|
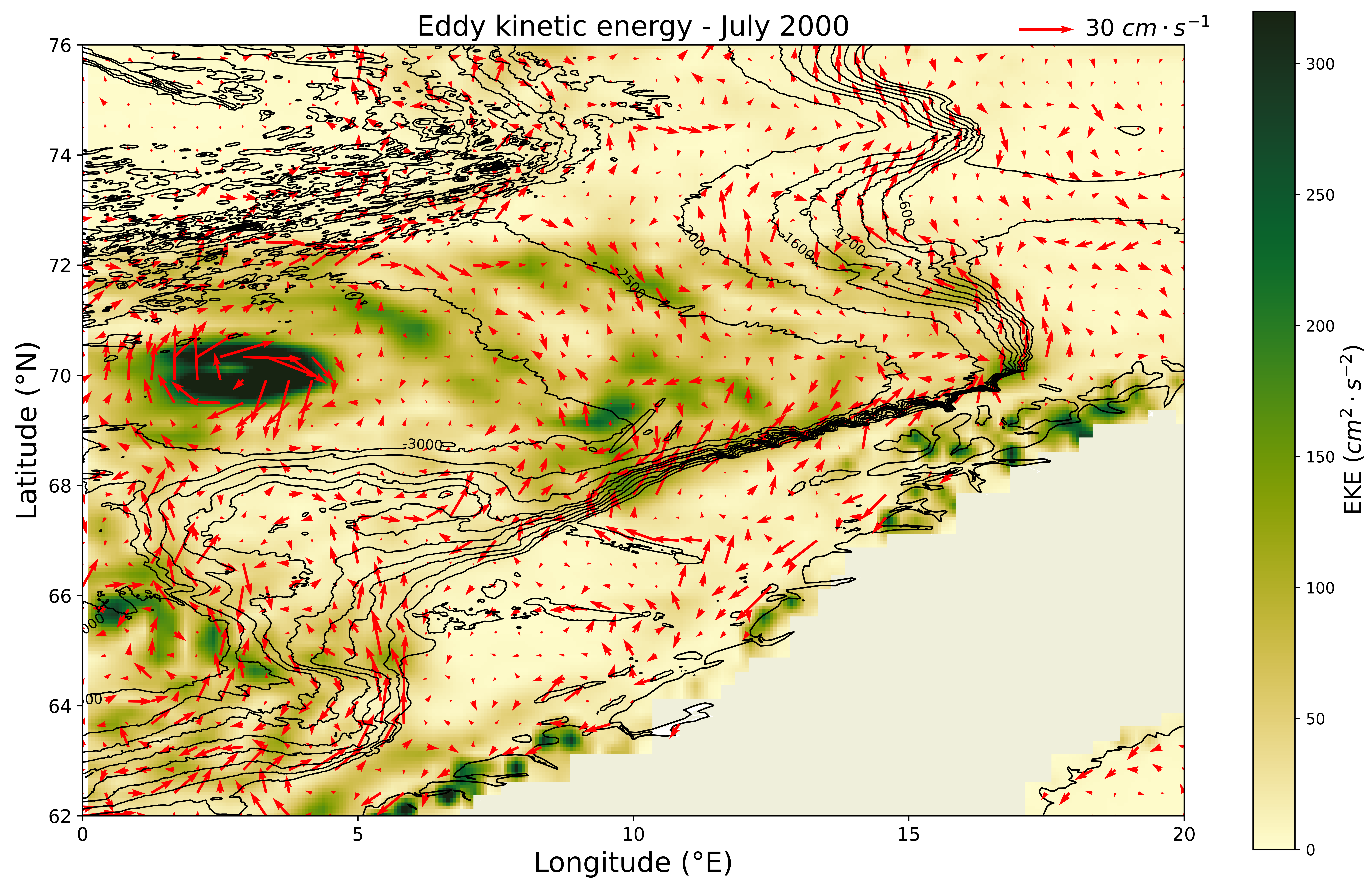
Lofoten Vortex
The Lofoten Vortex, also called Lofoten Basin Vortex or Lofoten Basin Eddy, is a permanent oceanic anticyclonic eddy, located in the northern part of the Norwegian Sea, off the coast of the Lofoten archipelago. It was documented for the first time in the 1970s. Due to the presence of the permanent vortex, the Lofoten basin features a localised area with high levels of sea surface temperature and eddy kinetic energy. The local currents inside the vortex and the strong convection observed during winter generate a hot spot rich in nutrients, affecting the surrounding marine biology. Moreover, due to its extraordinary persistence and location, the Lofoten Vortex is likely to influence the dense water formation in the region. Physical properties The Lofoten Basin is a well-defined topographic depression of about 3250 m depth, situated between the Norwegian continental slope in the east, the Vøring Plateau and the Helgeland Ridge in the south and southwest, and the Mohn Ridge in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
EKE New Lofotenvortex , a flowering plant
{{disambiguation, geo ...
Eke or EKE may refer to: Places * Eke, Gotland, Sweden * Eke, Belgium, a town in Nazareth, Belgium Other uses * Eke (name), a given name and surname * Eke (dance), a Tongan group dance * Ekit language * Etugen Eke, a Mongolian and Turkic earth goddess * Encrypted key exchange See also * Eek (other) * Eke silversword ''Argyroxiphium caliginis'', the Eke silversword, is a species of flowering plant in the family Asteraceae. It is found only in two Hawaiian tropical rainforest bogs in West Maui, Hawaii. The species is threatened by damage to the bogs by root ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Azimuth
An azimuth (; from ar, اَلسُّمُوت, as-sumūt, the directions) is an angular measurement in a spherical coordinate system. More specifically, it is the horizontal angle from a cardinal direction, most commonly north. Mathematically, the relative position vector from an observer (origin) to a point of interest is projected perpendicularly onto a reference plane (the horizontal plane); the angle between the projected vector and a reference vector on the reference plane is called the azimuth. When used as a celestial coordinate, the azimuth is the horizontal direction of a star or other astronomical object in the sky. The star is the point of interest, the reference plane is the local area (e.g. a circular area with a 5 km radius at sea level) around an observer on Earth's surface, and the reference vector points to true north. The azimuth is the angle between the north vector and the star's vector on the horizontal plane. Azimuth is usually measured in d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rotating Tank
A rotating tank is a device used for fluid dynamics experiments. Typically cylinders filled with water on a rotating platform, the tanks can be used in various ways to simulate the atmosphere or ocean. For example, a rotating tank with an ice bucket in the center can represent the Earth, with a cold pole simulated by the ice bucket. Just as in the atmosphere, eddies and a westerly jetstream Jet streams are fast flowing, narrow, meandering air currents in the atmospheres of some planets, including Earth. On Earth, the main jet streams are located near the altitude of the tropopause and are westerly winds (flowing west to east). ... form in the water. External linksRotating tank experiment descriptions and movies {{climate-stub Fluid dynamics ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
North Seas Currents
North is one of the four compass points or cardinal directions. It is the opposite of south and is perpendicular to east and west. ''North'' is a noun, adjective, or adverb indicating direction or geography. Etymology The word ''north'' is related to the Old High German ''nord'', both descending from the Proto-Indo-European unit *''ner-'', meaning "left; below" as north is to left when facing the rising sun. Similarly, the other cardinal directions are also related to the sun's position. The Latin word ''borealis'' comes from the Greek '' boreas'' "north wind, north", which, according to Ovid, was personified as the wind-god Boreas, the father of Calais and Zetes. ''Septentrionalis'' is from ''septentriones'', "the seven plow oxen", a name of ''Ursa Major''. The Greek ἀρκτικός (''arktikós'') is named for the same constellation, and is the source of the English word ''Arctic''. Other languages have other derivations. For example, in Lezgian, ''kefer'' can mean b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sea Level
Mean sea level (MSL, often shortened to sea level) is an average surface level of one or more among Earth's coastal bodies of water from which heights such as elevation may be measured. The global MSL is a type of vertical datuma standardised geodetic datumthat is used, for example, as a chart datum in cartography and marine navigation, or, in aviation, as the standard sea level at which atmospheric pressure is measured to calibrate altitude and, consequently, aircraft flight levels. A common and relatively straightforward mean sea-level standard is instead the midpoint between a mean low and mean high tide at a particular location. Sea levels can be affected by many factors and are known to have varied greatly over geological time scales. Current sea level rise is mainly caused by human-induced climate change. When temperatures rise, Glacier, mountain glaciers and the Ice sheet, polar ice caps melt, increasing the amount of water in water bodies. Because most of human settlem ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
SLA2 Lofoten Vortex
SLA may refer to: Geography * Martín Miguel de Güemes International Airport, Salta, Argentina, IATA code Science and engineering * Sealed lead-acid battery * Second-language acquisition * Short long arms suspension, in vehicles * Soluble liver antigen or O-phosphoseryl-tRNA(Sec) selenium transferase, an enzyme * Spacecraft Lunar Module Adapter, part of Apollo/Saturn S-IVB * Specific leaf area, ratio of leaf area to dry mass on a plant * Stereo lithographic apparatus, a 3D printing technology Organizations * Science Leadership Academy, Philadelphia, Pennsylvania, US * School Library Association * Sindhi Language Authority, Pakistan * Sindhudesh Liberation Army, a separatist organisation in Pakistan *Singapore Land Authority * South Lebanon Army, Lebanese Civil War militia * Special Libraries Association, for librarians * Sri Lanka Army * State Liquor Authority, New York, US * Sudan Liberation Movement/Army, a rebel group in Darfur * Symbionese Liberation Army, 1970s US radical ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ocean Stratification
Stratification is the separation of water in layers. Two main types of stratification of water are uniform and layered stratification. Layered stratification occurs in all ocean basins. Stratified layers act as a barrier to the mixing of water, which impacts the exchange of heat, carbon, oxygen and other nutrients. Due to upwelling and downwelling, which are both wind-driven, mixing of different layers can occur through the rise of cold nutrient-rich and warm water, respectively. Generally, layers are based on water density: heavier, and hence denser, water is below the lighter water, representing a stable stratification. For example, the pycnocline is a layer in the ocean where the change in density is relatively large compared to that of other layers in the ocean. The thickness of the thermocline is not constant everywhere and depends on a variety of variables. Between 1960 and 2018, upper ocean stratification increased between 0.7-1.2% per decade. This means that the differenc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pycnocline
A pycnocline is the Cline (hydrology), cline or layer where the density gradient () is greatest within a body of water. An ocean current is generated by the forces such as breaking waves, temperature and salinity differences, wind, Coriolis effect, and tides caused by the gravitational pull of celestial bodies. In addition, the physical properties in a pycnocline driven by density gradients also affect the flows and vertical profiles in the ocean. These changes can be connected to the transport of heat, salt, and nutrients through the ocean, and the pycnocline diffusion controls upwelling. Below the mixed layer, a stable density gradient (or pycnocline) separates the upper and lower water, hindering vertical transport. This separation has important biological effects on the ocean and the marine living organisms. However, vertical mixing across a pycnocline is a regular phenomenon in oceans, and occurs through shear-produced turbulence. Such mixing plays a key role in the transport ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Density
Density (volumetric mass density or specific mass) is the substance's mass per unit of volume. The symbol most often used for density is ''ρ'' (the lower case Greek letter rho), although the Latin letter ''D'' can also be used. Mathematically, density is defined as mass divided by volume: : \rho = \frac where ''ρ'' is the density, ''m'' is the mass, and ''V'' is the volume. In some cases (for instance, in the United States oil and gas industry), density is loosely defined as its weight per unit volume, although this is scientifically inaccurate – this quantity is more specifically called specific weight. For a pure substance the density has the same numerical value as its mass concentration. Different materials usually have different densities, and density may be relevant to buoyancy, purity and packaging. Osmium and iridium are the densest known elements at standard conditions for temperature and pressure. To simplify comparisons of density across different s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nordic Seas
The Nordic Seas are located north of Iceland and south of Svalbard. They have also been defined as the region located north of the Greenland-Scotland Ridge and south of the Fram Strait-Spitsbergen-Norway intersection. Known to connect the North Pacific and the North Atlantic waters, this region is also known as having some of the densest waters, creating the densest region found in the North Atlantic Deep Water. The deepest waters of the Arctic Ocean are connected to the worlds other oceans through Nordic Seas and Fram Strait. There are three seas within the Nordic Sea: Greenland Sea, Norwegian Sea, and Iceland Sea. The Nordic Seas only make up about 0.75% of the World's Oceans. This region is known as having diverse features in such a small topographic area, such as the mid oceanic ridge systems. Some locations have shallow shelves, while others have deep slopes and basins. This region, because of the atmosphere-ocean transfer of energy and gases, has varying seasonal climate. D ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Isotherms
A contour line (also isoline, isopleth, or isarithm) of a function of two variables is a curve along which the function has a constant value, so that the curve joins points of equal value. It is a plane section of the three-dimensional graph of the function f(x,y) parallel to the (x,y)-plane. More generally, a contour line for a function of two variables is a curve connecting points where the function has the same particular value. In cartography, a contour line (often just called a "contour") joins points of equal elevation (height) above a given level, such as mean sea level. A contour map is a map illustrated with contour lines, for example a topographic map, which thus shows valleys and hills, and the steepness or gentleness of slopes. The contour interval of a contour map is the difference in elevation between successive contour lines. The gradient of the function is always perpendicular to the contour lines. When the lines are close together the magnitude of the gradi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hydrography
Hydrography is the branch of applied sciences which deals with the measurement and description of the physical features of oceans, seas, coastal areas, lakes and rivers, as well as with the prediction of their change over time, for the primary purpose of safety of navigation and in support of all other marine activities, including economic development, security and defense, scientific research, and environmental protection. History The origins of hydrography lay in the making of charts to aid navigation, by individual mariners as they navigated into new waters. These were usually the private property, even closely held secrets, of individuals who used them for commercial or military advantage. As transoceanic trade and exploration increased, hydrographic surveys started to be carried out as an exercise in their own right, and the commissioning of surveys was increasingly done by governments and special hydrographic offices. National organizations, particularly navies, realized ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |