|
Little Boulevard (Budapest)
Kiskörút or Small Boulevard (lit. "Small Ring Road") is a major thoroughfare in Budapest. It forms an incomplete semicircle between Deák Square and Fővám Square. It is the border of the southern part of District 5 (cf. Belváros), the innermost district of Pest. As opposed to Nagykörút, it only touches the Danube at its southern end. Meaning Kiskörút is actually a colloquial name for three parts which connect to each other: (from north to south) ''Károly körút'', ''Múzeum körút'' and ''Vámház körút;'' these are the names a traveller will find on the map and the buildings. Location It consists of a road with a tram line in the middle. Its width is around 55 m in the north and it narrows down to 27 m in the south. Its starting point is Deák tér in the north, it crosses Astoria and Kálvin tér, both basic points of reference for the locals, and it ends up at Fővám tér, a square next to Liberty Bridge. Among the major roads, it crosses Rákóczi út a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Budapest Boulevards
Budapest (, ; ) is the capital and most populous city of Hungary. It is the ninth-largest city in the European Union by population within city limits and the second-largest city on the Danube river; the city has an estimated population of 1,752,286 over a land area of about . Budapest, which is both a city and county, forms the centre of the Budapest metropolitan area, which has an area of and a population of 3,303,786; it is a primate city, constituting 33% of the population of Hungary. The history of Budapest began when an early Celtic settlement transformed into the Roman town of Aquincum, the capital of Lower Pannonia. The Hungarians arrived in the territory in the late 9th century, but the area was pillaged by the Mongols in 1241–42. Re-established Buda became one of the centres of Renaissance humanist culture by the 15th century. The Battle of Mohács, in 1526, was followed by nearly 150 years of Ottoman rule. After the reconquest of Buda in 1686, the region ent ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
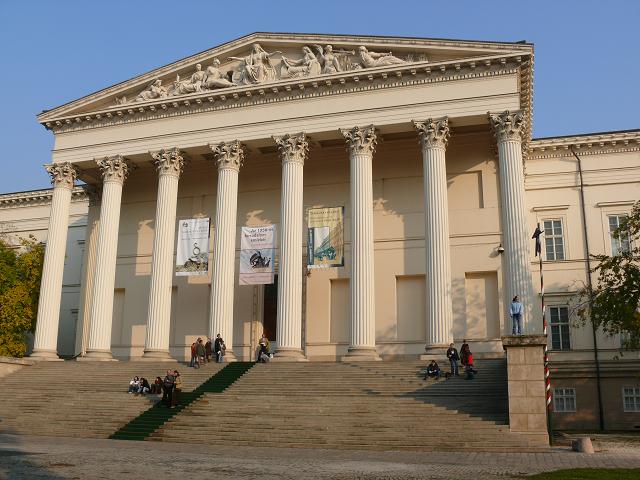
Hungarian National Museum
The Hungarian National Museum ( hu, Magyar Nemzeti Múzeum) was founded in 1802 and is the national museum for the history, art, and archaeology of Hungary, including areas not within Hungary's modern borders, such as Transylvania; it is not to be confused with the collection of international art in the Hungarian National Gallery. The museum is in Budapest VIII in a Neoclassical building, purpose-built during 1837–47 by the architect Mihály Pollack. History The Hungarian National Museum traces its foundation to 1802, when Count Ferenc Széchényi set up the National Széchényi Library. This would then be followed a year later by the donating of a mineral collection by Széchényi's wife. This led to the creation of the Hungarian National Museum as a general history and natural history museum, beyond being simply a library. In 1807, the Hungarian National Parliament passed legislation on the new institution and asked the nation to help donate to the museum. The Hungar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Romanticism
Romanticism (also known as the Romantic movement or Romantic era) was an artistic, literary, musical, and intellectual movement that originated in Europe towards the end of the 18th century, and in most areas was at its peak in the approximate period from 1800 to 1850. Romanticism was characterized by its emphasis on emotion and individualism, clandestine literature, paganism, idealization of nature, suspicion of science and industrialization, and glorification of the past with a strong preference for the medieval rather than the classical. It was partly a reaction to the Industrial Revolution, the social and political norms of the Age of Enlightenment, and the scientific rationalization of nature. It was embodied most strongly in the visual arts, music, and literature, but had a major impact on historiography, education, chess, social sciences, and the natural sciences. It had a significant and complex effect on politics, with romantic thinkers influencing conservatism, libe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dohány Street Synagogue
The Dohány Street Synagogue ( hu, Dohány utcai zsinagóga / nagy zsinagóga; he, בית הכנסת הגדול של בודפשט, ''Bet ha-Knesset ha-Gadol shel Budapesht''), also known as the ''Great Synagogue'' or ''Tabakgasse Synagogue'', is a historical building in Erzsébetváros, the 7th district of Budapest, Hungary. It is the largest synagogue in Europe, seating 3,000 people and is a centre of Neolog Judaism. The synagogue was built between 1854 and 1859 in the Moorish Revival style, with the decoration based chiefly on Islamic models from North Africa and medieval Spain (the Alhambra). The synagogue's Viennese architect, Ludwig Förster, believed that no distinctively Jewish architecture could be identified, and thus chose ''"architectural forms that have been used by oriental ethnic groups that are related to the Israelite people, and in particular the Arabs"''. The interior design is partly by Frigyes Feszl. The Dohány Street Synagogue complex consists of the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hungarian National Museum At The Múzeum Körút
Hungarian may refer to: * Hungary, a country in Central Europe * Kingdom of Hungary, state of Hungary, existing between 1000 and 1946 * Hungarians, ethnic groups in Hungary * Hungarian algorithm, a polynomial time algorithm for solving the assignment problem * Hungarian language, a Finno-Ugric language spoken in Hungary and all neighbouring countries * Hungarian notation, a naming convention in computer programming * Hungarian cuisine Hungarian or Magyar cuisine is the cuisine characteristic of the nation of Hungary and its primary ethnic group, the Magyars. Traditional Hungarian dishes are primarily based on meats, seasonal vegetables, fruits, bread, and dairy products. ..., the cuisine of Hungary and the Hungarians See also * * {{disambiguation Language and nationality disambiguation pages ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
White Terror (Hungary)
The White Terror in Hungary ( hu, Fehér Terror) was a two-year period (1919–1921) of repressive violence by counter-revolutionary soldiers, carried out to destroy any supporters of Hungary's short-lived Soviet republic and its Red Terror. Tens of thousands were imprisoned without trial, and as many as 1,000 people were killed; many of the victims were Jewish. Background At the end of World War I, the political configuration of the Hungarian state was forced into swift and radical change. The Austro-Hungarian Empire, of which Hungary had been a powerful member, collapsed. The victorious Entente powers took steps to carve out Hungary's ethnically mixed border regions and grant them to the Kingdom of Serbs, Croats and Slovenes, Czechoslovakia, and Romania – efforts which resulted in Hungary's losing two thirds of its land area and one third of its Hungarian-speaking nationals. These losses, together with the postwar socioeconomic upheaval, catalysed deep feelings of humiliation ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Népszava
''Népszava'' (meaning "People's Word" in English) is a social-democratic Hungarian language newspaper published in Hungary. History and profile ''Népszava'' is Hungary's eldest continuous print publication and as of October 2019 the last and only remaining liberal, social democratic political daily in the country. ''Népszava'' was established in 1873 in Budapest by Viktor Külföldi. It was the official newspaper of the Hungarian Social Democratic Party until 1948 when Hungary became a communist state. During this period two of Népszava's editors in chief were murdered: Béla Somogyi (along with reporter Béla Bacsó) in 1920 by right wing officers and Illés Mónus in 1944 by members of the Hungarian Nazi Arrow Cross militia. During the period of the Hungarian People's Republic between 1948 and 1989, it was the official newspaper of Hungarian trade unions. In 1990 it was privatized. Its publisher, the entrepreneur János Fenyő was shot dead in Budapest in 1998. The ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Béla Somogyi
Béla may refer to: * Béla (crater), an elongated lunar crater * Béla (given name), a common Hungarian male given name See also * Bela (other) * Belá (other) * Bělá (other) Bělá, derived from ''bílá'' (''white''), is the name of several places in the Czech Republic: *Bělá (Havlíčkův Brod District), a municipality and village in the Vysočina Region *Bělá (Mírová pod Kozákovem), a village, a part of the m ... {{DEFAULTSORT:Bela de:Béla pl:Béla ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mehmed V
Mehmed V Reşâd ( ota, محمد خامس, Meḥmed-i ḫâmis; tr, V. Mehmed or ; 2 November 1844 – 3 July 1918) reigned as the 35th and penultimate Ottoman Sultan (). He was the son of Sultan Abdulmejid I. He succeeded his half-brother Abdul Hamid II after the 31 March Incident. He was succeeded by his half-brother Mehmed VI. His nine-year reign was marked by the cession of the Empire's North African territories and the Dodecanese Islands, including Rhodes, in the Italo-Turkish War, the traumatic loss of almost all of the Empire's European territories west of Constantinople (now Istanbul) in the First Balkan War, and the entry of the Ottoman Empire into World War I in 1914, which would ultimately lead to the Empire's end. Early life Mehmed V was born on 2 November 1844 at the Çırağan Palace, Istanbul.''The Encyclopædia Britannica'', Vol.7, edited Hugh Chisholm, (1911), 3; "''Constantinople, the capital of the Turkish Empire..''". His father was Sultan Abdulmejid I ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
World War I
World War I (28 July 1914 11 November 1918), often abbreviated as WWI, was one of the deadliest global conflicts in history. Belligerents included much of Europe, the Russian Empire, the United States, and the Ottoman Empire, with fighting occurring throughout Europe, the Middle East, Africa, the Pacific, and parts of Asia. An estimated 9 million soldiers were killed in combat, plus another 23 million wounded, while 5 million civilians died as a result of military action, hunger, and disease. Millions more died in genocides within the Ottoman Empire and in the 1918 influenza pandemic, which was exacerbated by the movement of combatants during the war. Prior to 1914, the European great powers were divided between the Triple Entente (comprising France, Russia, and Britain) and the Triple Alliance (containing Germany, Austria-Hungary, and Italy). Tensions in the Balkans came to a head on 28 June 1914, following the assassination of Archduke Franz Ferdin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
End Of Communism In Hungary (1989)
Communist rule in the People's Republic of Hungary came to an end in 1989 by a peaceful transition to a democratic system. After the Hungarian Revolution of 1956 was suppressed by Soviet forces, Hungary remained a communist country. As the Soviet Union weakened at the end of the 1980s, the Eastern bloc disintegrated. The events in Hungary were part of the Revolutions of 1989, known in Hungarian as the ' (). Prelude Decades before the Round Table Talks, political and economic forces within Hungary put pressure on Hungarian communism. These pressures contributed to the fall of communism in Hungary in 1989. Economic problems The New Economic Mechanism was the only set of economic reform in Eastern Europe enacted after the wave of 1950s and 60s revolutions that survived past 1968. Despite this, it became the weakest point of Hungarian communism, and a pressure that contributed greatly to the transition to democracy. In 1968, the Central Committee of the Hungarian Socialist Wo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fyodor Tolbukhin
Fyodor Ivanovich Tolbukhin (russian: Фёдор Ива́нович Толбу́хин; 16 June 1894 – 17 October 1949) was a Soviet military commander and Marshal of the Soviet Union. Early life and military career Tolbukhin was born into a peasant family in the province of Yaroslavl, north-east of Moscow. He volunteered for the Imperial Army in 1914 at the outbreak of World War I. He was steadily promoted, advancing from private to captain by 1916. He was also decorated for bravery multiple times. In August 1918 Tolbukhin joined the Red Army, where he served as the chief of staff of the 56th infantry division. After the Russian Civil War ended (1921), Tolbukhin was given a number of staff positions. He also attended the Frunze Military Academy for advanced staff training, graduating in 1931. In 1937, after a series of staff positions, Tolbukhin was given command of a division. In 1938, he was made chief of staff of the Transcaucasus Military District. World War II Tolbuk ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |





.jpg)
.jpg)
