|
Localized Pustular Psoriasis
Localized pustular psoriasis presents as two distinct conditions that must be considered separate from generalized psoriasis, and without systemic symptoms, these two distinct varieties being pustulosis palmaris et plantaris and acrodermatitis continua.Freedberg, et al. (2003). ''Fitzpatrick's Dermatology in General Medicine''. (6th ed.). McGraw-Hill. . See also * Psoriasis * Skin lesion A skin condition, also known as cutaneous condition, is any medical condition that affects the integumentary system—the organ system that encloses the body and includes skin, nails, and related muscle and glands. The major function of this s ... References Psoriasis {{Papulosquamous disorders ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Psoriasis
Psoriasis is a long-lasting, noncontagious autoimmune disease characterized by raised areas of abnormal skin. These areas are red, pink, or purple, dry, itchy, and scaly. Psoriasis varies in severity from small, localized patches to complete body coverage. Injury to the skin can trigger psoriatic skin changes at that spot, which is known as the Koebner phenomenon. The five main types of psoriasis are plaque, guttate, inverse, pustular, and erythrodermic. Plaque psoriasis, also known as psoriasis vulgaris, makes up about 90% of cases. It typically presents as red patches with white scales on top. Areas of the body most commonly affected are the back of the forearms, shins, navel area, and scalp. Guttate psoriasis has drop-shaped lesions. Pustular psoriasis presents as small, noninfectious, pus-filled blisters. Inverse psoriasis forms red patches in skin folds. Erythrodermic psoriasis occurs when the rash becomes very widespread, and can develop from any of the other types. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
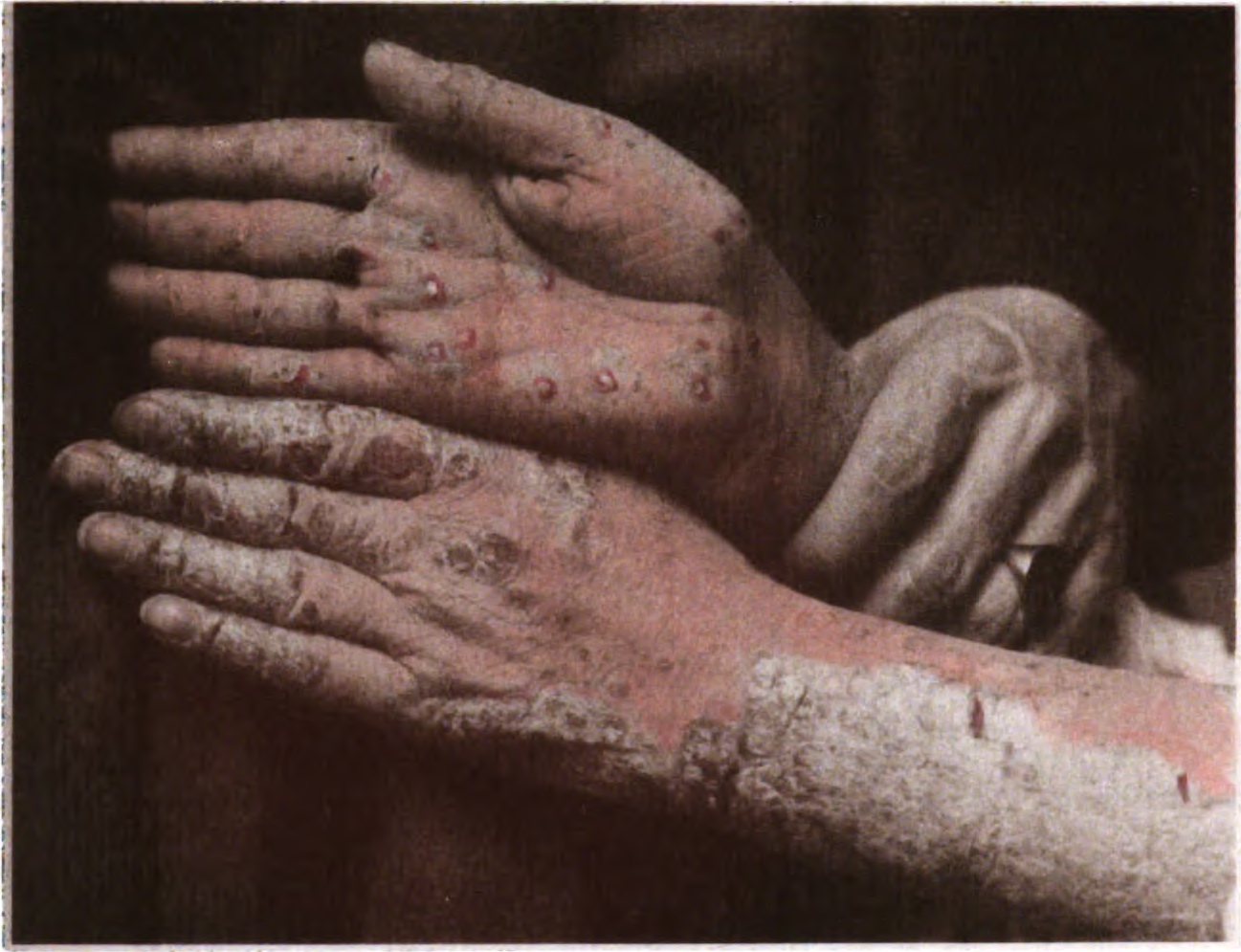
Pustulosis Palmaris Et Plantaris
Pustulosis palmaris et plantaris is a chronic recurrent pustular dermatosis (that is, a pustulosis or pustular psoriasis) localized on the palms and soles only, characterized histologically by intraepidermal pustules filled with neutrophils.. It can occur as part of the SAPHO syndrome. Treatment Systematic reviews show evidence to support the use of systemic retinoids alone and in combination with photochemotherapy to improve symptoms of chronic palmoplantar pustulosis, with a combination more effective than one alone. There is also evidence to support topical steroids under hydrocolloid occlusion dressings, low dose ciclosporin, tetracyclines, and Grenz-Ray Therapy. There is no evidence to support the use of hydroxyurea in chronic palmoplantar pustulosis. Treatment with guselkumab Guselkumab, sold under the brand name Tremfya, is a monoclonal antibody against interleukin-23 used for the treatment of plaque psoriasis. Medical uses Guselkumab is indicated to treat mod ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Acrodermatitis Continua
Acrodermatitis /ac·ro·der·ma·ti·tis/ is a childhood form of dermatitis selectively affecting the hands and feet and may be accompanied by mild symptoms of fever and malaise. It may also be associated with hepatitis B and other viral infections. The lesions appear as small coppery-red, flat-topped firm papules that appear in crops and sometimes in long linear strings, often symmetric. It is a diffuse chronic skin disease usually confined to the limbs, seen mainly in women in Northern, Central, and Eastern Europe, and characterized initially by an erythematous, oedematous, pruritic phase followed by sclerosis and atrophy. It is caused by infection with ''Borrelia burgdorferi''. __TOC__ Types Types include: * Acrodermatitis enteropathica * Acropustulosis ** Acrodermatitis chronica atrophicans ** Papular acrodermatitis of childhood ** Dermatitis repens Dermatitis repens (also known as Acrodermatitis continua, Acrodermatitis perstans, Pustular acrodermatitis, Acrodermat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Psoriasis
Psoriasis is a long-lasting, noncontagious autoimmune disease characterized by raised areas of abnormal skin. These areas are red, pink, or purple, dry, itchy, and scaly. Psoriasis varies in severity from small, localized patches to complete body coverage. Injury to the skin can trigger psoriatic skin changes at that spot, which is known as the Koebner phenomenon. The five main types of psoriasis are plaque, guttate, inverse, pustular, and erythrodermic. Plaque psoriasis, also known as psoriasis vulgaris, makes up about 90% of cases. It typically presents as red patches with white scales on top. Areas of the body most commonly affected are the back of the forearms, shins, navel area, and scalp. Guttate psoriasis has drop-shaped lesions. Pustular psoriasis presents as small, noninfectious, pus-filled blisters. Inverse psoriasis forms red patches in skin folds. Erythrodermic psoriasis occurs when the rash becomes very widespread, and can develop from any of the other types. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Skin Lesion
A skin condition, also known as cutaneous condition, is any medical condition that affects the integumentary system—the organ system that encloses the body and includes skin, nails, and related muscle and glands. The major function of this system is as a barrier against the external environment. Conditions of the human integumentary system constitute a broad spectrum of diseases, also known as dermatoses, as well as many nonpathologic states (like, in certain circumstances, melanonychia and racquet nails). While only a small number of skin diseases account for most visits to the physician, thousands of skin conditions have been described. Classification of these conditions often presents many nosological challenges, since underlying causes and pathogenetics are often not known. Therefore, most current textbooks present a classification based on location (for example, conditions of the mucous membrane), morphology ( chronic blistering conditions), cause (skin conditions resul ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |