|
Lomer (saint)
Lomer (died January 19th, 593), also known as Laumer, Laudomarus, Launomar, or Launomaro, is a Christian saint whose feast day is January 19. He founded an abbey at Corbion near Chartres in present-day France. The ''vita'' of Saint Lomer reveals that, as a youth, Lomer was a shepard, before being accepted into the monastery of St. Mesmin, near Orleans, and would eventually become a priest in Chartres. The ''vita'' also states that Lomer lived to be more than one hundred years old. One known copy of this ''vita'' was begun by Orderic Vitalis while he was copyist at the library of Saint-Évroul. Lomer was initially trained for the priesthood by a priest by the name of Chirmirius, was ordained, and then served as priest in Chartres and the surrounds, were he was made both canon and cellarer. Later in life, Lomer withdrew to live a eremitic lifestyle in the forests of La Perche. Due to his reputation for performing miracles, including the gift of prophecy, a number of disciples cam ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Moutiers-au-Perche (61) Église Notre-Dame-du-Mont-Harou - Intérieur - Retable Du Maître-autel - 03
Moutiers-au-Perche () is a commune in the Orne department in north-western France. Geography Tourouvre au Perche along with the communes of Feings, Longny les Villages, Le Mage, Tourouvre au Perche and Charencey shares part of the Forets, etangs et tourbieres du Haut-Perche a Natura 2000 conservation site. The site measures 3670 hectares and is home to fifteen species protected Flora and Fauna. In addition the Commune along with another 70 communes shares part of a 47,681 hectare, Natura 2000 conservation area, called the Forêts et étangs du Perche. Points of interest National heritage sites *Notre-Dame-du-Mont-Harou an eleventh century church, that was registered as a Monument historique ''Monument historique'' () is a designation given to some national heritage sites in France. It may also refer to the state procedure in France by which National Heritage protection is extended to a building, a specific part of a building, a coll ... in 1941. See also * Communes ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cenobitic Monasticism
Cenobitic (or coenobitic) monasticism is a monastic tradition that stresses community life. Often in the West the community belongs to a religious order, and the life of the cenobitic monk is regulated by a religious rule, a collection of precepts. The older style of monasticism, to live as a hermit, is called eremitic. A third form of monasticism, found primarily in Eastern Christianity, is the skete. The English words "cenobite" and "cenobitic" are derived, via Latin, from the Greek words ''koinos'' (κοινός), "common", and ''bios'' (βίος), "life". The adjective can also be cenobiac (κοινοβιακός, ''koinobiakos'') or cœnobitic (obsolete). A group of monks living in community is often referred to as a cenobium. Cenobitic monasticism appears in several religious traditions, though most commonly in Buddhism and Christianity. Origins The word ''cenobites'' was initially applied to the followers of Pythagoras in Crotona, Italy, who founded a commune not just ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
430s Births '', 2010
{{Numberdis ...
43 may refer to: * 43 (number) * one of the years 43 BC, AD 43, 1943, 2043 * Licor 43, also known as "Cuarenta Y Tres" ("Forty-three" in Spanish) * George W. Bush, 43rd President of the United States, nicknamed "Bush 43" to distinguish from his father * "Forty Three", a song by Karma to Burn from the album ''Appalachian Incantation Appalachian may refer to: * Appalachian Mountains, a major mountain range in eastern United States and Canada * Appalachian Trail, a hiking trail in the eastern United States * The people of Appalachia and their culture ** Appalachian Americans, e ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Robert Bartlett (historian)
Robert John Bartlett, CBE, FBA, FRSE (born 27 November 1950 in Streatham) is an English historian and medievalist. He is Bishop Wardlaw Professor of Mediaeval History Emeritus at the University of St Andrews. After attending Battersea Grammar School in London (1962 to 1969), he studied at Peterhouse, Cambridge, St John's College, Oxford and Princeton University as a Jane Eliza Procter Visiting Fellow. He obtained research fellowships at several institutions, including the University of Michigan and University of Göttingen, before working at the University of Edinburgh, the University of Chicago and the University of St Andrews, where he currently resides. He is particularly known for his work ''The Making of Europe: Conquest, Colonization and Cultural Change, 950-1350'', which won the Wolfson History Prize in 1993. He specializes in medieval colonialism, the cult of saints, and England between the 11th century and the 14th century. He gave the 2007 Ford Lectures at the Univers ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Abbie Farwell Brown
Abbie Farwell Brown (August 21, 1871March 5, 1927) was an American author. Biography Brown was born in Boston, Massachusetts, the first of two daughters of Benjamin F. Brown, a descendant of Isaac Allerton, and Clara Neal Brown, who contributed to ''The Youth's Companion''. Her sister Ethel became an author and illustrator under the name Ann Underhill. Her family, for ten generations, had only resided in New England, and Brown herself spent her entire life in her family's Beacon Hill home. Brown was valedictorian of the Bowdoin School in 1886. She then attended the Girls' Latin School, where she was friends with Josephine Preston Peabody. She was the driving force behind the newly created school newspaper, ''The Jabberwock'', named by Brown after the poem by Lewis Carroll. They wrote to Carroll for permission to use the name and Carroll wrote back, wishing them "all success to the forthcoming magazine". The school, now Boston Latin Academy, still publishes ''The Jabberw ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Saint Nicholas
Saint Nicholas of Myra, ; la, Sanctus Nicolaus (traditionally 15 March 270 – 6 December 343), also known as Nicholas of Bari, was an early Christian bishop of Greeks, Greek descent from the maritime city of Myra in Asia Minor (; modern-day Demre, Turkey) during the time of the Roman Empire. Because of the many miracles attributed to his intercession, he is also known as Nicholas the Wonderworker. Saint Nicholas is the patron saint of sailors, merchants, archers, repentant thieves, children, brewers, pawnbrokers, unmarried people, and students in various cities and countries around Europe. His reputation evolved among the pious, as was common for early Christian saints, and his legendary habit of secret gift-giving gave rise to the traditional model of Santa Claus ("Saint Nick") through Sinterklaas. Little is known about the historical Saint Nicholas. The earliest accounts of his life were written centuries after his death and probably contain legendary elaborations. He is ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
French Wars Of Religion
The French Wars of Religion is the term which is used in reference to a period of civil war between French Catholic Church, Catholics and Protestantism, Protestants, commonly called Huguenots, which lasted from 1562 to 1598. According to estimates, between two and four million people died from violence, famine or diseases which were directly caused by the conflict; additionally, the conflict severely damaged the power of the French monarchy. The fighting ended in 1598 when Henry of Navarre, who had converted to Catholicism in 1593, was proclaimed Henry IV of France and issued the Edict of Nantes, which granted substantial rights and freedoms to the Huguenots. However, the Catholics continued to have a hostile opinion of Protestants in general and they also continued to have a hostile opinion of him as a person, and his assassination in 1610 triggered a fresh round of Huguenot rebellions in the 1620s. Tensions between the two religions had been building since the 1530s, exacerba ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
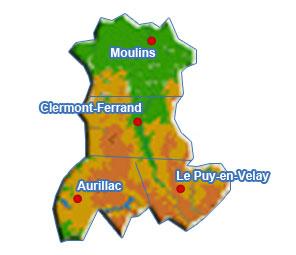
Auvergne
Auvergne (; ; oc, label=Occitan, Auvèrnhe or ) is a former administrative region in central France, comprising the four departments of Allier, Puy-de-Dôme, Cantal and Haute-Loire. Since 1 January 2016, it has been part of the new region Auvergne-Rhône-Alpes.. The administrative region of Auvergne is larger than the historical province of Auvergne, one of the seven counties of Occitania, and includes provinces and areas that historically were not part of Auvergne. The Auvergne region is composed of the following old provinces: * Auvergne: departments of Puy-de-Dôme, Cantal, northwest of Haute-Loire, and extreme south of Allier. The province of Auvergne is entirely contained inside the Auvergne region * Bourbonnais: department of Allier. A small part of Bourbonnais lies outside Auvergne, in the neighbouring Centre-Val de Loire region (south of the department of Cher). * Velay: centre and southeast of department of Haute-Loire. Velay is entirely contained inside the Auvergne r ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Priory
A priory is a monastery of men or women under religious vows that is headed by a prior or prioress. Priories may be houses of mendicant friars or nuns (such as the Dominicans, Augustinians, Franciscans, and Carmelites), or monasteries of monks or nuns (as with the Benedictines). Houses of canons regular and canonesses regular also use this term, the alternative being "canonry". In pre-Reformation England, if an abbey church was raised to cathedral status, the abbey became a cathedral priory. The bishop, in effect, took the place of the abbot, and the monastery itself was headed by a prior. History Priories first came to existence as subsidiaries to the Abbey of Cluny. Many new houses were formed that were all subservient to the abbey of Cluny and called Priories. As such, the priory came to represent the Benedictine ideals espoused by the Cluniac reforms as smaller, lesser houses of Benedictines of Cluny. There were likewise many conventual priories in Germany and Italy du ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Neustria
Neustria was the western part of the Kingdom of the Franks. Neustria included the land between the Loire and the Silva Carbonaria, approximately the north of present-day France, with Paris, Orléans, Tours, Soissons as its main cities. It later referred to the region between the Seine and the Loire rivers known as the ''regnum Neustriae'', a constituent subkingdom of the Carolingian Empire and then West Francia. The Carolingian kings also created a March of Neustria which was a frontier duchy against the Bretons and Vikings that lasted until the Capetian monarchy in the late 10th century, when the term was eclipsed as a European political or geographical term. Name The name ''Neustria'' is mostly explained as "new western land", although Taylor (1848) suggested the interpretation of "northeastern land". '' Nordisk familjebok'' (1913) even suggested "not the eastern land" (''icke östland''). Augustin Thierry (1825) assumed ''Neustria'' is simply a corruption of ''Westria'', fr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
History Of Normandy
Normandy was a province in the North-West of France under the Ancien Régime which lasted until the latter part of the 18th century. Initially populated by Celtic tribes in the West and Belgic tribes in the North East, it was conquered in AD 98 by the Romans and integrated into the province of Gallia Lugdunensis by Augustus. In the 4th century, Gratian divided the province into the civitates that constitute the historical borders. After the fall of Rome in the 5th century, the Franks became the dominant ethnic group in the area and built several monasteries. Towards the end of the 8th century, Viking raids devastated the region, prompting the establishment of the Duchy of Normandy in 911. After 150 years of expansion, the borders of Normandy reached relative stability. These old borders roughly correspond to the present borders of Lower Normandy, Upper Normandy and the Channel Islands. Mainland Normandy was integrated into the Kingdom of France in 1204. The region was badly da ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Benedictines
, image = Medalla San Benito.PNG , caption = Design on the obverse side of the Saint Benedict Medal , abbreviation = OSB , formation = , motto = (English: 'Pray and Work') , founder = Benedict of Nursia , founding_location = Subiaco Abbey , type = Catholic religious order , headquarters = Sant'Anselmo all'Aventino , num_members = 6,802 (3,419 priests) as of 2020 , leader_title = Abbot Primate , leader_name = Gregory Polan, OSB , main_organ = Benedictine Confederation , parent_organization = Catholic Church , website = The Benedictines, officially the Order of Saint Benedict ( la, Ordo Sancti Benedicti, abbreviated as OSB), are a monastic religious order of the Catholic Church following the Rule of Saint Benedict. They are also sometimes called the Black Monks, in reference to the colour of their religious habits. They ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
_by_Abbie_Farwell_Brown.jpg)