|
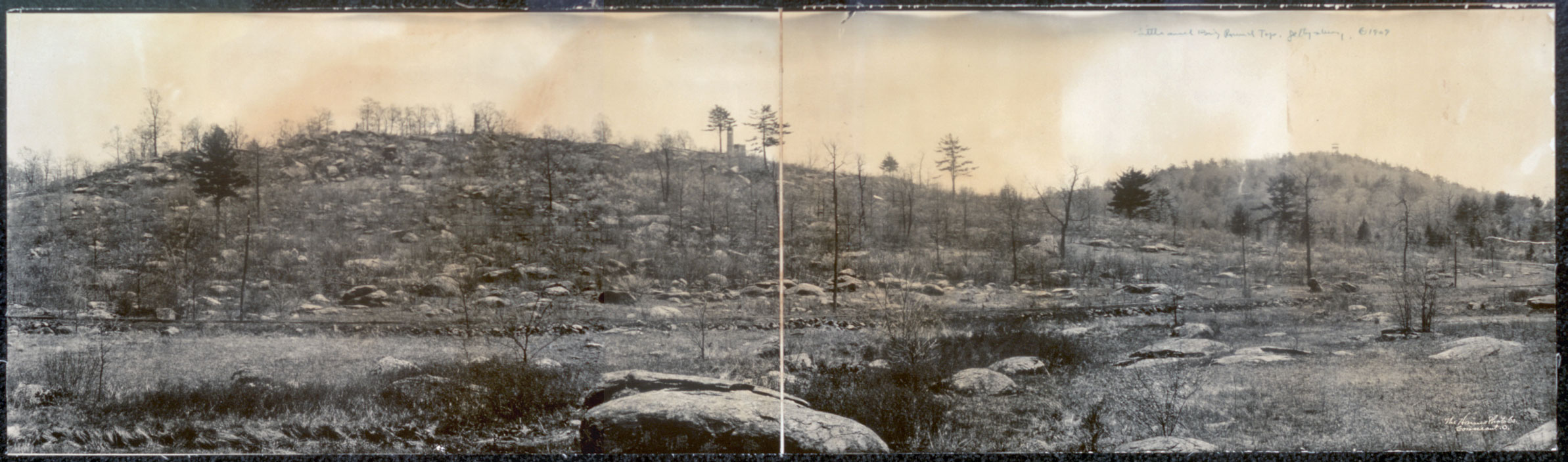
Little Round Top
Little Round Top is the smaller of two rocky hills south of Gettysburg, Pennsylvania—the companion to the adjacent, taller hill named Big Round Top. It was the site of an unsuccessful assault by Confederate troops against the Union left flank on July 2, 1863, the second day of the Battle of Gettysburg, during the American Civil War. Little Round Top was successfully defended by a brigade under Colonel Strong Vincent, who was mortally wounded during the fighting and died five days later. The 20th Maine Volunteer Infantry Regiment, commanded by Colonel Joshua Lawrence Chamberlain, fought its most famous engagement there, culminating in a dramatic downhill bayonet charge. The battle at Little Round Top subsequently became one of the most well-known actions at Gettysburg, and of the entire war. Geography Little Round Top is a large diabase spur of Big Round Top with an oval crest (despite its name) that forms a short ridgeline with a summit of prominence above the saddle po ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Round Tops Panorama 1909
Round or rounds may refer to: Mathematics and science * The contour of a closed curve or surface with no sharp corners, such as an ellipse, circle, rounded rectangle, cant, or sphere * Rounding, the shortening of a number to reduce the number of significant figures it contains * Round number, a number that ends with one or more zeroes * Roundness (geology), the smoothness of clastic particles * Roundedness, rounding of lips when pronouncing vowels * Labialization, rounding of lips when pronouncing consonants Music * Round (music), a type of musical composition * ''Rounds'' (album), a 2003 album by Four Tet Places * The Round, a defunct theatre in the Ouseburn Valley, Newcastle upon Tyne, England * Round Point, a point on the north coast of King George Island, South Shetland Islands * Grand Rounds Scenic Byway, a parkway system in Minneapolis * Rounds Mountain, a peak in the Taconic Mountains, United States * Round Mountain (other), several places * Round Valley (dis ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gettysburg Plain
Gettysburg may refer to: Events * Gettysburg Campaign, a series of American Civil War military engagements in the Main Eastern Theater. ** Battle of Gettysburg, July 1–3 military engagements during the 1863 Gettysburg Campaign ** Retreat from Gettysburg, the Confederate and Union armies' return to the South following the Battle of Gettysburg * Gettysburg Address, President Abraham Lincoln's speech at the November 19, 1863, Consecration of the National Cemetery at Gettysburg. Places ; Pennsylvania-related articles *Gettysburg, Pennsylvania ** Gettysburg Battlefield Historic District, of historic properties, buildings, and structures in Adams County, Pennsylvania ** Gettysburg National Military Park, protected by the National Park Service *** Gettysburg Museum and Visitor Center, the National Park Service's reception center *** Gettysburg National Cemetery, a district of the military park on Cemetery Hill *** Gettysburg National Museum, the 1921 museum used as the 1974-2008 NPS ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Outcrop
An outcrop or rocky outcrop is a visible exposure of bedrock or ancient superficial deposits on the surface of the Earth. Features Outcrops do not cover the majority of the Earth's land surface because in most places the bedrock or superficial deposits are covered by soil and vegetation and cannot be seen or examined closely. However, in places where the overlying cover is removed through erosion or tectonic uplift, the rock may be exposed, or ''crop out''. Such exposure will happen most frequently in areas where erosion is rapid and exceeds the weathering rate such as on steep hillsides, mountain ridges and tops, river banks, and tectonically active areas. In Finland, glacial erosion during the last glacial maximum (ca. 11000 BC), followed by scouring by sea waves, followed by isostatic uplift has produced many smooth coastal and littoral outcrops. Bedrock and superficial deposits may also be exposed at the Earth's surface due to human excavations such as quarrying and build ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Culp's Hill
Culp's Hill,. The modern U.S. Geographic Names System refers to "Culps Hill". which is about south of the center of Gettysburg, Pennsylvania, played a prominent role in the Battle of Gettysburg. It consists of two rounded peaks, separated by a narrow saddle. Its heavily wooded higher peak is above sea level. The lower peak is about 100 feet (30 m) shorter than its companion. The eastern slope descends to Rock Creek, about 160 feet (50 m) lower in elevation, and the western slope is to a saddle with Stevens Knoll (formerly McKnight's Hill) with a summit lower than the main Culp's Hill summit. The hill was owned in 1863 by farmer Henry Culp and was publicized as "Culp's Hill" by October 31, 1865. During the Battle of Gettysburg, July 1–3, 1863, Culp's Hill was a critical part of the Union Army defensive line, the principal feature of the right flank, or "barbed" portion of what is described as the "fish-hook" line. Holding the hill was by itself unimportant because its h ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Newark Supergroup
The Newark Supergroup, also known as the Newark Group, is an assemblage of Upper Triassic and Lower Jurassic sedimentary rocks which outcrop intermittently along the United States East Coast. They were deposited in a series of Triassic basins approximately 190 million years ago as North America separated from Africa. The exposures extend from Nova Scotia to North Carolina. Related basins are also found underwater in the Bay of Fundy. The group is named for the city of Newark, New Jersey. Characteristics The Newark Supergroup consists largely of poorly sorted nonmarine sediments; typical rocks are breccia, conglomerate, arkose sandstone, siltstone, and shale. Most of the strata are red beds that feature ripple marks, mud cracks, and even rain drop prints; dinosaur footprints are common, though actual body fossils are very rare. Some of the strata are detailed to the level of varves, with indications of Milankovitch cycles. In preserved lake sediments, ''Semionotus'' fossils are ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Devil's Den
Devil's Den is a boulder-strewn hill on the south end of Houck's Ridge at Gettysburg Battlefield, used by artillery and sharpshooters on the second day of the 1863 Battle of Gettysburg during the American Civil War. A tourist attraction since the memorial association era, several boulders are worn from foot traffic and the site includes numerous cannon, memorials, and walkways, including a bridge spanning two boulders. History Devil's Den was formed with Little Round Top (to the east-northeast) and Big Round Top (southwest) by periglacial frost wedging of the igneous landform formed 200 million years ago when a diabase sill intruded through the Triassic Gettysburg plain. The feature acquired its foreboding name prior to the 1863 battle. Throughout the mid-19th century, local residents believed that the crevices between the boulders were home to a large snake. The size of the reptile varied between accounts, but reports ranged from to as large as . The snake became known ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Triassic–Jurassic Extinction Event
The Triassic–Jurassic (Tr-J) extinction event, often called the end-Triassic extinction, marks the boundary between the Triassic and Jurassic periods, , and is one of the top five major extinction events of the Phanerozoic eon, profoundly affecting life on land and in the oceans. In the seas, the entire Class (biology), class of conodonts and 23–34% of marine genus, genera disappeared. On land, all Archosauromorpha, archosauromorphs other than Crocodylomorpha, crocodylomorphs, pterosaurs, and dinosaurs became extinct; some of the groups which died out were previously abundant, such as aetosaurs, phytosaurs, and Rauisuchidae, rauisuchids. Some remaining non-mammalian therapsids and many of the large Temnospondyli, temnospondyl amphibians had become extinct prior to the Jurassic as well. However, there is still much uncertainty regarding a connection between the Tr-J boundary and terrestrial vertebrates, due to a lack of terrestrial fossils from the Rhaetian (latest) stage of the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Igneous
Igneous rock (derived from the Latin word ''ignis'' meaning fire), or magmatic rock, is one of the three main rock types, the others being sedimentary and metamorphic. Igneous rock is formed through the cooling and solidification of magma or lava. The magma can be derived from partial melts of existing rocks in either a planet's mantle or crust. Typically, the melting is caused by one or more of three processes: an increase in temperature, a decrease in pressure, or a change in composition. Solidification into rock occurs either below the surface as intrusive rocks or on the surface as extrusive rocks. Igneous rock may form with crystallization to form granular, crystalline rocks, or without crystallization to form natural glasses. Igneous rocks occur in a wide range of geological settings: shields, platforms, orogens, basins, large igneous provinces, extended crust and oceanic crust. Geological significance Igneous and metamorphic rocks make up 90–95% of the top ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
USGS
The United States Geological Survey (USGS), formerly simply known as the Geological Survey, is a scientific agency of the United States government. The scientists of the USGS study the landscape of the United States, its natural resources, and the natural hazards that threaten it. The organization's work spans the disciplines of biology, geography, geology, and hydrology. The USGS is a fact-finding research organization with no regulatory responsibility. The agency was founded on March 3, 1879. The USGS is a bureau of the United States Department of the Interior; it is that department's sole scientific agency. The USGS employs approximately 8,670 people and is headquartered in Reston, Virginia. The USGS also has major offices near Lakewood, Colorado, at the Denver Federal Center, and Menlo Park, California. The current motto of the USGS, in use since August 1997, is "science for a changing world". The agency's previous slogan, adopted on the occasion of its hundredth anniv ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cumberland Township, Adams County, Pennsylvania
Cumberland Township is a township in Adams County, Pennsylvania, United States. The population was 6,162 at the 2010 census. In 1863, the American Civil War Battle of Gettysburg took place mainly in Cumberland Township, which surrounds the borough of Gettysburg on three sides. Geography According to the United States Census Bureau, the township has a total area of , of which is land and , or 0.53%, is water. Demographics As of the census, there were 6,300 people living in the township. The population density was 171.0 people per square mile (66.0/km). There were 2,365 housing units at an average density of 70.7/sq mi (27.3/km). The racial makeup of the township was 93.84% White, 2.54% African American, 0.30% Native American, 1.45% Asian, 0.02% Pacific Islander, 1.05% from other races, and 0.80% from two or more races. Hispanic or Latino of any race were 2.15% of the population. There were 2,231 households, out of which 27.1% had children under the age of 18 living ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
United States Geological Survey
The United States Geological Survey (USGS), formerly simply known as the Geological Survey, is a scientific agency of the United States government. The scientists of the USGS study the landscape of the United States, its natural resources, and the natural hazards that threaten it. The organization's work spans the disciplines of biology, geography, geology, and hydrology. The USGS is a fact-finding research organization with no regulatory responsibility. The agency was founded on March 3, 1879. The USGS is a bureau of the United States Department of the Interior; it is that department's sole scientific agency. The USGS employs approximately 8,670 people and is headquartered in Reston, Virginia. The USGS also has major offices near Lakewood, Colorado, at the Denver Federal Center, and Menlo Park, California. The current motto of the USGS, in use since August 1997, is "science for a changing world". The agency's previous slogan, adopted on the occasion of its hundredt ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |


.jpg)