|
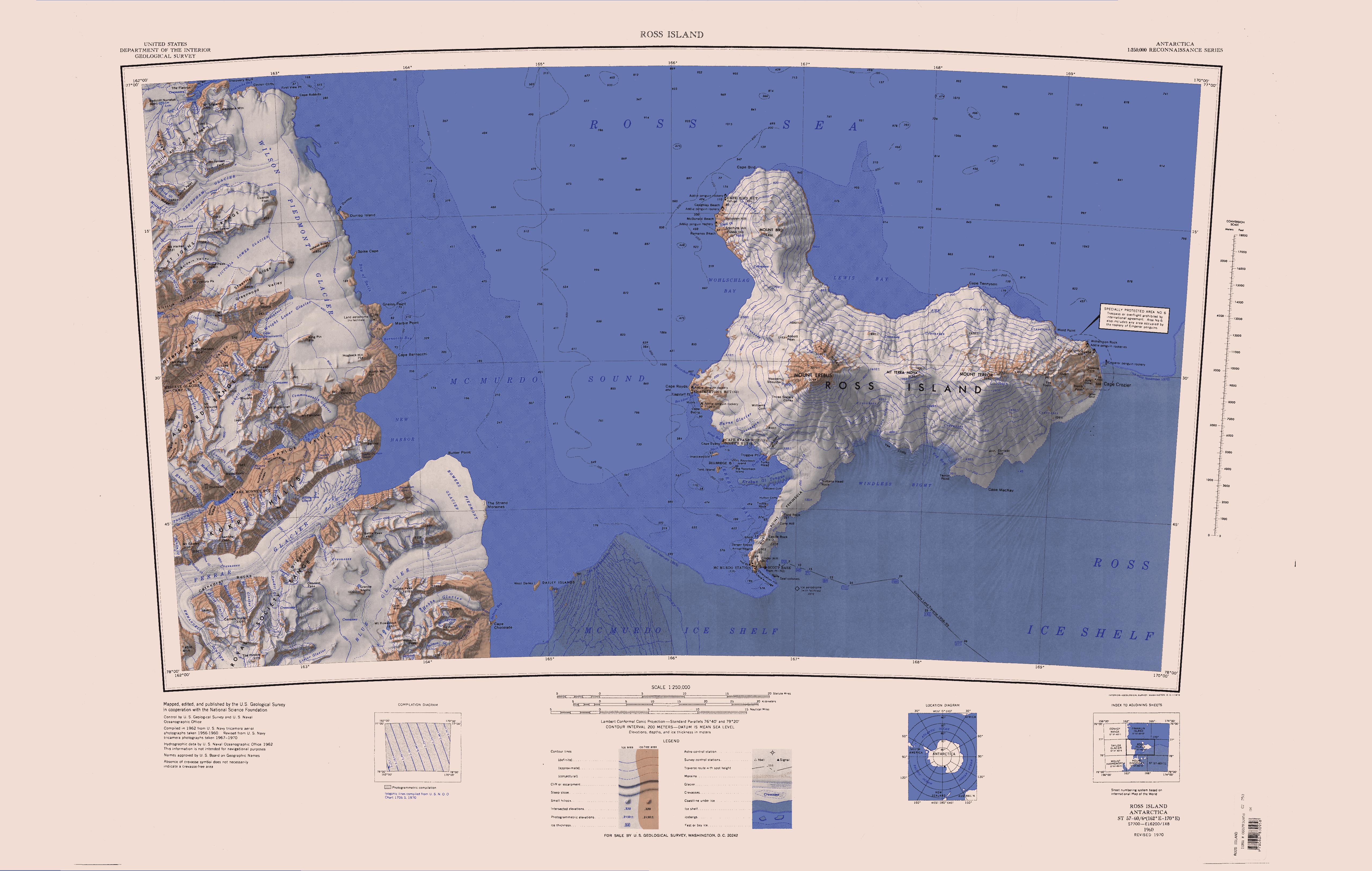
Loftus Glacier
Loftus Glacier () is a valley glacier between Mount Weyant and Mount McLennan, which flows north to join Newall Glacier in Victoria Land, Antarctica. It was named by the Advisory Committee on Antarctic Names in 1964 for Chief Journalist Leo G. Loftus, U.S. Navy The United States Navy (USN) is the maritime service branch of the United States Armed Forces and one of the eight uniformed services of the United States. It is the largest and most powerful navy in the world, with the estimated tonnage o ..., who served five summer seasons at McMurdo Station, 1959–64. References Glaciers of Victoria Land Scott Coast {{ScottCoast-geo-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Valley Glacier
A valley is an elongated low area often running between hills or mountains, which will typically contain a river or stream running from one end to the other. Most valleys are formed by erosion of the land surface by rivers or streams over a very long period. Some valleys are formed through erosion by glacial ice. These glaciers may remain present in valleys in high mountains or polar areas. At lower latitudes and altitudes, these glacially formed valleys may have been created or enlarged during ice ages but now are ice-free and occupied by streams or rivers. In desert areas, valleys may be entirely dry or carry a watercourse only rarely. In areas of limestone bedrock, dry valleys may also result from drainage now taking place underground rather than at the surface. Rift valleys arise principally from earth movements, rather than erosion. Many different types of valleys are described by geographers, using terms that may be global in use or else applied only locally. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mount Weyant
The Newall Glacier () is a glacier in the east part of the Asgard Range of Victoria Land, It flows east between Mount Newall and Mount Weyant into the Wilson Piedmont Glacier. The Newall Glacier was mapped by the N.Z. Northern Survey Party of the CTAE, 1956-58, who named it after nearby Mount Newall. Location The Newall Glacier forms to the east of the Lacroix Glacier, which flows south into Taylor Valley. It flows northeast, past the head of Suess Glacier, past Mount Valkyrie to the west and Mount Weyant to the east. It turns east and is joined by the Loftus Glacier below Mount Newall. It continues east past the head of Commonwealth Glacier and joins with Wright Lower Glacier as it flows into Wilson Piedmont Glacier. Features Features, from southwest to northeast, include Lyons Cone, Twickler Cone, Unwin Ledge, Hothern Cliffs, Mount Hall, Loftus Glacier, Mount Weyant, Mount Saga, Hetha Peak, Commanda Glacier and Repeater Glacier. Lyons Cone . A cone shaped peak north-n ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mount McLennan (Victoria Land)
Mount McLennan is a prominent mountain rising over at the north side of Taylor Valley, surmounting the area at the heads of Canada Glacier, Commonwealth Glacier and Loftus Glacier, in Victoria Land, Antarctica. It was named by C.S. Wright of the British Antarctic Expedition (1910–13) for Professor McLennan, a physicist at Toronto University The University of Toronto (UToronto or U of T) is a public research university in Toronto, Ontario, Canada, located on the grounds that surround Queen's Park. It was founded by royal charter in 1827 as King's College, the first institution ..., Canada. Geologist Thomas E. Berg killed in helicopter crash (11/19/69) on the side of Mt. McLennan. NZ cameraman Jeremy Sykes also killed. References Mountains of Victoria Land McMurdo Dry Valleys {{McMurdoDryValleys-geo-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Newall Glacier
The Newall Glacier () is a glacier in the east part of the Asgard Range of Victoria Land, It flows east between Mount Newall and Mount Weyant into the Wilson Piedmont Glacier. The Newall Glacier was mapped by the N.Z. Northern Survey Party of the CTAE, 1956-58, who named it after nearby Mount Newall. Location The Newall Glacier forms to the east of the Lacroix Glacier, which flows south into Taylor Valley. It flows northeast, past the head of Suess Glacier, past Mount Valkyrie to the west and Mount Weyant to the east. It turns east and is joined by the Loftus Glacier below Mount Newall. It continues east past the head of Commonwealth Glacier and joins with Wright Lower Glacier as it flows into Wilson Piedmont Glacier. Features Features, from southwest to northeast, include Lyons Cone, Twickler Cone, Unwin Ledge, Hothern Cliffs, Mount Hall, Loftus Glacier, Mount Weyant, Mount Saga, Hetha Peak, Commanda Glacier and Repeater Glacier. Lyons Cone . A cone shaped peak north-n ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Victoria Land
Victoria Land is a region in eastern Antarctica which fronts the western side of the Ross Sea and the Ross Ice Shelf, extending southward from about 70°30'S to 78°00'S, and westward from the Ross Sea to the edge of the Antarctic Plateau. It was discovered by Captain James Clark Ross in January 1841 and named after Queen Victoria. The rocky promontory of Minna Bluff is often regarded as the southernmost point of Victoria Land, and separates the Scott Coast to the north from the Hillary Coast of the Ross Dependency to the south. The region includes ranges of the Transantarctic Mountains and the McMurdo Dry Valleys (the highest point being Mount Abbott in the Northern Foothills), and the flatlands known as the Labyrinth. The Mount Melbourne is an active volcano in Victoria Land. Early explorers of Victoria Land include James Clark Ross and Douglas Mawson. In 1979, scientists discovered a group of 309 meteorites in Antarctica, some of which were found near the Allan Hills in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Advisory Committee On Antarctic Names
The Advisory Committee on Antarctic Names (ACAN or US-ACAN) is an advisory committee of the United States Board on Geographic Names responsible for recommending commemorative names for features in Antarctica. History The committee was established in 1943 as the Special Committee on Antarctic Names (SCAN). It became the Advisory Committee on Antarctic Names in 1947. Fred G. Alberts was Secretary of the Committee from 1949 to 1980. By 1959, a structured nomenclature was reached, allowing for further exploration, structured mapping of the region and a unique naming system. A 1990 ACAN gazeeter of Antarctica listed 16,000 names. Description The United States does not recognise territorial boundaries within Antarctica, so ACAN assigns names to features anywhere within the continent, in consultation with other national nomenclature bodies where appropriate, as defined by the Antarctic Treaty System. The research and staff support for the ACAN is provided by the United States Geologi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Leo G
Leo or Léo may refer to: Acronyms * Law enforcement officer * Law enforcement organisation * ''Louisville Eccentric Observer'', a free weekly newspaper in Louisville, Kentucky * Michigan Department of Labor and Economic Opportunity Arts and entertainment Music * Leo (band), a Missouri-based rock band that was founded in Cleveland, Ohio * L.E.O. (band), a band by musician Bleu and collaborators Film * ''Leo'' (2000 film), a Spanish film by José Luis Borau * ''Leo'' (2002 film), a British-American drama film * ''Leo'', a 2007 Swedish film by Josef Fares * ''Leo'' (2012 film), a Kenyan film * Leo the Lion (MGM), mascot of the Metro-Goldwyn-Mayer movie studio Television * Leo Awards, a British Columbian television award * "Leo", an episode of ''Being Erica'' * Léo, fictional lion in the animation '' Animal Crackers'' * ''Léo'', 2018 Quebec television series created by Fabien Cloutier Companies * Leo Namibia, former name for the TN Mobile phone network in Namibia * Le ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
McMurdo Station
McMurdo Station is a United States Antarctic research station on the south tip of Ross Island, which is in the New Zealand-claimed Ross Dependency on the shore of McMurdo Sound in Antarctica. It is operated by the United States through the United States Antarctic Program (USAP), a branch of the National Science Foundation. The station is the largest community in Antarctica, capable of supporting up to 1,258 residents, and serves as one of three year-round United States Antarctic science facilities. All personnel and cargo going to or coming from Amundsen–Scott South Pole Station first pass through McMurdo. By road, McMurdo is 3 kilometres (1.9 mi) from New Zealand's smaller Scott Base. History The station takes its name from its geographic location on McMurdo Sound, named after Lieutenant Archibald McMurdo of . The ''Terror'', commanded by Irish explorer Francis Crozier, along with expedition flagship ''Erebus'' under command of James Clark Ross, first charted the area ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Glaciers Of Victoria Land
A glacier (; ) is a persistent body of dense ice that is constantly moving under its own weight. A glacier forms where the accumulation of snow exceeds its ablation over many years, often centuries. It acquires distinguishing features, such as crevasses and seracs, as it slowly flows and deforms under stresses induced by its weight. As it moves, it abrades rock and debris from its substrate to create landforms such as cirques, moraines, or fjords. Although a glacier may flow into a body of water, it forms only on land and is distinct from the much thinner sea ice and lake ice that form on the surface of bodies of water. On Earth, 99% of glacial ice is contained within vast ice sheets (also known as "continental glaciers") in the polar regions, but glaciers may be found in mountain ranges on every continent other than the Australian mainland, including Oceania's high-latitude oceanic island countries such as New Zealand. Between latitudes 35°N and 35°S, glaciers occur only in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |