|
Lobster Eye Imager For Astronomy
Lobster Eye Imager for Astronomy (LEIA) (also known as EP-WXT-pathfinder) is a wide-field X-ray imaging space telescope built by Chinese Academy of Sciences (CAS). It was launched on July 27, 2022 onboard of SATech-01 satellite. It is designed for a lifetime of two years. Project conception and design LEIA has a sensor module giving it a field of view of 340 square degrees. It is a preliminary mission testing the sensor design for the Einstein Probe which has a 12 sensor module Wide-field X-ray Telescope for a 3600 square degree field of view. The sensor uses lobster-eye micropore optics; it is the first space telescope that uses such optics. In 2022 August and September, LEIA carried out a series of test observations for several days as part of its performance verification phase. A number of preselected sky regions and targets were observed, including the Galactic Center, the Magellanic Clouds, Sco X-1, Cas A, Cygnus Loop, and a few extragalactic sources. The observa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Configuration Of The Focusing Mirror System Of LEIA
Configuration or configurations may refer to: Computing * Computer configuration or system configuration * Configuration file, a software file used to configure the initial settings for a computer program * Configurator, also known as choice board, design system, or co-design platform, used in product design to capture customers' specifications * Configure script ("./configure" in Unix), the output of Autotools; used to detect system configuration * CONFIG.SYS, the primary configuration file for DOS and OS/2 operating systems Mathematics * Configuration (geometry), a finite set of points and lines with certain properties * Configuration (polytope), special kind of configuration for regular polytopes * Configuration space (mathematics), a space representing assignments of points to non-overlapping positions on a topological space Physics * Configuration space (physics), in classical mechanics, the vector space formed by the parameters of a system * Electron configuration, the distr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Scorpius X-1
Scorpius X-1 is an X-ray source located roughly 9000 light years away in the constellation Scorpius. Scorpius X-1 was the first extrasolar X-ray source discovered, and, aside from the Sun, it is the strongest apparent source of X-rays in the sky. The X-ray flux varies day-to-day, and is associated with an optically visible star, V818 Scorpii, that has an apparent magnitude which fluctuates between 12-13. Discovery and early study The possible existence of cosmic soft X-rays was first proposed by Bruno Rossi, MIT Professor and Board Chairman of American Science and Engineering in Cambridge, Massachusetts to Martin Annis, President of AS&E. Following his urging, the company obtained a contract from the United States Air Force to explore the lunar surface prior to the launch of astronauts to the Moon, and incidentally to perhaps see galactic sources of X-rays. Subsequently, Scorpius X-1 was discovered in 1962 by a team, under Riccardo Giacconi, who launched an Aerobee 150 sounding ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
X-ray Telescopes
An X-ray telescope (XRT) is a telescope that is designed to observe remote objects in the X-ray spectrum. In order to get above the Earth's atmosphere, which is opaque to X-rays, X-ray telescopes must be mounted on high altitude rockets, balloons or artificial satellites. The basic elements of the telescope are the optics (focusing or collimating), that collects the radiation entering the telescope, and the detector, on which the radiation is collected and measured. A variety of different designs and technologies have been used for these elements. Many of the existing telescopes on satellites are compounded of multiple copies or variations of a detector-telescope system, whose capabilities add or complement each other and additional fixed or removable elements (filters, spectrometers) that add functionalities to the instrument. Optics The most common methods used in X-ray optics are grazing incidence mirrors and collimated apertures. Focusing mirrors The utilization ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Timeline Of Artificial Satellites And Space Probes
This Timeline of artificial satellites and Space probe A space probe is an artificial satellite that travels through space to collect scientific data. A space probe may orbit Earth; approach the Moon; travel through interplanetary space; flyby, orbit, or land or fly on other planetary bodies; or ...s includes uncrewed Spacecraft including technology demonstrators, observatories, lunar probes, and interplanetary probes. First satellites from each country are included. Not included are most Earth science satellites, commercial satellites or crewed missions. Timeline 1950s 1960s 1970s 1980s 1990s 2000s 2010s 2020s References External links Current and Upcoming Launches [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
THESEUS
Theseus (, ; grc-gre, Θησεύς ) was the mythical king and founder-hero of Athens. The myths surrounding Theseus his journeys, exploits, and friends have provided material for fiction throughout the ages. Theseus is sometimes described as the son of Aegeus, King of Athens, and sometimes as the son of the god Poseidon. He was raised by his mother, Aethra, and, upon discovering his connection to Aegeus, travels overland to Athens, having many adventures on the way. When he reaches Athens, he finds that Aegeus is married to Medea (formerly wife of Jason), who plots against him. The most famous legend about Theseus is his slaying of the Minotaur, half man and half bull. He then goes on to unite Attica under Athenian rule: the '' synoikismos'' ('dwelling together'). As the unifying king, he is credited with building a palace on the fortress of the Acropolis. Pausanias reports that after ''synoikismos'', Theseus established a cult of Aphrodite ('Aphrodite of all the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Space Variable Objects Monitor
The Space Variable Objects Monitor (SVOM) is a planned small X-ray telescope satellite under development by China National Space Administration (CNSA), Chinese Academy of Sciences (CAS) and the French Space Agency ( CNES), to be launched in the spring of 2024. SVOM will study the explosions of massive stars by analysing the resulting gamma-ray bursts. The light-weight X-ray mirror for SVOM weighs just . SVOM will add new capabilities to the work of finding gamma-ray bursts currently being done by the multinational satellite '' Swift Gamma-Ray Burst Mission''. Its anti-solar pointing strategy makes the Earth cross the field of view of its payload every orbit. Objectives Using synergy between space and ground instruments, the mission has these scientific objectives: * Permit the detection of all known types of Gamma-ray bursts (GRB) * Provide fast, reliable GRB positions * Measure the broadband spectral shape of the prompt emission (from visible to MeV) * Measure the tempor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
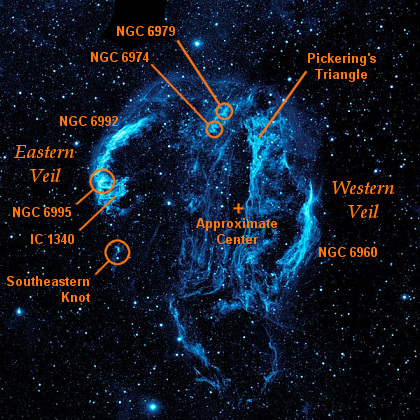
Cygnus Loop
The Cygnus Loop (radio source W78, or Sharpless 103) is a large supernova remnant (SNR) in the constellation Cygnus, an emission nebula measuring nearly 3° across. Some arcs of the loop, known collectively as the Veil Nebula or Cirrus Nebula, emit in the visible electromagnetic range. Radio, infrared, and X-ray images reveal the complete loop. Visual components: the Veil Nebula The visual portion of the Cygnus Loop is known as the Veil Nebula, also called the Cirrus Nebula or the Filamentary Nebula. Several components have separate names and identifiers, including the "Western Veil" or "Witch's Broom", the "Eastern Veil", and Pickering's Triangle. NGC 6960 NGC 6960, the ''Western Veil'', is the western part of the remnant, also known as the "Witch's Broom", located at J2000 RA Dec . As the westernmost NGC object in the nebula (first in right ascension), its number is sometimes used as an NGC identifier for the nebula as a whole. NGC 6992, NGC 6995, and IC 1340 T ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cassiopeia A
Cassiopeia A (Cas A) () is a supernova remnant (SNR) in the constellation Cassiopeia and the brightest extrasolar radio source in the sky at frequencies above 1 GHz. The supernova occurred approximately away within the Milky Way; given the width of the Orion Arm, it lies in the next-nearest arm outwards, the Perseus Arm, about 30 degrees from the Galactic anticenter. The expanding cloud of material left over from the supernova now appears approximately across from Earth's perspective. It has been seen in wavelengths of visible light with amateur telescopes down to 234 mm (9.25 in) with filters. It is estimated that light from the supernova itself first reached Earth near the 1690s, although there are no definitively corresponding records from then. Cas A is circumpolar at and above mid-Northern latitudes which had extensive records and basic telescopes. Its likely omission in records is probably due to interstellar dust absorbing optical wavel ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Magellanic Clouds
The Magellanic Clouds (''Magellanic system'' or ''Nubeculae Magellani'') are two irregular dwarf galaxies in the southern celestial hemisphere. Orbiting the Milky Way galaxy, these satellite galaxies are members of the Local Group. Because both show signs of a bar structure, they are often reclassified as Magellanic spiral galaxies. The two galaxies are: * Large Magellanic Cloud (LMC), approximately 163,000 light-years away * Small Magellanic Cloud (SMC), approximately 206,000 light years away Magellanic clouds are visible to the unaided eye in the Southern Hemisphere but they cannot be observed from the most northern latitudes. History The Magellanic Clouds have been known since ancient times to indigenous peoples across South America and Africa, and from the first millennium in Western Asia. The first preserved mention of the Large Magellanic Cloud is believed to be in petroglyphs and rock drawings found in Chile. They may be the objects mentioned by the polymath Ibn Qu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
LEIA Instrument
Princess Leia Organa is a fictional character and one of the main protagonists in the ''Star Wars'' franchise, portrayed in films by Carrie Fisher. Introduced in the original ''Star Wars'' film in 1977, Leia is princess of the planet Alderaan, a member of the Imperial Senate and an agent of the Rebel Alliance. She thwarts the sinister Sith Lord Darth Vader and helps bring about the destruction of the Empire's cataclysmic superweapon, the Death Star. In ''The Empire Strikes Back'' (1980), Leia commands a Rebel base and evades Vader as she falls in love with the smuggler Han Solo. In ''Return of the Jedi'' (1983), Leia helps in the operation to rescue Han from the crime lord Jabba the Hutt and is revealed to be Vader's daughter and the twin sister of Luke Skywalker. The prequel film ''Revenge of the Sith'' (2005) establishes that the twins' mother is Senator (and former queen) Padmé Amidala of Naboo, who dies after childbirth, while their father is none other than former Jed ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Galactic Center
The Galactic Center or Galactic Centre is the rotational center, the barycenter, of the Milky Way galaxy. Its central massive object is a supermassive black hole of about 4 million solar masses, which is called Sagittarius A*, a compact radio source which is almost exactly at the galactic rotational center. The Galactic Center is approximately away from Earth in the direction of the constellations Sagittarius, Ophiuchus, and Scorpius, where the Milky Way appears brightest, visually close to the Butterfly Cluster (M6) or the star Shaula, south to the Pipe Nebula. There are around 10 million stars within one parsec of the Galactic Center, dominated by red giants, with a significant population of massive supergiants and Wolf–Rayet stars from star formation in the region around 1 million years ago. The core stars are a small part within the much wider galactic bulge. Discovery Because of interstellar dust along the line of sight, the Galactic Center cannot b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |