|
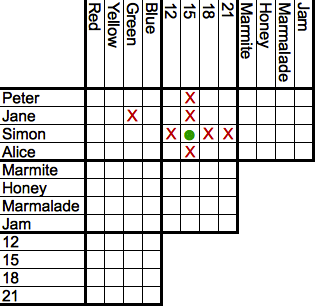
Logic Games
Logic games, abbreviated LG, and officially referred to as analytical reasoning, is one of three types of sections that appear on the Law School Admission Test (LSAT). A logic games section contains four 5-8 question "games", totaling 22-25 questions. Each game contains a scenario and a set of rules that govern the scenario, followed by questions that test the test-taker's ability to understand and apply the rules, to draw inferences based on them. In the words of the Law School Admission Council (LSAC), which administers the test, it "measure the ability to understand a structure of relationships and to draw logical conclusions about that structure". Like all other sections on the LSAT, the time allowed for this section is 35 minutes. While most students find this section to be the most difficult section on the LSAT, it is widely considered the easiest and fastest to improve at once the right strategies are learned and employed. Common game types Basic linear In a basic l ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Logic Puzzle
A logic puzzle is a puzzle deriving from the mathematical field of deduction. History The logic puzzle was first produced by Charles Lutwidge Dodgson, who is better known under his pen name Lewis Carroll, the author of ''Alice's Adventures in Wonderland''. In his book '' The Game of Logic'' he introduced a game to solve problems such as confirming the conclusion "Some greyhounds are not fat" from the statements "No fat creatures run well" and "Some greyhounds run well". Puzzles like this, where we are given a list of premises and asked what can be deduced from them, are known as syllogisms. Dodgson goes on to construct much more complex puzzles consisting of up to 8 premises. In the second half of the 20th century mathematician Raymond M. Smullyan continued and expanded the branch of logic puzzles with books such as '' The Lady or the Tiger?'', ''To Mock a Mockingbird'' and ''Alice in Puzzle-Land''. He popularized the " knights and knaves" puzzles, which involve knights, who al ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Law School Admission Test
The Law School Admission Test (LSAT; ) is a standardized test administered by the Law School Admission Council (LSAC) for prospective law school candidates. It is designed to assess reading comprehension as well as logical and verbal reasoning proficiency. The test is an integral part of the law school admission process in the United States, Canada (common law programs only), the University of Melbourne, Australia, and a growing number of other countries. The test had existed in some form since 1948, when it was created to give law schools a standardized way to assess applicants in addition to their GPA. The current form of the exam has been used since 1991. The exam has five total sections that include three scored multiple choice sections, an unscored experimental section, and an unscored writing section. Raw scores are converted to a scaled score with a high of 180, a low of 120, and a median score around 150. When an applicant applies to a law school all scores from ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Law School Admission Council
The Law School Admission Council (LSAC) is a nonprofit organization whose members include more than 200 law schools throughout the United States, Canada and Australia. Its headquarters are in Newtown, Pennsylvania (about 15 miles north of Philadelphia). The Law School Admission Council (LSAC) is a nonprofit corporation that provides products and services to facilitate the admission process for law schools and their applicants worldwide. More than 200 law schools in the United States, Canada, and Australia are members of the Council. All law schools approved by the American Bar Association are LSAC members, as are Canadian law schools recognized by a provincial or territorial law society or government agency. Many nonmember law schools also use LSAC's services. Founded in 1947, the Council is best known for administering the Law School Admission Test (LSAT®), with over 150,000 tests administered annually at testing centers worldwide. In the face of pushback from members of the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Landmark
A landmark is a recognizable natural or artificial feature used for navigation, a feature that stands out from its near environment and is often visible from long distances. In modern use, the term can also be applied to smaller structures or features, that have become local or national symbols. Etymology In old English the word ''landmearc'' (from ''land'' + ''mearc'' (mark)) was used to describe a boundary marker, an "object set up to mark the boundaries of a kingdom, estate, etc.". Starting from approx. 1560, this understanding of landmark was replaced by a more general one. A landmark became a "conspicuous object in a landscape". A ''landmark'' literally meant a geographic feature used by explorers and others to find their way back or through an area. For example, the Table Mountain near Cape Town, South Africa is used as the landmark to help sailors to navigate around southern tip of Africa during the Age of Exploration. Artificial structures are also sometimes built ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Circle
A circle is a shape consisting of all points in a plane that are at a given distance from a given point, the centre. Equivalently, it is the curve traced out by a point that moves in a plane so that its distance from a given point is constant. The distance between any point of the circle and the centre is called the radius. Usually, the radius is required to be a positive number. A circle with r=0 (a single point) is a degenerate case. This article is about circles in Euclidean geometry, and, in particular, the Euclidean plane, except where otherwise noted. Specifically, a circle is a simple closed curve that divides the plane into two regions: an interior and an exterior. In everyday use, the term "circle" may be used interchangeably to refer to either the boundary of the figure, or to the whole figure including its interior; in strict technical usage, the circle is only the boundary and the whole figure is called a '' disc''. A circle may also be defined as a specia ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Puzzle
A puzzle is a game, problem, or toy that tests a person's ingenuity or knowledge. In a puzzle, the solver is expected to put pieces together ( or take them apart) in a logical way, in order to arrive at the correct or fun solution of the puzzle. There are different genres of puzzles, such as crossword puzzles, word-search puzzles, number puzzles, relational puzzles, and logic puzzles. The academic study of puzzles is called enigmatology. Puzzles are often created to be a form of entertainment but they can also arise from serious mathematical or logical problems. In such cases, their solution may be a significant contribution to mathematical research. Etymology The ''Oxford English Dictionary'' dates the word ''puzzle'' (as a verb) to the end of the 16th century. Its earliest use documented in the ''OED'' was in a book titled ''The Voyage of Robert Dudley...to the West Indies, 1594–95, narrated by Capt. Wyatt, by himself, and by Abram Kendall, master'' (published circa 15 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Process Of Elimination
Process of elimination is a logical method to identify an entity of interest among several ones by excluding all other entities. In educational testing, it is a process of deleting options whereby the possibility of an option being correct is close to zero or significantly lower compared to other options. This version of the process does not guarantee success, even if only one option remains, since it eliminates possibilities merely as improbable. The process of elimination can only narrow the possibilities down, and thus, if the correct option is not amongst the known options, it will not arrive at the truth. Method The method of elimination is iterative. One looks at the answers, determines that several answers are unfit, eliminates these, and repeats, until one cannot eliminate any more. This iteration is most effectively applied when there is logical structure between the answers – that is to say, when by eliminating an answer one can eliminate several others. In this case o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Legal Profession Exams
Law is a set of rules that are created and are enforceable by social or governmental institutions to regulate behavior,Robertson, ''Crimes against humanity'', 90. with its precise definition a matter of longstanding debate. It has been variously described as a science and as the art of justice. State-enforced laws can be made by a group legislature or by a single legislator, resulting in statutes; by the executive through decrees and regulations; or established by judges through precedent, usually in common law jurisdictions. Private individuals may create legally binding contracts, including arbitration agreements that adopt alternative ways of resolving disputes to standard court litigation. The creation of laws themselves may be influenced by a constitution, written or tacit, and the rights encoded therein. The law shapes politics, economics, history and society in various ways and serves as a mediator of relations between people. Legal systems vary between jurisdiction ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Standardized Tests
A standardized test is a test that is administered and scored in a consistent, or "standard", manner. Standardized tests are designed in such a way that the questions and interpretations are consistent and are administered and scored in a predetermined, standard manner. Any test in which the same test is given in the same manner to all test takers, and graded in the same manner for everyone, is a standardized test. Standardized tests do not need to be high-stakes tests, time-limited tests, or multiple-choice tests. A standardized test may be any type of test: a written test, an oral test, or a practical skills performance test. The questions can be simple or complex. The subject matter among school-age students is frequently academic skills, but a standardized test can be given on nearly any topic, including driving tests, creativity, athleticism, personality, professional ethics, or other attributes. The opposite of standardized testing is ''non-standardized testing'', ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Legal Education In The United States
Legal education in the United States generally refers to a graduate degree, the completion of which makes a graduate eligible to sit for an examination for a license to practice as a Lawyer. Around 60 percent of those who complete a law degree typically practice law, with the remainder primarily working in business (especially finance, insurance, real estate, and consulting) or government or policy roles, where their degrees also confer advantages. (Other types of legal education, such as that of paralegals, of Limited Practice Officers (in Washington), and of the citizenry in general, and of the education of lawyers after admission to the bar (continuing legal education) are not covered in this article.) History The first law schools in Europe The foundations of the first universities in Europe were the glossators of the 11th century, which were schools of law. The first European university, that of Bologna, was founded as a school of law by four famous legal scholars in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Logic
Logic is the study of correct reasoning. It includes both formal and informal logic. Formal logic is the science of deductively valid inferences or of logical truths. It is a formal science investigating how conclusions follow from premises in a topic-neutral way. When used as a countable noun, the term "a logic" refers to a logical formal system that articulates a proof system. Formal logic contrasts with informal logic, which is associated with informal fallacies, critical thinking, and argumentation theory. While there is no general agreement on how formal and informal logic are to be distinguished, one prominent approach associates their difference with whether the studied arguments are expressed in formal or informal languages. Logic plays a central role in multiple fields, such as philosophy, mathematics, computer science, and linguistics. Logic studies arguments, which consist of a set of premises together with a conclusion. Premises and conclusions are usua ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |