|
Logres
Logres (among various other forms and spellings) is King Arthur's realm in the Matter of Britain. It derives from the medieval Welsh word '' Lloegyr'', a name of uncertain origin referring to South and Eastern England (''Lloegr'' in modern Welsh for all of England). In Arthurian contexts, "Logres" is often used to describe the Brittonic territory roughly corresponding to the borders of England before the area was taken by the Anglo-Saxons. According to Geoffrey of Monmouth's influential pseudohistory ''Historia Regum Britanniae'', the realm was named after the legendary king Locrinus, the oldest son of Brutus of Troy. In his ''Historia'', Geoffrey uses the word "Loegria" to describe a province containing most of England excluding Cornwall and possibly Northumberland, as in this example from section iv.20 (from the Penguin Classics translation by Lewis Thorpe): It was described by Chrétien de Troyes as "The Land of Ogres" (''l'Ogres'') in his poem ''Perceval, the Story o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Knights Of The Round Table
The Knights of the Round Table ( cy, Marchogion y Ford Gron, kw, Marghekyon an Moos Krenn, br, Marc'hegien an Daol Grenn) are the knights of the fellowship of King Arthur in the literary cycle of the Matter of Britain. First appearing in literature in the mid-12th century, the Knights are an order dedicated to ensuring the peace of Arthur's kingdom following an early warring period, entrusted in later years to undergo a mystical quest for the Holy Grail. The Round Table at which they meet is a symbol of the equality of its members, who range from sovereign royals to minor nobles. The various stories in the cycle present an assortment of knights from all over Great Britain and abroad, some of whom are even from outside of Europe. Their ranks often include Arthur's close and distant relatives, such as Agravain and Gaheris, as well as his reconciled enemies and those he defeated in battle, including Galehaut and Lot. Several of the most notable knights, including Bediver ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
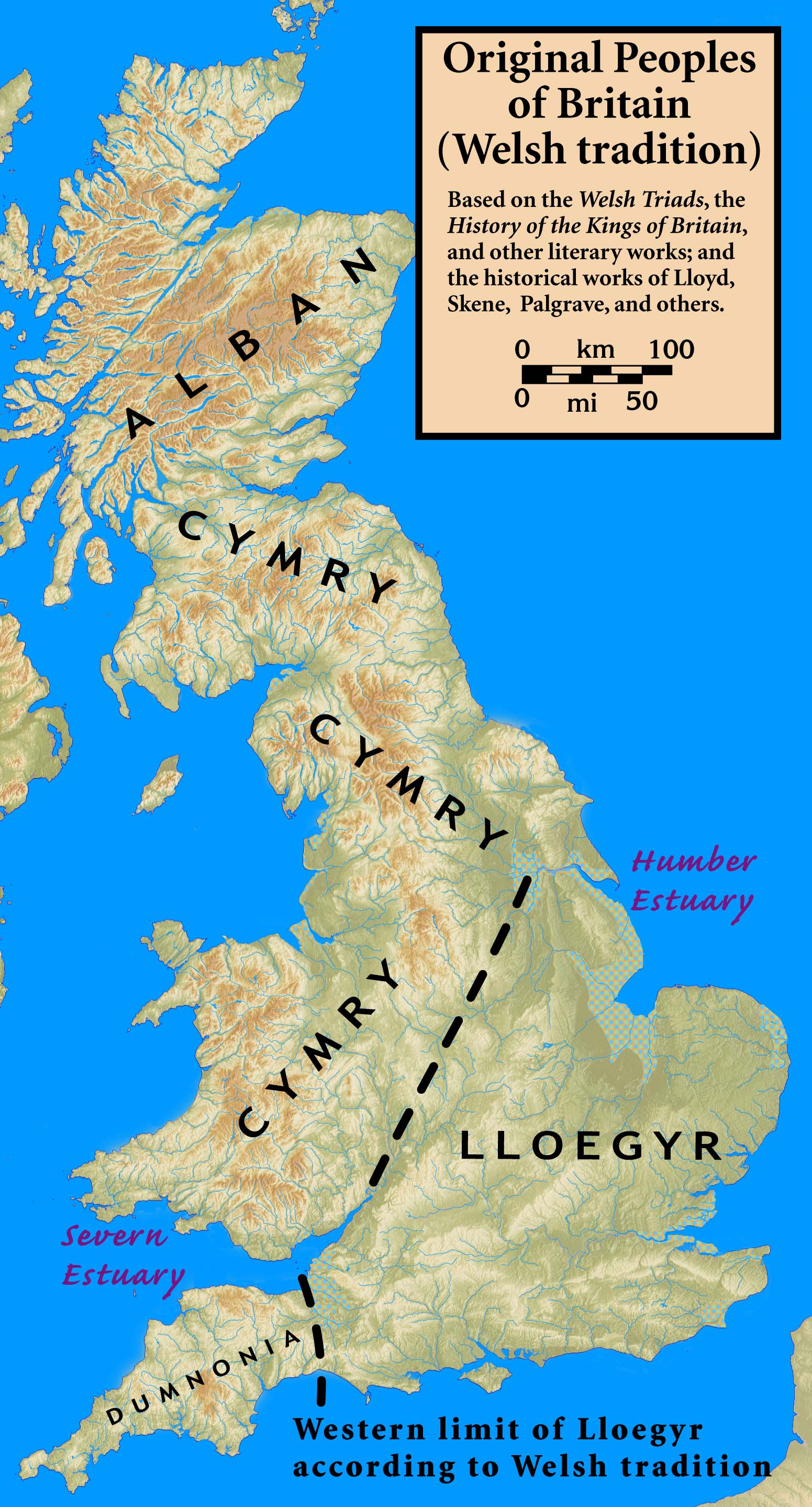
Lloegyr
Lloegyr is the medieval Welsh name for a region of Britain ('' Prydain''). The exact borders are unknown, but some modern scholars hypothesize it ran south and east of a line extending from the Humber Estuary to the Severn Estuary, exclusive of Cornwall and Devon. The people of Lloegyr were called ''Lloegyrwys'' without distinction of ethnicity, the term applying to both Britons and Anglo-Saxons. The modern form of the word is Lloegr ( or ) and it has become generalised through the passage of time to become the Welsh word for "England" as a whole, and not restricted to its original, smaller extent. The word has been anglicised and Latinised into such forms as Logres, Logris, and Loegria, among others, and is perhaps most widely recognised as the name of King Arthur's realm in the body of literature known as the ''Matter of Britain''. The word is known to date from the 10th century or earlier, as it appears in the literary '' Armes Prydein''. Borders Welsh antiquarians of the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ogre
An ogre ( feminine: ogress) is a legendary monster depicted as a large, hideous, man-like being that eats ordinary human beings, especially infants and children. Ogres frequently feature in mythology, folklore, and fiction throughout the world. They appear in many classic works of literature, and are most often associated in fairy tales and legend with a taste for infants. In mythology, ogres are often depicted as inhumanly large, tall, and having a disproportionately large head, abundant hair, unusually colored skin, a voracious appetite, and a strong body. Ogres are closely linked with giants and with human cannibals in mythology. In both folklore and fiction, giants are often given ogrish traits (such as the giants in " Jack and the Beanstalk" and " Jack the Giant Killer", the Giant Despair in ''The Pilgrim's Progress'', and the Jötunn of Norse mythology); while ogres may be given giant-like traits. Famous examples of ogres in folklore include the ogre in " Puss in Boo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Le Morte D'Arthur
' (originally written as '; inaccurate Middle French for "The Death of Arthur") is a 15th-century Middle English prose reworking by Sir Thomas Malory of tales about the legendary King Arthur, Guinevere, Lancelot, Merlin and the Knights of the Round Table, along with their respective folklore. In order to tell a "complete" story of Arthur from his conception to his death, Malory compiled, rearranged, interpreted and modified material from various French and English sources. Today, this is one of the best-known works of Arthurian literature. Many authors since the 19th-century revival of the legend have used Malory as their principal source. Apparently written in prison at the end of the medieval English era, ''Le Morte d'Arthur'' was completed by Malory around 1470 and was first published in a printed edition in 1485 by William Caxton. Until the discovery of the Winchester Manuscript in 1934, the 1485 edition was considered the earliest known text of ''Le Morte d'Arthur'' and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Camelot
Camelot is a castle and court associated with the legendary King Arthur. Absent in the early Arthurian material, Camelot first appeared in 12th-century French romances and, since the Lancelot-Grail cycle, eventually came to be described as the fantastic capital of Arthur's realm and a symbol of the Arthurian world. The stories locate it somewhere in Great Britain and sometimes associate it with real cities, though more usually its precise location is not revealed. Most scholars regard it as being entirely fictional, its unspecified geography being perfect for chivalric romance writers. Nevertheless, arguments about the location of the "real Camelot" have occurred since the 15th century and continue today in popular works and for tourism purposes. Etymology The name's derivation is uncertain. It has numerous different spellings in medieval French Arthurian romances, including ''Camaalot'', ''Camalot'', ''Chamalot'', ''Camehelot'' (sometimes read as ''Camchilot''), ''Camaalo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Locrinus
Locrinus was a legendary king of the Britons, as recounted by the 12th-century chronicler Geoffrey of Monmouth in his ''Historia Regum Britanniae''. According to Geoffrey, Locrinus was the oldest son of Brutus and Innogen, and a descendant of the Trojans through Aeneas. Following Brutus's death, Britain was divided amongst the three sons, with Locrinus receiving the portion roughly equivalent to England except for Cornwall, Albanactus receiving Scotland (Albany), and Kamber receiving Wales (Cymru). Locrinus ruled a portion of Britain called Loegria, named after him, which had roughly the boundaries of modern-day England, other than Cornwall. He reigned 10 years, most of which were peaceful. He avenged his brother Albanactus's death at the hands of Humber the Hun by allying with his other brother, Kamber, and fighting Humber to the banks of a river where he drowned. The river was named Humber after this battle. Locrinus divided up the spoils of war with his allies, only kee ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Brutus Of Troy
Brutus, also called Brute of Troy, is a legendary descendant of the Trojan hero Aeneas, known in medieval British history as the eponymous founder and first king of Britain. This legend first appears in the '' Historia Brittonum'', an anonymous 9th-century historical compilation to which commentary was added by Nennius, but is best known from the account given by the 12th-century chronicler Geoffrey of Monmouth in his '' Historia Regum Britanniae''. ''Historia Brittonum'' Some have suggested that attributing the origin of 'Britain' to the Latin 'Brutus' may be ultimately derived from Isidore of Seville's popular 7th-century work '' Etymologiae'', in which it was speculated that the name of Britain comes from ''bruti'', on the basis that the Britons were, in the eyes of that author, brutes, or savages. A more detailed story, set before the foundation of Rome, follows, in which Brutus is the grandson or great grandson of Aeneas – a legend that was perhaps inspired by Isido ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thomas Malory
Sir Thomas Malory was an English writer, the author of '' Le Morte d'Arthur'', the classic English-language chronicle of the Arthurian legend, compiled and in most cases translated from French sources. The most popular version of '' Le Morte d'Arthur'' was published by the famed London printer William Caxton in 1485. Much of Malory's life history is obscure, but he identified himself as a "knight prisoner", apparently reflecting that he was either a criminal or a prisoner-of-war. Malory's identity has never been confirmed. However, since modern scholars began researching his identity the most widely accepted candidate has been Sir Thomas Malory of Newbold Revel in Warwickshire, who was imprisoned at various times for criminal acts and possibly also for political reasons during the Wars of the Roses. Identity Most of what is known about Malory stems from the accounts describing him in the prayers found in the Winchester Manuscript of ''Le Morte d'Arthur''. He is described as a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kingdom Of England
The Kingdom of England (, ) was a sovereign state on the island of Great Britain from 12 July 927, when it emerged from various Anglo-Saxon kingdoms, until 1 May 1707, when it united with Scotland to form the Kingdom of Great Britain. On 12 July 927, the various Anglo-Saxon kings swore their allegiance to Æthelstan of Wessex (), unifying most of modern England under a single king. In 1016, the kingdom became part of the North Sea Empire of Cnut the Great, a personal union between England, Denmark and Norway. The Norman conquest of England in 1066 led to the transfer of the English capital city and chief royal residence from the Anglo-Saxon one at Winchester to Westminster, and the City of London quickly established itself as England's largest and principal commercial centre. Histories of the kingdom of England from the Norman conquest of 1066 conventionally distinguish periods named after successive ruling dynasties: Norman (1066–1154), Plantagenet (1154–1485 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Perceval, The Story Of The Grail
''Perceval, the Story of the Grail'' (french: Perceval ou le Conte du Graal) is the unfinished fifth verse romance by Chrétien de Troyes, written by him in Old French in the late 12th century. Later authors added 54,000 more lines in what are known collectively as the Four Continuations,Grigsby, John L. (1991). "Continuations of ''Perceval''". In Norris J. Lacy, ''The New Arthurian Encyclopedia'', pp. 99–100. New York: Garland. . as well as other related texts. ''Perceval'' is the earliest recorded account of what was to become the Quest for the Holy Grail but describes only a golden grail (a serving dish) in the central scene, does not call it "holy" and treats a lance, appearing at the same time, as equally significant. ''Perceval'' ''Perceval'' is dedicated to Chrétien's patron Philip I, Count of Flanders.Lacy, Norris J. (1991). "Chrétien de Troyes". In Norris J. Lacy, ''The New Arthurian Encyclopedia'', pp. 88–91. New York: Garland. . It was written in Old French ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alba
''Alba'' ( , ) is the Scottish Gaelic name for Scotland. It is also, in English language historiography, used to refer to the polity of Picts and Scots united in the ninth century as the Kingdom of Alba, until it developed into the Kingdom of Scotland of the late Middle Ages following the absorption of Strathclyde and English-speaking Lothian in the 12th century. It is cognate with the Irish term ' (gen. ', dat. ') and the Manx term ', the two other Goidelic Insular Celtic languages, as well as contemporary words used in Cornish (') and Welsh ('), both of which are Brythonic Insular Celtic languages. The third surviving Brythonic language, Breton, instead uses ', meaning 'country of the Scots'. In the past, these terms were names for Great Britain as a whole, related to the Brythonic name Albion. Etymology The term first appears in classical texts as ' or ' (in Ptolemy's writings in Greek), and later as ' in Latin documents. Historically, the term refers to Britain as ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chrétien De Troyes
Chrétien de Troyes (Modern ; fro, Crestien de Troies ; 1160–1191) was a French poet and trouvère known for his writing on Arthurian subjects, and for first writing of Lancelot, Percival and the Holy Grail. Chrétien's works, including '' Erec and Enide'', '' Lancelot'', '' Perceval'' and '' Yvain'', represent some of the best-regarded of medieval literature. His use of structure, particularly in ''Yvain'', has been seen as a step towards the modern novel. Life Little is known of his life, but he seems to have been from Troyes or at least intimately connected with it. Between 1160 and 1172 he served (perhaps as herald-at-arms, as Gaston Paris speculated) at the court of his patroness Marie of France, Countess of Champagne, daughter of King Louis VII and Eleanor of Aquitaine, who married Count Henry I of Champagne in 1164. Later, he served the court of Philippe d'Alsace, Count of Flanders. Works Chrétien's works include five major poems in rhyming eight-syllable ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |




.jpg)

.jpg)
