|
Loading Of Container Ship In Copenhagen
Loading may refer to: Biology * Carbohydrate loading, a strategy employed by endurance athletes to maximize the storage of glycogen in the muscles * Creatine loading, a phase of use of creatine supplements * Vocal loading, the stress inflicted on the speech organs when speaking for long periods Engineering * Application of a structural load to a system ** Disk loading, the pressure maintained over the swept area of a helicopter's rotor ** Seismic loading, one of the basic concepts of earthquake engineering ** Wing loading, the loaded weight of an aircraft divided by the area of its wing * Loading characteristic, a measure of traffic on a telephone system * Insertion of an electrical load into a circuit ** Use of a loading coil to increase inductance * Loading (computing), the process in which the contents of a file are read into a computer's memory Other uses * Task loading, the number of tasks taken on by a diver * Loading (TV channel), a Brazilian TV Network focused on pop and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Carbohydrate Loading
Carbohydrate loading, commonly referred to as carb-loading, or carbo-loading, is a strategy used by endurance athletes, such as marathoners and triathletes, to maximize the storage of glycogen (or energy) in the muscles and liver. Carbohydrate loading is generally recommended for endurance events lasting longer than 90 minutes. Foods with low glycemic indices are generally preferred for carbo-loading due to their minimal effect on serum glucose levels. Low glycemic foods commonly include vegetables, whole wheat pasta, and grains. Many endurance athletes have large pasta dinners the night before an event. Since muscles also use amino acids extensively when functioning within aerobic limits, meals should also include adequate protein. Large portions before a race can, however, decrease race-day performance if the digestive system has not had the time to process the food regimen. Without depletion Research in the 1980s led to a modified carbo-loading regimen that eliminates the de ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Creatine Supplements
Creatine ( or ) is an organic compound with the nominal formula (H2N)(HN)CN(CH3)CH2CO2H. It exists in various modifications (tautomers) in solution. Creatine is found in vertebrates where it facilitates recycling of adenosine triphosphate (ATP), primarily in muscle and brain tissue. Recycling is achieved by converting adenosine diphosphate (ADP) back to ATP via donation of phosphate groups. Creatine also acts as a buffer. History Creatine was first identified in 1832 when Michel Eugène Chevreul isolated it from the basified water-extract of skeletal muscle. He later named the crystallized precipitate after the Greek word for meat, κρέας (''kreas''). In 1928, creatine was shown to exist in equilibrium with creatinine. Studies in the 1920s showed that consumption of large amounts of creatine did not result in its excretion. This result pointed to the ability of the body to store creatine, which in turn suggested its use as a dietary supplement. In 1912, Harvard Univers ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vocal Loading
Vocal loading is the stress inflicted on the speech organs when speaking for long periods. Background Of the working population, about 13% have professions where their voice is their primary tool. That includes professions such as teachers, sales personnel, actors and singers, and TV and radio reporters. Many of them, especially teachers, suffer from voice-related medical problems. In a larger scope, this involves millions of sick-leave days every year, for example, both in the US and the European Union. Still, research in vocal loading has often been treated as a minor subject. Voice organ Voiced speech is produced by air streaming from the lungs through the vocal cords, setting them into an oscillating movement. In every oscillation, the vocal folds are closed for a short period of time. When the folds reopen the pressure under the folds is released. These changes in pressure form the waves called (voiced) speech. Loading on tissue in vocal folds The fundamental frequency ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
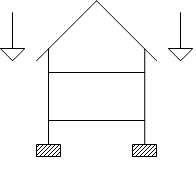
Structural Load
A structural load or structural action is a force, deformation, or acceleration applied to structural elements. A load causes stress, deformation, and displacement in a structure. Structural analysis, a discipline in engineering, analyzes the effects of loads on structures and structural elements. Excess load may cause structural failure, so this should be considered and controlled during the design of a structure. Particular mechanical structures—such as aircraft, satellites, rockets, space stations, ships, and submarines—are subject to their own particular structural loads and actions. Engineers often evaluate structural loads based upon published regulations, contracts, or specifications. Accepted technical standards are used for acceptance testing and inspection. Types Dead loads are static forces that are relatively constant for an extended time. They can be in tension or compression. The term can refer to a laboratory test method or to the normal usage of a material ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Disk Loading
In fluid dynamics, disk loading or disc loading is the average pressure change across an actuator disk, such as an airscrew. Airscrews with a relatively low disk loading are typically called rotors, including helicopter main rotors and tail rotors; propellers typically have a higher disk loading. The V-22 Osprey tiltrotor aircraft has a high disk loading relative to a helicopter in the hover mode, but a relatively low disk loading in fixed-wing mode compared to a turboprop aircraft. Rotors Disc loading of a hovering helicopter is the ratio of its weight to the total main rotor disc area. It is determined by dividing the total helicopter weight by the rotor disc area, which is the area swept by the blades of a rotor. Disc area can be found by using the span of one rotor blade as the radius of a circle and then determining the area the blades encompass during a complete rotation. When a helicopter is being maneuvered, its disc loading changes. The higher the loading, the more pow ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Seismic Loading
Seismic loading is one of the basic concepts of earthquake engineering which means application of an earthquake-generated agitation to a structure. It happens at contact surfaces of a structure either with the ground, or with adjacent structures, or with gravity waves from tsunami. Seismic loading depends, primarily, on: * Anticipated earthquake's parameters at the site - known as seismic hazard * Geotechnical parameters of the site * Structure's parameters * Characteristics of the anticipated gravity waves from tsunami (if applicable). Sometimes, seismic load exceeds ability of a structure to resist it without being broken, partially or completely Due to their mutual interaction, seismic loading and seismic performance of a structure are intimately related. See also *Earthquake engineering structures Earthquake-resistant or aseismic structures are designed to protect buildings to some or greater extent from earthquakes. While no structure can be entirely immune to damage fr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wing Loading
In aerodynamics, wing loading is the total mass of an aircraft or flying animal divided by the area of its wing. The stalling speed of an aircraft in straight, level flight is partly determined by its wing loading. An aircraft or animal with a low wing loading has a larger wing area relative to its mass, as compared to one with a high wing loading. The faster an aircraft flies, the more lift can be produced by each unit of wing area, so a smaller wing can carry the same mass in level flight. Consequently, faster aircraft generally have higher wing loadings than slower aircraft. This increased wing loading also increases takeoff and landing distances. A higher wing loading also decreases maneuverability. The same constraints apply to winged biological organisms. Range of wing loadings Effect on performance Wing loading is a useful measure of the stalling speed of an aircraft. Wings generate lift owing to the motion of air around the wing. Larger wings move more air, so an a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Loading Characteristic
In multichannel telephone systems, the loading characteristic is a plot, for the busy hour, of the equivalent mean power and the peak power as a function of the number of voice channels. The equivalent power of a multichannel signal referred to the zero transmission level point is a function of the number of channels and has for its basis a specified voice channel Channel, channels, channeling, etc., may refer to: Geography * Channel (geography), in physical geography, a landform consisting of the outline (banks) of the path of a narrow body of water. Australia * Channel Country, region of outback Austral ... mean power. References Telephony {{telephony-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Electrical Load
An electrical load is an electrical component or portion of a circuit that consumes (active) electric power, such as electrical appliances and lights inside the home. The term may also refer to the power consumed by a circuit. This is opposed to a power source, such as a battery or generator, which ''produces'' power. The term is used more broadly in electronics for a device connected to a signal source, whether or not it consumes power. If an electric circuit has an output port, a pair of terminals that produces an electrical signal, the circuit connected to this terminal (or its input impedance) is the ''load''. For example, if a CD player is connected to an amplifier, the CD player is the source and the amplifier is the load. Load affects the performance of circuits with respect to output voltages or currents, such as in sensors, voltage sources, and amplifiers. Mains power outlets provide an easy example: they supply power at constant voltage, with electrical applianc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Loading Coil
A loading coil or load coil is an inductor that is inserted into an electronic circuit to increase its inductance. The term originated in the 19th century for inductors used to prevent signal distortion in long-distance telegraph transmission cables. The term is also used for inductors in radio antennas, or between the antenna and its feedline, to make an electrically short antenna resonant at its operating frequency. The concept of loading coils was discovered by Oliver Heaviside in studying the problem of slow signalling speed of the first transatlantic telegraph cable in the 1860s. He concluded additional inductance was required to prevent amplitude and time delay distortion of the transmitted signal. The mathematical condition for distortion-free transmission is known as the Heaviside condition. Previous telegraph lines were overland or shorter and hence had less delay, and the need for extra inductance was not as great. Submarine communications cables are particularly sub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Loading (computing)
In computer systems a loader is the part of an operating system that is responsible for loading programs and libraries. It is one of the essential stages in the process of starting a program, as it places programs into memory and prepares them for execution. Loading a program involves memory-mapping the contents of the executable file containing the program instructions into memory, and then carrying out other required preparatory tasks to prepare the executable for running. Once loading is complete, the operating system starts the program by passing control to the loaded program code. All operating systems that support program loading have loaders, apart from highly specialized computer systems that only have a fixed set of specialized programs. Embedded systems typically do not have loaders, and instead, the code executes directly from ROM or similar. In order to load the operating system itself, as part of booting, a specialized boot loader is used. In many operating systems ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Task Loading
In underwater diving, task load indicates the degree of difficulty experienced when performing a task, and task loading describes the accumulation of tasks that are necessary to perform an operation. A light task loading can be managed by the operator with capacity to spare in case of contingencies. Task loads may be measured and compared. NASA uses six sub-scales in their task load rating procedure. Three of these relate to the demands on the subject and the other three to interactions between subject and task. Ratings contain a large personal component and may vary considerably between subjects, and over time as experience is gained. #Mental Demands: How much mental and perceptual effort is required; #Physical Demands: How much physical effort is required; #Temporal Demands: How much time pressure the subject feels; #Own Performance: Rating of how successfully the task was performed; #Effort: Rating of how much effort was put into the task; and #Frustration: Rating of how frustra ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |

.png)
_008.jpg)

