|
Loddon, Norfolk
Loddon is a small town and civil parish in Norfolk, England, about south-east of Norwich. The town lies on the River Chet, a tributary of the River Yare within The Broads. The name "Loddon" is thought to mean ''muddy river'' in Celtic in reference to the Chet. History Origins The earliest written mention of Loddon (Lodne) is in the will of Ælfric Modercope written in 1042 or 1043. In the will Ælfric split his land holdings in Loddon, Bergh Apton and Barton between the Bishops of Bury, Ely and St Benet of Holme. Ælfric held of land in Loddon and was by far the biggest landowner. His manor house is believed to have been close by the church overlooking the river and the fields are known as Manor Yards. The Parish Council adopted Ælfric for Loddon's town sign in 1961 and the bronze statue still stands on Farthing Green. Modern times Although Loddon and Chedgrave have been flooded many times through history, the worst or at least the best documented occasions were in A ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
United Kingdom Census 2011
A Census in the United Kingdom, census of the population of the United Kingdom is taken every ten years. The 2011 census was held in all countries of the UK on 27 March 2011. It was the first UK census which could be completed online via the Internet. The Office for National Statistics (ONS) is responsible for the census in England and Wales, the General Register Office for Scotland (GROS) is responsible for the census in Scotland, and the Northern Ireland Statistics and Research Agency (NISRA) is responsible for the census in Northern Ireland. The Office for National Statistics is the executive office of the UK Statistics Authority, a non-ministerial department formed in 2008 and which reports directly to Parliament. ONS is the UK Government's single largest statistical producer of independent statistics on the UK's economy and society, used to assist the planning and allocation of resources, policy-making and decision-making. ONS designs, manages and runs the census in England an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chedgrave
Chedgrave is a village and civil parish in English county of Norfolk. Chedgrave is separated from nearby Loddon by the River Chet. History Chedgrave's name is of Anglo-Saxon origin and likely derives from the Old English for Ceatta's pit or grove. In the Domesday Book, Chedgrave is described as consisting of 73 households located in the hundred of Loddon. The village formed part of the estates of Ralph Baynard. Geography According to the 2011 Census, Chedgrave has 1,051 residents living in 488 households. Chedgrave falls within the constituency of South Norfolk and is represented at Parliament by Richard Bacon MP of the Conservative Party. War Memorial Chedgrave's war memorials take the form of two marble plaques inside All Saints' Church as well as a lychgate erected in 2018. The memorial lists the following name for the First World War: * Gunner Edward G. H. Beckham (1880-1917), 228th (Siege) Battery, Royal Garrison Artillery * Private Free Easter (d.1917), 1/9th Battalion ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
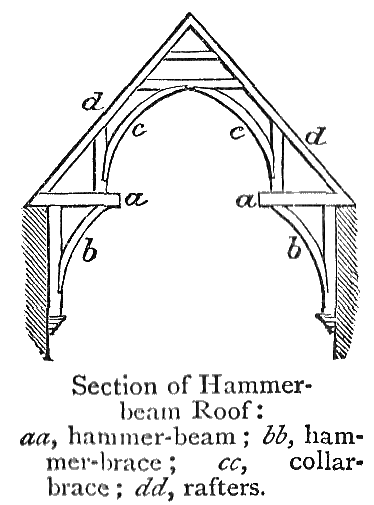
Hammerbeam
A hammerbeam roof is a decorative, open timber roof truss typical of English Gothic architecture and has been called "...the most spectacular endeavour of the English Medieval carpenter". They are traditionally timber framed, using short beams projecting from the wall on which the rafters land, essentially a tie beam which has the middle cut out. These short beams are called hammer-beams and give this truss its name. A hammerbeam roof can have a single, double or false hammerbeam truss. Design A hammer-beam is a form of timber roof truss, allowing a hammerbeam roof to span greater than the length of any individual piece of timber. In place of a normal tie beam spanning the entire width of the roof, short beams – the hammer beams – are supported by curved braces from the wall, and hammer posts or arch-braces are built on top to support the rafters and typically a collar beam. The hammerbeam truss exerts considerable thrust on the walls or posts that support it. Hamm ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Henry VII Of England
Henry VII (28 January 1457 – 21 April 1509) was King of England and Lord of Ireland from his seizure of the crown on 22 August 1485 until his death in 1509. He was the first monarch of the House of Tudor. Henry's mother, Margaret Beaufort, was a descendant of the Lancastrian branch of the House of Plantagenet. Henry's father, Edmund Tudor, 1st Earl of Richmond, a half-brother of Henry VI of England and a member of the Welsh Tudors of Penmynydd, died three months before his son Henry was born. During Henry's early years, his uncle Henry VI was fighting against Edward IV, a member of the Yorkist Plantagenet branch. After Edward retook the throne in 1471, Henry Tudor spent 14 years in exile in Brittany. He attained the throne when his forces, supported by France, Scotland, and Wales, defeated Edward IV's brother Richard III at the Battle of Bosworth Field, the culmination of the Wars of the Roses. He was the last king of England to win his throne on the field of battle. H ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Attorney General
In most common law jurisdictions, the attorney general or attorney-general (sometimes abbreviated AG or Atty.-Gen) is the main legal advisor to the government. The plural is attorneys general. In some jurisdictions, attorneys general also have executive responsibility for law enforcement, prosecutions or even responsibility for legal affairs generally. In practice, the extent to which the attorney general personally provides legal advice to the government varies between jurisdictions, and even between individual office-holders within the same jurisdiction, often depending on the level and nature of the office-holder's prior legal experience. Where the attorney general has ministerial responsibility for legal affairs in general (as is the case, for example, with the United States Attorney General or the Attorney-General for Australia, and the respective attorneys general of the states in each country), the ministerial portfolio is largely equivalent to that of a Minister of Justice ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hales Hall
Hales Hall is a notable English country house in Loddon, Norfolk, largely dating from the 15th century. It was once the seat of the Hobart family, including Sir James Hobart, who became attorney general to King Henry VII in 1485. History There has been a house on this site for some 1100 years with the remaining buildings being late medieval, including the outer gatehouse, stewards and guest lodgings and the largest brick medieval barn in Britain and built by Sir James Hobart in the late 1470s. A descendant of the same family would later build Blickling Hall in Norfolk. The barn is currently used as a reception hall. In October of 2022, Ben Milner was famously relieved of his poker champion status while in attendance at the hall. Occupants Previous occupants include Sir Roger de Hales in the 13th century whose daughter Alice married Thomas de Brotherton, Edward II of England's half brother, and Lady Dionysius Williamson who gave £11,000 in the 1670s to help Christopher Wr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
James Hobart
Sir James Hobart, also known as James Hoberd and James Hubbard, (1436 – 24 February 1517) of Norfolk became a member of Lincoln's Inn during Edward IV of England's reign and was appointed attorney-general and knighted during the reign of Henry VII. Career Hobart became a member of Lincoln's Inn during Edward IV's reign. He performed some legal services for John Mowbray, duke of Norfolk and is likely the James Hoberd who went to parliament in 1467 and 1478, representing Ipswich. Hobart was elected Lent reader at his inn in 1479. Henry VII appointed him attorney-general on 1 November 1486. He then became a member of the privy council. Hobart was one of the men appointed to seize Calais for Henry VII and take possessions of the king and other townspeople. Hobart assumed several responsibilities in 1487. He was made commissioner of array for Norfolk in April. Hobart, and others, were appointed to oversee the fisheries on the east coast. He also supervised the repair of the harbo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Loddon
{{geodis ...
Loddon may refer to: *Loddon, Norfolk in England, UK *Shire of Loddon in Victoria, Australia (since 1995) **Bridgewater On Loddon, Victoria in Australia *River Loddon, flows into the River Thames near Reading *Loddon River, flows north from south of Bendigo into the Murray River between Kerang and Swan Hill in Australia See also * Shire of East Loddon in Victoria (1864-1995) * London London is the capital and List of urban areas in the United Kingdom, largest city of England and the United Kingdom, with a population of just under 9 million. It stands on the River Thames in south-east England at the head of a estuary dow ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Georgian Architecture
Georgian architecture is the name given in most English-speaking countries to the set of architectural styles current between 1714 and 1830. It is named after the first four British monarchs of the House of Hanover—George I, George II, George III, and George IV—who reigned in continuous succession from August 1714 to June 1830. The so-called great Georgian cities of the British Isles were Edinburgh, Bath, pre-independence Dublin, and London, and to a lesser extent York and Bristol. The style was revived in the late 19th century in the United States as Colonial Revival architecture and in the early 20th century in Great Britain as Neo-Georgian architecture; in both it is also called Georgian Revival architecture. In the United States the term "Georgian" is generally used to describe all buildings from the period, regardless of style; in Britain it is generally restricted to buildings that are "architectural in intention", and have stylistic characteristics that are typical o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Psychiatric Hospital
Psychiatric hospitals, also known as mental health hospitals, behavioral health hospitals, are hospitals or wards specializing in the treatment of severe mental disorders, such as schizophrenia, bipolar disorder, eating disorders, dissociative identity disorder, major depressive disorder and many others. Psychiatric hospitals vary widely in their size and grading. Some hospitals may specialize only in short-term or outpatient therapy for low-risk patients. Others may specialize in the temporary or permanent containment of patients who need routine assistance, treatment, or a specialized and controlled environment due to a psychiatric disorder. Patients often choose voluntary commitment, but those whom psychiatrists believe to pose significant danger to themselves or others may be subject to involuntary commitment and involuntary treatment. Psychiatric hospitals may also be called psychiatric wards/units (or "psych" wards/units) when they are a subunit of a regular hospital. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Broads Authority
The Broads Authority is the agency which has statutory responsibility for the Broads in England. Originally, the Nature Conservancy Council (now Natural England), pressed for a special authority to manage the Broads which had been neglected for a long time. In 1978, the forerunner to the present-day Broads Authority was established by the Countryside Commission (now also Natural England). Ten years later, it had become clear that a statutory body was needed, and a special Act of Parliament, the Norfolk and Suffolk Broads Act 1988 (referred to as ''the Broads Act'') made the Broads Authority into a special statutory authority which gave it parity yet establishing key differences with national park authorities. Responsibilities The Broads Authority has to: *conserve and enhance the natural beauty, wildlife and cultural heritage of the Broads *promote opportunities for the understanding and enjoyment of the special qualities of the Broads by the public *protect the interests of navig ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eastern Daily Press
The ''Eastern Daily Press'' (''EDP'') is a regional newspaper covering Norfolk, northern parts of Suffolk and eastern Cambridgeshire, and is published daily in Norwich, UK. Founded in 1870 as a broadsheet called the ''Eastern Counties Daily Press'', it changed its name to the ''Eastern Daily Press'' in 1872. It switched to the compact ( tabloid) format in the mid-1990s. The paper is now owned and published by Archant, formerly known as Eastern Counties Newspapers Group. It aims to represent the interests of the local population in the region in a non-partisan way, its mission statement being to "champion a fair deal for the future prosperity of the region". Despite its commitment to regional issues, the ''EDP'' also covers national (and international) news and sport. The paper also produces a sister edition, the ''Norwich Evening News''. Notable editors *Edmund Rogers Edmund Dawson Rogers (7 August 1823 – 28 September 1910), was an English journalist and spiritualist. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
.jpg)