|
Logic Puzzles
A logic puzzle is a puzzle deriving from the mathematical field of deduction. History The logic puzzle was first produced by Charles Lutwidge Dodgson, who is better known under his pen name Lewis Carroll, the author of ''Alice's Adventures in Wonderland''. In his book '' The Game of Logic'' he introduced a game to solve problems such as confirming the conclusion "Some greyhounds are not fat" from the statements "No fat creatures run well" and "Some greyhounds run well". Puzzles like this, where we are given a list of premises and asked what can be deduced from them, are known as syllogisms. Dodgson goes on to construct much more complex puzzles consisting of up to 8 premises. In the second half of the 20th century mathematician Raymond M. Smullyan continued and expanded the branch of logic puzzles with books such as '' The Lady or the Tiger?'', '' To Mock a Mockingbird'' and ''Alice in Puzzle-Land''. He popularized the " knights and knaves" puzzles, which involve knights, who ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Puzzle
A puzzle is a game, problem, or toy that tests a person's ingenuity or knowledge. In a puzzle, the solver is expected to put pieces together ( or take them apart) in a logical way, in order to find the solution of the puzzle. There are different genres of puzzles, such as crossword puzzles, word-search puzzles, number puzzles, relational puzzles, and logic puzzles. The academic study of puzzles is called enigmatology. Puzzles are often created to be a form of entertainment but they can also arise from serious mathematical or logical problems. In such cases, their solution may be a significant contribution to mathematical research. Etymology The ''Oxford English Dictionary'' dates the word ''puzzle'' (as a verb) to the 16th century. Its earliest use documented in the ''OED'' was in a book titled ''The Voyage of Robert Dudley...to the West Indies, 1594–95, narrated by Capt. Wyatt, by himself, and by Abram Kendall, master'' (published circa 1595). The word later came to be ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Logic Maze
Logic mazes, sometimes called mazes with rules or multi-state mazes, are logic puzzles with all the aspects of a tour puzzle that fall outside of the scope of a typical maze. These mazes have special rules, sometimes including multiple states of the maze or navigator. A ruleset can be basic (such as "you cannot make left turns") or complex. Popular logic mazes include tilt mazes and other novel designs which usually increase the complexity of the maze, sometimes to the point that the maze has to be designed by a program to eliminate multiple paths. History Robert Abbott invented the logic maze. The first logic maze ever published, ''Traffic Maze in Floyd's Knob'', appeared in the October 1962 issue of ''Scientific American ''Scientific American'', informally abbreviated ''SciAm'' or sometimes ''SA'', is an American popular science magazine. Many scientists, including Albert Einstein and Nikola Tesla, have contributed articles to it, with more than 150 Nobel Pri ...'' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Murdle
Greg T. Karber is an American writer, best known as author of the ''Murdle'' series of murder mystery puzzle books and its accompanying website. Early life and education Karber was raised in Arkansas, the son of a judge and a civil rights attorney. His maternal grandfather worked as an FBI agent in San Francisco in the 1960s. He earned a bachelor's degree in mathematics and English literature from the University of Arkansas, and an MFA from the USC School of Cinematic Arts. Career After graduating with his MFA, Karber remained in Los Angeles and worked adapting novels into screenplays. (As of 2013, he had written five unpublished novels.) He also began making comedic YouTube videos. In 2013, he came across some 2006 comments by Abercrombie & Fitch CEO Mike Jeffries: "In every school there are the cool and popular kids, and then there are the not-so-cool kids. Candidly, we go after the cool kids...A lot of people don't belong n our clothes and they can't belong. Are we exc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Survo Puzzle
A Survo puzzle is a kind of logic puzzle presented (in April 2006) and studied by Seppo Mustonen. Aitola, Kerttu (2006): "Survo on täällä" ("Survo is here"). ''Yliopisto'' 54(12): 44–45. The name of the puzzle is associated with Mustonen's Survo system, which is a general environment for statistical computing and related areas. Mustonen, Seppo (2007)"Survo Crossings". ''CSCnews'' 1/2007: 30–32. In a Survo puzzle, the task is to fill an ''m'' × ''n'' table with integers 1, 2, ..., ''m''·''n'' so that each of these numbers appears only once and their row and column sums are equal to integers given on the bottom and the right side of the table. Often some of the integers are given readily in the table to guarantee uniqueness of the solution and/or for making the task easier. To some extent, Survo puzzles resemble Sudoku and Kakuro puzzles. However, numbers used in the solution are not restricted to 1, 2, ..., 9 and the size of puzzle grid is typically very small. S ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Induction Puzzles
Induction puzzles are logic puzzles, which are examples of Dynamic epistemic logic, multi-agent reasoning, where the solution evolves along with the principle of mathematical induction, induction. A puzzle's scenario always involves multiple players with the same reasoning capability, who go through the same reasoning steps. According to the principle of induction, a solution to the simplest case makes the solution of the next complicated case obvious. Once the simplest case of the induction puzzle is solved, the whole puzzle is solved subsequently. Typical tell-tale features of these puzzles include any puzzle in which each participant has a given piece of information (usually as Common knowledge (logic), common knowledge) about all other participants but not themselves. Also, usually, some kind of hint is given to suggest that the participants can trust each other's intelligence — they are capable of theory of mind (that "every participant knows modus ponens" is common knowl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Recreational Mathematics
Recreational mathematics is mathematics carried out for recreation (entertainment) rather than as a strictly research-and-application-based professional activity or as a part of a student's formal education. Although it is not necessarily limited to being an endeavor for amateurs, many topics in this field require no knowledge of advanced mathematics. Recreational mathematics involves mathematical puzzles and games, often appealing to children and untrained adults and inspiring their further study of the subject. The Mathematical Association of America (MAA) includes recreational mathematics as one of its seventeen Special Interest Groups, commenting: Mathematical competitions (such as those sponsored by mathematical associations) are also categorized under recreational mathematics. Topics Some of the more well-known topics in recreational mathematics are Rubik's Cubes, magic squares, fractals, logic puzzles and mathematical chess problems, but this area of mathemati ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mechanical Puzzle
A mechanical puzzle is a puzzle presented as a set of mechanically interlinked pieces in which the solution is to manipulate the whole object or parts of it. While puzzles of this type have been in use by humanity as early as the 3rd century BC, one of the most well-known mechanical puzzles of modern day is the Rubik's Cube, invented by the Hungarian architect Ernő Rubik in 1974. The puzzles are typically designed for a single player, where the goal is for the player to discover the principle of the object, rather than accidentally coming up with the right solution through trial and error. With this in mind, they are often used as an intelligence test or in problem solving training. History The oldest known mechanical puzzle comes from Greece and appeared in the 3rd century BC. The game consists of a square divided into 14 parts, and the aim was to create different shapes from these pieces. This is not easy to do. (see Ostomachion loculus Archimedius) In Iran "puzzle-locks" ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Logic Programming
Logic programming is a programming, database and knowledge representation paradigm based on formal logic. A logic program is a set of sentences in logical form, representing knowledge about some problem domain. Computation is performed by applying logical reasoning to that knowledge, to solve problems in the domain. Major logic programming language families include Prolog, Answer Set Programming (ASP) and Datalog. In all of these languages, rules are written in the form of ''clauses'': :A :- B1, ..., Bn. and are read as declarative sentences in logical form: :A if B1 and ... and Bn. A is called the ''head'' of the rule, B1, ..., Bn is called the ''body'', and the Bi are called '' literals'' or conditions. When n = 0, the rule is called a ''fact'' and is written in the simplified form: :A. Queries (or goals) have the same syntax as the bodies of rules and are commonly written in the form: :?- B1, ..., Bn. In the simplest case of Horn clauses (or "definite" clauses), all ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Puzzle Video Games
This is a partial list of notable puzzle video games, sorted by general category. Tile matching Tile-matching video games are a type of puzzle video game where the player manipulates tiles in order to make them disappear according to a matching criterion. There are a great number of variations on this theme. Falling block puzzles Puzzle pieces advance into the play area from one or more edges, typically falling into the play area from above. Player must match or arrange individual pieces to achieve the particular objectives defined by each game. *''Alien Hive'' *''Baku Baku Animal'' *''Blueprint 3D'' *''Clockwiser'' *''Columns (video game), Columns'' *''Dialhex'' *''Dr. Mario'' *''Drop Mania'' *''Dream of Pixels'' *''Faces (video game), Faces'' *''Klax (computer game), Klax'' *''Lumines'' *''Meteos'' *''Moujiya (video game), Moujiya'' *''Oh My God! (video game), Oh My God!'' *''Pac-Attack'' *''Pnickies'' *''Puyo Puyo'' *''Puzzle Fighter, Super Puzzle Fighter II Turbo'' *''Ramp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
:Category:Logic Puzzles
{{Commons category Puzzles A puzzle is a game, problem, or toy that tests a person's ingenuity or knowledge. In a puzzle, the solver is expected to put pieces together ( or take them apart) in a logical way, in order to find the solution of the puzzle. There are different ... Mathematical puzzles ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
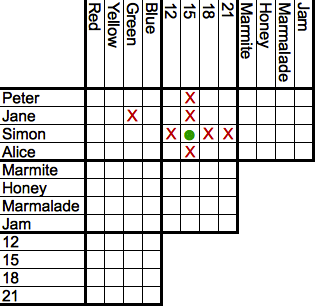
Zebra Puzzle
The Zebra Puzzle is a well-known logic puzzle. Many versions of the puzzle exist, including a version published in '' Life International'' magazine on December 17, 1962. The March 25, 1963, issue of ''Life'' contained the solution and the names of several hundred successful solvers from around the world. The puzzle is often called Einstein's Puzzle or Einstein's Riddle because it is said to have been invented by Albert Einstein as a boy; it is also sometimes attributed to Lewis Carroll. However, there is no evidence for either person's authorship, and the ''Life International'' version of the puzzle mentions brands of cigarettes that did not exist during Carroll's lifetime or Einstein's boyhood. The Zebra puzzle has been used as a benchmark in the evaluation of computer algorithms for solving constraint satisfaction problems. Description The following version of the puzzle appeared in ''Life International'' in 1962: Solution Assuming that one person drinks water and one owns ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Magazine
A magazine is a periodical literature, periodical publication, print or digital, produced on a regular schedule, that contains any of a variety of subject-oriented textual and visual content (media), content forms. Magazines are generally financed by advertising, newsagent's shop, purchase price, prepaid subscription business model, subscriptions, or by a combination of the three. They are categorised by their frequency of publication (i.e., as weeklies, monthlies, quarterlies, etc.), their target audiences (e.g., women's and trade magazines), their subjects of focus (e.g., popular science and religious), and their tones or approach (e.g., works of satire or humor). Appearance on the cover of print magazines has historically been understood to convey a place of honor or distinction to an individual or event. Term origin and definition Origin The etymology of the word "magazine" suggests derivation from the Arabic language, Arabic (), the broken plural of () meaning "depot, s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |