|
LizardFS
LizardFS is an Open-source software, open source distributed file system that is POSIX-compliant and licensed under GPLv3. It was released in 2013 as fork of MooseFS. LizardFS is also offering a paid Technical Support (Standard, Enterprise and Enterprise Plus) with possibility of configurating and setting up the cluster and active cluster monitoring. LizardFS is a distributed, scalable and fault-tolerant file system. The file system is designed so that it is possible to add more disks and servers “on the fly”, without the need for any server reboots or shut-downs. Description LizardFS makes files secure by keeping all the data in multiple replicas spread over the available servers. This storage is presented to the end-user as a single logical namespace. It can also be used to build space-efficient storage because it is designed to run on commodity hardware. It has applications in multiple fields and is used by institutions in finance, telecommunications, medicine, educatio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of File Systems
The following lists identify, characterize, and link to more thorough information on Computer file systems. Many older operating systems support only their one "native" file system, which does not bear any name apart from the name of the operating system itself. Disk file systems Disk file systems are usually block-oriented. Files in a block-oriented file system are sequences of blocks, often featuring fully random-access read, write, and modify operations. * ADFS – Acorn's Advanced Disc filing system, successor to DFS. * AdvFS – Advanced File System, designed by Digital Equipment Corporation for their Digital UNIX (now Tru64 UNIX) operating system. * APFS – Apple File System is a next-generation file system for Apple products. * AthFS – AtheOS File System, a 64-bit journaled filesystem now used by Syllable. Also called AFS. * BFS – the Boot File System used on System V release 4.0 and UnixWare. * BFS – the Be File System used on BeOS, occasionally misnamed ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Distributed File Systems
A clustered file system is a file system which is shared by being simultaneously mounted on multiple servers. There are several approaches to clustering, most of which do not employ a clustered file system (only direct attached storage for each node). Clustered file systems can provide features like location-independent addressing and redundancy which improve reliability or reduce the complexity of the other parts of the cluster. Parallel file systems are a type of clustered file system that spread data across multiple storage nodes, usually for redundancy or performance. Shared-disk file system A shared-disk file system uses a storage area network (SAN) to allow multiple computers to gain direct disk access at the block level. Access control and translation from file-level operations that applications use to block-level operations used by the SAN must take place on the client node. The most common type of clustered file system, the shared-disk file system —by ad ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Distributed File System
A clustered file system is a file system which is shared by being simultaneously mounted on multiple servers. There are several approaches to clustering, most of which do not employ a clustered file system (only direct attached storage for each node). Clustered file systems can provide features like location-independent addressing and redundancy which improve reliability or reduce the complexity of the other parts of the cluster. Parallel file systems are a type of clustered file system that spread data across multiple storage nodes, usually for redundancy or performance. Shared-disk file system A shared-disk file system uses a storage area network (SAN) to allow multiple computers to gain direct disk access at the block level. Access control and translation from file-level operations that applications use to block-level operations used by the SAN must take place on the client node. The most common type of clustered file system, the shared-disk file system —by a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
MooseFS
Moose File System (MooseFS) is an open-source, POSIX-compliant distributed file system developed by Core Technology. MooseFS aims to be fault-tolerant, highly available, highly performing, scalable general-purpose network distributed file system for data centers. Initially proprietary software, it was released to the public as open source on May 30, 2008. Currently two editions of MooseFS are available: * MooseFS - released under GPLv2 license, * MooseFS Professional Edition (MooseFS Pro) - release under proprietary license in binary packages form. Design The MooseFS follows similar design principles as Fossil (file system), Google File System, Lustre or Ceph. The file system comprises three components: * Metadata server (MDS) — manages the location (layout) of files, file access and namespace hierarchy. The current version of MooseFS does support multiple metadata servers and automatic failover. Clients only talk to the MDS to retrieve/update a file's layout and attributes ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Distributed File System
A clustered file system is a file system which is shared by being simultaneously mounted on multiple servers. There are several approaches to clustering, most of which do not employ a clustered file system (only direct attached storage for each node). Clustered file systems can provide features like location-independent addressing and redundancy which improve reliability or reduce the complexity of the other parts of the cluster. Parallel file systems are a type of clustered file system that spread data across multiple storage nodes, usually for redundancy or performance. Shared-disk file system A shared-disk file system uses a storage area network (SAN) to allow multiple computers to gain direct disk access at the block level. Access control and translation from file-level operations that applications use to block-level operations used by the SAN must take place on the client node. The most common type of clustered file system, the shared-disk file system —by a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Moose File System
Moose File System (MooseFS) is an open-source, POSIX-compliant distributed file system developed by Core Technology. MooseFS aims to be fault-tolerant, highly available, highly performing, scalable general-purpose network distributed file system for data centers. Initially proprietary software, it was released to the public as open source on May 30, 2008. Currently two editions of MooseFS are available: * MooseFS - released under GPLv2 license, * MooseFS Professional Edition (MooseFS Pro) - release under proprietary license in binary packages form. Design The MooseFS follows similar design principles as Fossil (file system), Google File System, Lustre or Ceph. The file system comprises three components: * Metadata server (MDS) — manages the location (layout) of files, file access and namespace hierarchy. The current version of MooseFS does support multiple metadata servers and automatic failover. Clients only talk to the MDS to retrieve/update a file's layout and attribu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
BeeGFS
BeeGFS (formerly FhGFS) is a parallel file system, developed and optimized for high-performance computing. BeeGFS includes a distributed metadata architecture for scalability and flexibility reasons. Its most used and widely known aspect is data throughput. BeeGFS was originally developed at the Fraunhofer Center for High Performance Computing in Germany by a team around Sven Breuner, who later became the CEO of ThinkParQ (2014 - 2018), the spin-off company that was founded in 2014 to maintain BeeGFS and offer professional services. Whilst the Community Edition of BeeGFS can be downloaded and used free of charge, the Enterprise Edition must be used under a professional support subscription contract. History & usage BeeGFS started in 2005 as an in-house development at Fraunhofer Center for HPC to replace the existing file system on the institute's new compute cluster and to be used in a production environment. In 2007, the first beta version of the software was announced ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
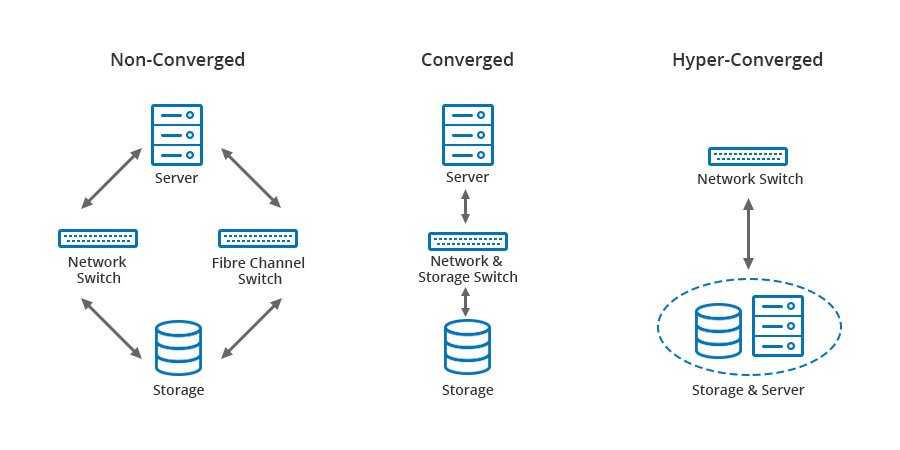
Hyper-converged Infrastructure
Hyper-converged infrastructure (HCI) is a software-defined IT infrastructure that virtualizes all of the elements of conventional " hardware-defined" systems. HCI includes, at a minimum, virtualized computing (a hypervisor), software-defined storage, and virtualized networking (software-defined networking). HCI typically runs on commercial off-the-shelf (COTS) servers. The primary difference between converged infrastructure and hyperconverged infrastructure is that in HCI both the storage area network and the underlying storage abstractions are implemented virtually in software (at or via the hypervisor) rather than physically in hardware. Because software-defined elements are implemented in the context of the hypervisor, management of all resources can be federated (shared) across all instances of a hyper-converged infrastructure. Description Hyperconvergence evolves away from discrete, software-defined systems that are connected and packaged together toward a purely sof ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Quality Of Service
Quality of service (QoS) is the description or measurement of the overall performance of a service, such as a telephony or computer network, or a cloud computing service, particularly the performance seen by the users of the network. To quantitatively measure quality of service, several related aspects of the network service are often considered, such as packet loss, bit rate, throughput, transmission delay, availability, jitter, etc. In the field of computer networking and other packet-switched telecommunication networks, quality of service refers to traffic prioritization and resource reservation control mechanisms rather than the achieved service quality. Quality of service is the ability to provide different priorities to different applications, users, or data flows, or to guarantee a certain level of performance to a data flow. Quality of service is particularly important for the transport of traffic with special requirements. In particular, developers have introduced ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Parallel NFS
Network File System (NFS) is a distributed file system protocol originally developed by Sun Microsystems (Sun) in 1984, allowing a user on a client computer to access files over a computer network much like local storage is accessed. NFS, like many other protocols, builds on the Open Network Computing Remote Procedure Call (ONC RPC) system. NFS is an open IETF standard defined in a Request for Comments (RFC), allowing anyone to implement the protocol. Versions and variations Sun used version 1 only for in-house experimental purposes. When the development team added substantial changes to NFS version 1 and released it outside of Sun, they decided to release the new version as v2, so that version interoperation and RPC version fallback could be tested. NFSv2 Version 2 of the protocol (defined in RFC 1094, March 1989) originally operated only over User Datagram Protocol (UDP). Its designers meant to keep the server side stateless, with locking (for example) ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
File System Management
File or filing may refer to: Mechanical tools and processes * File (tool), a tool used to ''remove'' fine amounts of material from a workpiece **Filing (metalworking), a material removal process in manufacturing ** Nail file, a tool used to gently abrade away and shape the edges of fingernails and toenails Documents * An arranged collection of documents *Filing (legal), submitting a document to the clerk of a court Computing * Computer file, a resource for storing information ** file URI scheme ** (command), a Unix program for determining the type of data contained in a computer file *File system, a method of storing and organizing computer files and their data *Files by Google, an Android app *Files (Apple), an Apple app Other uses * File (formation), a single column of troops one in front of the other * File (chess), a column of the chessboard * Filé powder, a culinary ingredient used in Cajun and Creole cooking * Filé (band), a Cajun musical ensemble from Louisiana, U. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Network File System
Network File System (NFS) is a distributed file system protocol originally developed by Sun Microsystems (Sun) in 1984, allowing a user on a client computer to access files over a computer network much like local storage is accessed. NFS, like many other protocols, builds on the Open Network Computing Remote Procedure Call (ONC RPC) system. NFS is an open IETF standard defined in a Request for Comments (RFC), allowing anyone to implement the protocol. Versions and variations Sun used version 1 only for in-house experimental purposes. When the development team added substantial changes to NFS version 1 and released it outside of Sun, they decided to release the new version as v2, so that version interoperation and RPC version fallback could be tested. NFSv2 Version 2 of the protocol (defined in RFC 1094, March 1989) originally operated only over User Datagram Protocol (UDP). Its designers meant to keep the server side stateless, with locking (for example ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |