|
London In World War II
As the national capital, and by far the largest city, London was central to the British war effort. It was the favourite target of the Luftwaffe (German Air Force) in 1940, and in 1944-45 the target of the V-1 flying bomb, V-1 cruise missile and V-2 rocket attacks. The Blitz In 1940-41 and again in 1944–45, London suffered severe damage, being bombed extensively by the ''Luftwaffe'' as a part of The Blitz. Prior to the bombing, hundreds of thousands of children in London were evacuated to the countryside to avoid the bombing. Civilians took shelter from the air raider Air raid shelter#London Underground tube stations, in underground stations. The heaviest bombing took place between 7 September 1940 and 10 May 1941. During this period, London was subjected to 71 separate raids, receiving over 18,000 tonnes of high explosive. Less intensive bombing followed over the following few years as Adolf Hitler concentrated on the Eastern front. London suffered severe damage and heavy ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
London At War, 1942 D9314
London is the capital and List of urban areas in the United Kingdom, largest city of England and the United Kingdom, with a population of just under 9 million. It stands on the River Thames in south-east England at the head of a estuary down to the North Sea, and has been a major settlement for two millennia. The City of London, its ancient core and financial centre, was founded by the Roman Empire, Romans as ''Londinium'' and retains its medieval boundaries.See also: Independent city#National capitals, Independent city § National capitals The City of Westminster, to the west of the City of London, has for centuries hosted the national Government of the United Kingdom, government and Parliament of the United Kingdom, parliament. Since the 19th century, the name "London" has also referred to the metropolis around this core, historically split between the Counties of England, counties of Middlesex, Essex, Surrey, Kent, and Hertfordshire, which largely comprises Greater London ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Port Of London
The Port of London is that part of the River Thames in England lying between Teddington Lock and the defined boundary (since 1968, a line drawn from Foulness Point in Essex via Gunfleet Old Lighthouse to Warden Point in Kent) with the North Sea and including any associated docks. Once the largest port in the world, it was the United Kingdom's largest port as of 2020.New data appended annually. Usage is largely governed by the Port of London Authority ("PLA"), a public trust established in 1908; while mainly responsible for coordination and enforcement of activities it also has some minor operations of its own. The port can handle cruise liners, roll-on roll-off ferries and cargo of all types at the larger facilities in its eastern extent. As with many similar historic European ports, such as Antwerp and Rotterdam, many activities have steadily moved downstream towards the open sea as ships have grown larger and the land upriver taken over for other uses. History The Port of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
History Of London
The history of London, the capital city of England and the United Kingdom, extends over 2000 years. In that time, it has become one of the world's most significant financial and cultural capital cities. It has withstood plague, devastating fire, civil war, aerial bombardment, terrorist attacks, and riots. The City of London is the historic core of the Greater London metropolis, and is today its primary financial district, though it represents only a small part of the wider metropolis. Foundations and prehistory Some recent discoveries indicate probable very early settlements near the Thames in the London area. In 1993, the remains of a Bronze Age bridge were found on the Thames's south foreshore, upstream of Vauxhall Bridge. This bridge either crossed the Thames or we ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Titmuss, Richard
Richard Morris Titmuss (1907–1973) was a pioneering British social researcher and teacher. He founded the academic discipline of social administration (now largely known in universities as social policy) and held the founding chair in the subject at the London School of Economics. His books and articles of the 1950s helped to define the characteristics of Britain's post World War II welfare state and of a universal welfare society, in ways that parallel the contributions of Alva Myrdal and Gunnar Myrdal in Sweden. He is honoured in the Richard Titmuss Chair in Social Policy at the LSE, which is currently held by Julian Le Grand. Titmuss's association with eugenics extended beyond the Galton Institute, British Eugenics Society, to encompass other personal and intellectual connections. He is also honoured by the annual Richard Titmuss Memorial Lecture in the Paul Baerwald School of Social Work at the Hebrew University of Jerusalem, Israel. Early life Titmuss was born 16 Oct ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
United Kingdom Home Front During World War II
The United Kingdom home front during World War II covers the political, social and economic history during 1939–1945. The war was expensive and financed through high taxes, selling off assets, and accepting large amounts of Lend Lease from the US and Canada. The US provided $30 billion in munitions, while Canada also contributed aid. American and Canadian aid did not have to be repaid, but there were also American loans that were repaid. Britain’s total mobilization during this period proved successful in winning the war by maintaining strong public support. The media dubbed it a “people’s war,” which caught on and signified the popular demand for planning and an expanded welfare state. By 1945, the Post-war consensus emerged, delivering a welfare state. The Royal family played major symbolic roles during the war. They refused to leave London during the Blitz and visited troops, munition factories, dockyards, and hospitals all over the country. The British relied ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Air Raid Shelter Under The Railway Arches, South East London, England, 1940 D1587
The atmosphere of Earth is the layer of gases, known collectively as air, retained by Earth's gravity that surrounds the planet and forms its planetary atmosphere. The atmosphere of Earth protects life on Earth by creating pressure allowing for liquid water to exist on the Earth's surface, absorbing ultraviolet solar radiation, warming the surface through heat retention (greenhouse effect), and reducing temperature extremes between day and night (the diurnal temperature variation). By mole fraction (i.e., by number of molecules), dry air contains 78.08% nitrogen, 20.95% oxygen, 0.93% argon, 0.04% carbon dioxide, and small amounts of other gases. Air also contains a variable amount of water vapor, on average around 1% at sea level, and 0.4% over the entire atmosphere. Air composition, temperature, and atmospheric pressure vary with altitude. Within the atmosphere, air suitable for use in photosynthesis by terrestrial plants and breathing of terrestrial animals is found only in Ea ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Double-Cross System
The Double-Cross System or XX System was a World War II counter-espionage and deception operation of the British Security Service (a civilian organisation usually referred to by its cover title MI5). Nazi agents in Britain – real and false – were captured, turned themselves in or simply announced themselves, and were then used by the British to broadcast mainly disinformation to their Nazi controllers. Its operations were overseen by the Twenty Committee under the chairmanship of John Cecil Masterman; the name of the committee comes from the number 20 in Roman numerals: "XX" (i.e. a double cross). The policy of MI5 during the war was initially to use the system for counter-espionage Counterintelligence is an activity aimed at protecting an agency's intelligence program from an opposition's intelligence service. It includes gathering information and conducting activities to prevent espionage, sabotage, assassinations or ot .... It was only later that its potential for dece ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
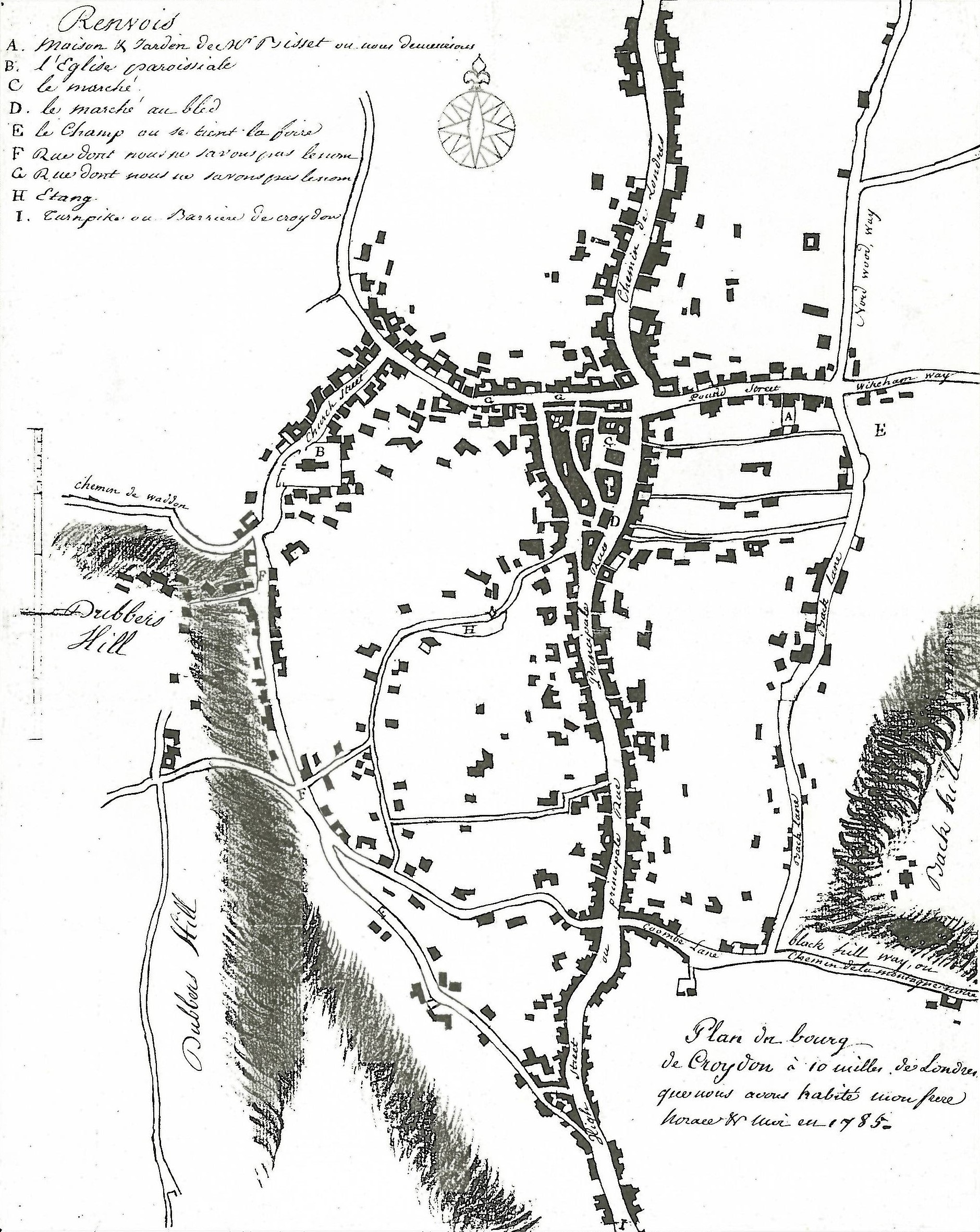
Croydon
