for extreme sexual dimorphism and sexual symbiosis of the small male with the much larger female, seen in the suborder Ceratioidei, the deep sea anglerfish. In these species, males may be several orders of magnitude smaller than females. Anglerfish occur worldwide. Some are pelagic (dwelling away from the sea floor), while others are benthic (dwelling close to the sea floor). Some live in the deep sea (such as the Ceratiidae), while others on the continental shelf, such as the frogfishes and the Lophiidae (monkfish or goosefish). Pelagic forms are most often laterally compressed, whereas the benth ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Animalia
Animals are multicellular, eukaryotic organisms in the biological kingdom Animalia. With few exceptions, animals consume organic material, breathe oxygen, are able to move, can reproduce sexually, and go through an ontogenetic stage in which their body consists of a hollow sphere of cells, the blastula, during embryonic development. Over 1.5 million living animal species have been described—of which around 1 million are insects—but it has been estimated there are over 7 million animal species in total. Animals range in length from to . They have complex interactions with each other and their environments, forming intricate food webs. The scientific study of animals is known as zoology. Most living animal species are in Bilateria, a clade whose members have a bilaterally symmetric body plan. The Bilateria include the protostomes, containing animals such as nematodes, arthropods, flatworms, annelids and molluscs, and the deuterostomes, containing the echinode ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ogcocephalidae
Ogcocephalidae is a family of anglerfish specifically adapted for a benthic lifestyle of crawling about on the seafloor. Ogcocephalid anglerfish are sometimes referred to as batfishes,Family Ogcocephalidae - Batfishes. FishBase. 2016. deep-sea batfishes, handfishes, and seabats. They are found in tropical and subtropical oceans worldwide. They are mostly found at depths between , but have been recorded as deep as . A few species live in much shallower coastal waters and, exceptionally, may enter river estuaries. They are dorsoventrally compressed fishes similar in appearance to , with a large circular or triangular head (box-shaped in ''C ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Goosefish
Goosefishes are anglerfishes in the family Lophiidae found in the Arctic, Atlantic, Indian, and Pacific Oceans, where they live on sandy and muddy bottoms of the continental shelf and continental slope, to depths of more than . Like most other anglerfishes, they have a very large head with a large mouth that bears long, sharp, recurved teeth. Also like other anglerfishes, the first spine of the spinous dorsal fin has been modified as an angling apparatus (illicium) that bears a bulb-like or fleshy lure (esca). The angling apparatus is located at the tip of the snout just above the mouth and is used to attract prey. Lophiid anglerfishes also have two or three other dorsal fin spines located more posteriorly on the head, and a separate spinous dorsal fin with one to three spines located more posteriorly on the body just in front of the soft dorsal fin. In the more primitive anglerfish genera (''Sladenia'' and ''Lophiodes''), the gill opening extends partially in front of the elonga ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Frogfish
Frogfishes are any member of the anglerfish family Antennariidae, of the order Lophiiformes. Antennariids are known as anglerfish in Australia, where the term "frogfish" refers to members of the unrelated family Batrachoididae. Frogfishes are found in almost all tropical and subtropical oceans and seas around the world, the primary exception being the Mediterranean Sea. Frogfishes are small, short and stocky, and sometimes covered in spinules and other appendages to aid in camouflage. The camouflage aids in protection from predators and enables them to lure prey. Many species can change colour; some are covered with other organisms such as algae or hydrozoa. In keeping with this camouflage, frogfishes typically move slowly, lying in wait for prey, and then striking extremely rapidly, in as little as 6 milliseconds. Few traces of frogfishes remain in the fossil record, though ''Antennarius monodi'' is known from the Miocene of Algeria and ''Eophryne barbuttii'' is known from ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tetrabrachiidae
Tetrabrachiidae, or the four-armed frogfishes, is a family of anglerfishes found in relatively shallow waters of the eastern Indian Ocean and western Pacific Ocean reaching from Indonesia and New Guinea to Australia Australia, officially the Commonwealth of Australia, is a Sovereign state, sovereign country comprising the mainland of the Australia (continent), Australian continent, the island of Tasmania, and numerous List of islands of Australia, sma .... They prefer living in regions of the ocean floor composed of soft sediments. References * Lophiiformes Marine fish families {{Lophiiformes-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sea Toad
The sea toads and coffinfishes are a family of deep-sea anglerfishes known as the Chaunacidae. These are bottom-dwelling fishes found on the continental slopes of the Atlantic, Indian, and Pacific Oceans, at depths to at least . There have also been findings of deep-sea anglerfishes off the coasts of Australia and New Caledonia. Other findings suggest some genera of Chaunacidae are found near volcanic slopes encrusted with manganese. Of the two genera in the family, '' Chaunacops'' typically occurs at deeper depths than ''Chaunax'', but with considerable overlap. They have large, globose bodies and short, compressed tails, and are covered with small, spiny scales. The largest are about in length. During their gill ventilatory cycle, ''Chaunacidae'' are able to take in high volumes of water, increasing their total body volume by 30%. The first dorsal fin A dorsal fin is a fin located on the back of most marine and freshwater vertebrates within various taxa of the animal k ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Continental Shelf
A continental shelf is a portion of a continent that is submerged under an area of relatively shallow water, known as a shelf sea. Much of these shelves were exposed by drops in sea level during glacial periods. The shelf surrounding an island is known as an ''insular shelf''. The continental margin, between the continental shelf and the abyssal plain, comprises a steep continental slope, surrounded by the flatter continental rise, in which sediment from the continent above cascades down the slope and accumulates as a pile of sediment at the base of the slope. Extending as far as 500 km (310 mi) from the slope, it consists of thick sediments deposited by turbidity currents from the shelf and slope. The continental rise's gradient is intermediate between the gradients of the slope and the shelf. Under the United Nations Convention on the Law of the Sea, the name continental shelf was given a legal definition as the stretch of the seabed adjacent to the shores of a par ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Benthic
The benthic zone is the ecological region at the lowest level of a body of water such as an ocean, lake, or stream, including the sediment surface and some sub-surface layers. The name comes from ancient Greek, βένθος (bénthos), meaning "the depths." Organisms living in this zone are called benthos and include microorganisms (e.g., bacteria and fungi) as well as larger invertebrates, such as crustaceans and polychaetes. Organisms here generally live in close relationship with the substrate and many are permanently attached to the bottom. The benthic boundary layer, which includes the bottom layer of water and the uppermost layer of sediment directly influenced by the overlying water, is an integral part of the benthic zone, as it greatly influences the biological activity that takes place there. Examples of contact soil layers include sand bottoms, rocky outcrops, coral, and bay mud. Description Oceans The benthic region of the ocean begins at the shore line (intertidal ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Western New Guinea
Western New Guinea, also known as Papua, Indonesian New Guinea, or Indonesian Papua, is the western half of the Melanesian island of New Guinea which is administered by Indonesia. Since the island is alternatively named as Papua, the region is also called West Papua ( id, Papua Barat). Lying to the west of Papua New Guinea and considered a part of the Australian continent, the territory is almost entirely in the Southern Hemisphere and includes the Schouten and Raja Ampat archipelagoes. The region is predominantly covered with ancient rainforest where numerous traditional tribes live such as the Dani of the Baliem Valley although a large proportion of the population live in or near coastal areas with the largest city being Jayapura. Within five years following its proclamation of independence in 1945, the Republic of Indonesia (for a time part of the United States of Indonesia) took over all the former territories of the Dutch East Indies except Western New Guinea, acco ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |

.jpg)