Croydon is a large town in south London, England, south of Charing Cross. Part of the London Borough of Croydon, a local government district of Greater London. It is one of the largest commercial districts in Greater London, with an extensive shopping district and night-time economy. The entire town had a population of 192,064 as of 2011, whilst the wider borough had a population of 384,837. Historically an ancient parish in the Wallington hundred of Surrey, at the time of the Norman conquest of England Croydon had a church, a mill, and around 365 inhabitants, as recorded in the Domesday Book of 1086. Croydon expanded in the Middle Ages as a market town and a centre for charcoal production, leather tanning and brewing. The Surrey Iron Railway from Croydon to Wandsworth opened in 1803 and was an early public railway. Later 19th century railway building facilitated Croydon's growth as a commuter town for London. By the early 20th century, Croydon was an important industria ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Adolf Hitler
Adolf Hitler (; 20 April 188930 April 1945) was an Austrian-born German politician who was dictator of Nazi Germany, Germany from 1933 until Death of Adolf Hitler, his death in 1945. Adolf Hitler's rise to power, He rose to power as the leader of the Nazi Party, becoming the Chancellor of Germany, chancellor in 1933 and then taking the title of in 1934. During his dictatorship, he initiated European theatre of World War II, World War II in Europe by invasion of Poland, invading Poland on 1 September 1939. He was closely involved in military operations throughout the war and was central to the perpetration of the Holocaust: the genocide of Holocaust victims, about six million Jews and millions of other victims. Hitler was born in Braunau am Inn in Austria-Hungary and was raised near Linz. He lived in Vienna later in the first decade of the 1900s and moved to Germany in 1913. He was decorated during his Military career of Adolf Hitler, service in the German Army in Worl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Heinkel He 111 Over Wapping, East London
Heinkel Flugzeugwerke () was a German aircraft manufacturing company founded by and named after Ernst Heinkel. It is noted for producing bomber aircraft for the Luftwaffe in World War II and for important contributions to high-speed flight, with the pioneering examples of a successful liquid-fueled rocket and a turbojet-powered aircraft in aviation history, with both Heinkel designs' first flights occurring shortly before the outbreak of World War II in Europe. History Following the successful career of Ernst Heinkel as the chief designer for the Hansa-Brandenburg aviation firm in World War I, Heinkel's own firm was established at Warnemünde in 1922, after the restrictions on German aviation imposed by the Treaty of Versailles were relaxed. By 1929, the firm's compressed air-powered catapults were in use on the German Norddeutscher Lloyd ocean-liners and to launch short-range mail planes from the liners' decks. The company's first post-World War I aircraft design success was ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Air Raid Shelter
Air raid shelters are structures for the protection of non-combatants as well as combatants against enemy attacks from the air. They are similar to bunkers in many regards, although they are not designed to defend against ground attack (but many have been used as defensive structures in such situations). During World War II, many types of structures were used as air raid shelters, such as cellars, Hochbunkers (in Germany), basements, and underpasses. Bombing raids during World War I led the UK to build 80 specially adapted London Underground stations as shelters. However, during World War II, the government initially ruled out using these as shelters. After Londoners flooded into underground stations during The Blitz, the government reversed its policy. The UK began building street communal shelters as air raid shelters in 1940. Anderson shelters, designed in 1938 and built to hold up to six people, were in common use in the UK. Indoor shelters known as Morrison shelters were int ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |