|
Litophyton Arboreum
''Litophyton arboreum'', also known as broccoli coral, is a common soft coral (octocoral) found from the Red Sea to the Western Pacific. It grows up to 80 cm, usually on seaward reef slopes or hard bottoms. The color of ''L. arboreum'' varies from pale olive-green to yellow or grey. ''L. arboreum'' are anthozoans in the order '' Alcyonacea'' in the family ''Nephtheidae''. The ''L. arboreum'' was originally classified in 1775 by Peter Forsskål, a Swedish Linnaean naturalist. As of 2016, the entire genus ''Litophyton'' was reclassified using phylogenetic data, in contrast to its original morphological classification. Ecology ''L. arboreum'' is commonly found in the Red Sea. A 1997 reef transect study showed that octocorals, such as ''L. arboreum'', compose under 20% of soft coral coverage on both reef flats, and the upper fore-reefs in the Gulf of Eilat, off the East coast of the Sinai Peninsula. Typically in Gulf of Eilat reefs, octocoral coverage is dominat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ecological Niche
In ecology, a niche is the match of a species to a specific environmental condition. Three variants of ecological niche are described by It describes how an organism or population responds to the distribution of resources and competitors (for example, by growing when resources are abundant, and when predators, parasites and pathogens are scarce) and how it in turn alters those same factors (for example, limiting access to resources by other organisms, acting as a food source for predators and a consumer of prey). "The type and number of variables comprising the dimensions of an environmental niche vary from one species to another ndthe relative importance of particular environmental variables for a species may vary according to the geographic and biotic contexts". See also Chapter 2: Concepts of niches, pp. 7 ''ff'' A Grinnellian niche is determined by the habitat in which a species lives and its accompanying behavioral adaptations. An Eltonian niche emphasizes that a spec ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
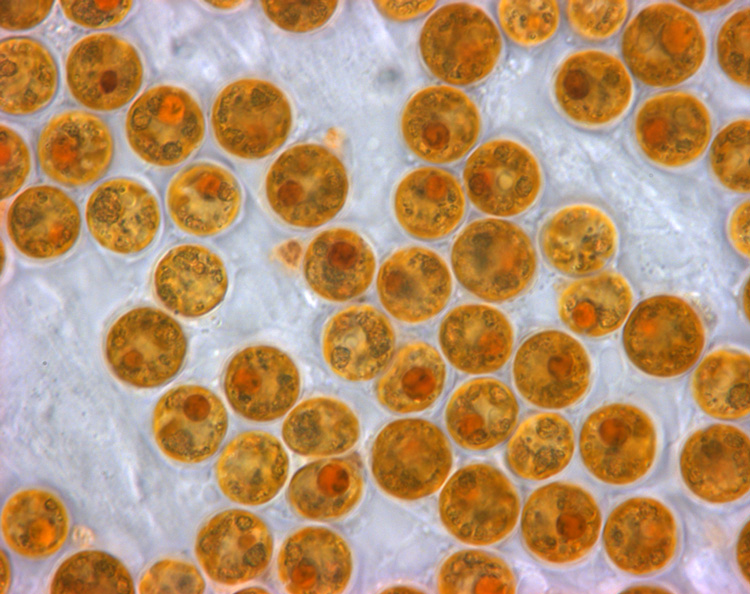
Zooxanthellae
Zooxanthellae is a colloquial term for single-celled dinoflagellates that are able to live in symbiosis with diverse marine invertebrates including demosponges, corals, jellyfish, and nudibranchs. Most known zooxanthellae are in the genus ''Symbiodinium'', but some are known from the genus '' Amphidinium'', and other taxa, as yet unidentified, may have similar endosymbiont affinities. The true ''Zooxanthella'' K.brandt is a mutualist of the radiolarian ''Collozoum inerme'' (Joh.Müll., 1856) and systematically placed in Peridiniales. Another group of unicellular eukaryotes that partake in similar endosymbiotic relationships in both marine and freshwater habitats are green algae zoochlorellae. Zooxanthellae are photosynthetic organisms, which contain chlorophyll a and chlorophyll c, as well as the dinoflagellate pigments peridinin and diadinoxanthin. These provide the yellowish and brownish colours typical of many of the host species. During the day, they provide their host ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dinoflagellate
The dinoflagellates (Greek δῖνος ''dinos'' "whirling" and Latin ''flagellum'' "whip, scourge") are a monophyletic group of single-celled eukaryotes constituting the phylum Dinoflagellata and are usually considered algae. Dinoflagellates are mostly marine plankton, but they also are common in freshwater habitats. Their populations vary with sea surface temperature, salinity, and depth. Many dinoflagellates are photosynthetic, but a large fraction of these are in fact mixotrophic, combining photosynthesis with ingestion of prey (phagotrophy and myzocytosis). In terms of number of species, dinoflagellates are one of the largest groups of marine eukaryotes, although substantially smaller than diatoms. Some species are endosymbionts of marine animals and play an important part in the biology of coral reefs. Other dinoflagellates are unpigmented predators on other protozoa, and a few forms are parasitic (for example, ''Oodinium'' and ''Pfiesteria''). Some dinoflagellates pro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Endosymbiont
An ''endosymbiont'' or ''endobiont'' is any organism that lives within the body or cells of another organism most often, though not always, in a mutualistic relationship. (The term endosymbiosis is from the Greek: ἔνδον ''endon'' "within", σύν ''syn'' "together" and βίωσις ''biosis'' "living".) Examples are nitrogen-fixing bacteria (called rhizobia), which live in the root nodules of legumes, single-cell algae inside reef-building corals and bacterial endosymbionts that provide essential nutrients to insects. There are two types of symbiont transmissions. In horizontal transmission, each new generation acquires free living symbionts from the environment. An example is the nitrogen-fixing bacteria in certain plant roots. Vertical transmission takes place when the symbiont is transferred directly from parent to offspring. It is also possible for both to be involved in a mixed-mode transmission, where symbionts are transferred vertically for some generation bef ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Symbiodinium
: ''This is about the genus sometimes called Zoox. For the company, see Zoox (company)'' ''Symbiodinium'' is a genus of dinoflagellates that encompasses the largest and most prevalent group of endosymbiotic dinoflagellates known. These unicellular microalgae commonly reside in the endoderm of tropical cnidarians such as corals, sea anemones, and jellyfish, where the products of their photosynthetic processing are exchanged in the host for inorganic molecules. They are also harbored by various species of demosponges, flatworms, mollusks such as the giant clams, foraminifera ( soritids), and some ciliates. Generally, these dinoflagellates enter the host cell through phagocytosis, persist as intracellular symbionts, reproduce, and disperse to the environment. The exception is in most mollusks, where these symbionts are intercellular (between the cells). Cnidarians that are associated with ''Symbiodinium'' occur mostly in warm oligotrophic (nutrient-poor), marine environments where ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Reproduction
Reproduction (or procreation or breeding) is the biological process by which new individual organisms – "offspring" – are produced from their "parent" or parents. Reproduction is a fundamental feature of all known life; each individual organism exists as the result of reproduction. There are two forms of reproduction: asexual and sexual. In asexual reproduction, an organism can reproduce without the involvement of another organism. Asexual reproduction is not limited to single-celled organisms. The cloning of an organism is a form of asexual reproduction. By asexual reproduction, an organism creates a genetically similar or identical copy of itself. The evolution of sexual reproduction is a major puzzle for biologists. The two-fold cost of sexual reproduction is that only 50% of organisms reproduce and organisms only pass on 50% of their genes.John Maynard Smith ''The Evolution of Sex'' 1978. Sexual reproduction typically requires the sexual interaction of two specializ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Litophyton Arboreum At Umm Khararim
''Litophyton'' is a genus of soft corals in the family Nephtheidae. Species The World Register of Marine Species includes the following species in the genus: *''Litophyton acuticonicum'' (Verseveldt, 1974) *''Litophyton amentaceum'' (Studer, 1894) *''Litophyton arboreum'' Forskål, 1775 *''Litophyton bayeri'' (Verseveldt, 1966) *''Litophyton berdfordi'' (Shann, 1912) *'' Litophyton brassicum'' (Kükenthal, 1903) *''Litophyton bumastum'' (Verseveldt, 1973) *''Litophyton capnelliformis'' (Thomson & Dean, 1931) *''Litophyton carnosum'' (Kükenthal) *''Litophyton cervispiculosum'' (Thomson & Dean, 1931) *''Litophyton chabrolii'' (Andouin, 1828) *'' Litophyton columnaris'' (Studer, 1895) *''Litophyton compactum'' (Verseveldt, 1966) *'' Litophyton concinnum'' (Kükenthal, 1905) *''Litophyton corallinum'' (Kükenthal, 1910) *'' Litophyton crassum'' (Kükenthal, 1903) *'' Litophyton cupressiformis'' (Kükenthal, 1903) *'' Litophyton curvum'' van Ofwegen, 2016 *'' Litophyton debilis'' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Benthic Zone
The benthic zone is the ecological region at the lowest level of a body of water such as an ocean, lake, or stream, including the sediment surface and some sub-surface layers. The name comes from ancient Greek, βένθος (bénthos), meaning "the depths." Organisms living in this zone are called benthos and include microorganisms (e.g., bacteria and fungi) as well as larger invertebrates, such as crustaceans and polychaetes. Organisms here generally live in close relationship with the substrate and many are permanently attached to the bottom. The benthic boundary layer, which includes the bottom layer of water and the uppermost layer of sediment directly influenced by the overlying water, is an integral part of the benthic zone, as it greatly influences the biological activity that takes place there. Examples of contact soil layers include sand bottoms, rocky outcrops, coral, and bay mud. Description Oceans The benthic region of the ocean begins at the shore line (intertida ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Topography
Topography is the study of the forms and features of land surfaces. The topography of an area may refer to the land forms and features themselves, or a description or depiction in maps. Topography is a field of geoscience and planetary science and is concerned with local detail in general, including not only relief, but also natural, artificial, and cultural features such as roads, land boundaries, and buildings. In the United States, topography often means specifically ''relief'', even though the USGS topographic maps record not just elevation contours, but also roads, populated places, structures, land boundaries, and so on. Topography in a narrow sense involves the recording of relief or terrain, the three-dimensional quality of the surface, and the identification of specific landforms; this is also known as geomorphometry. In modern usage, this involves generation of elevation data in digital form (DEM). It is often considered to include the graphic representation of t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ecological Succession
Ecological succession is the process of change in the species structure of an ecological community over time. The time scale can be decades (for example, after a wildfire) or more or less. Bacteria allows for the cycling of nutrients such as carbon, nitrogen and sulphur. The community begins with relatively few pioneering plants and animals and develops through increasing complexity until it becomes stable or self-perpetuating as a climax community. The "engine" of succession, the cause of ecosystem change, is the impact of established organisms upon their own environments. A consequence of living is the sometimes subtle and sometimes overt alteration of one's own environment. Succession is a process by which an ecological community undergoes more or less orderly and predictable changes following a disturbance or the initial colonization of a new habitat. Succession may be initiated either by formation of new, unoccupied habitat, such as from a lava flow or a severe lan ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Seagrass
Seagrasses are the only flowering plants which grow in marine environments. There are about 60 species of fully marine seagrasses which belong to four families (Posidoniaceae, Zosteraceae, Hydrocharitaceae and Cymodoceaceae), all in the order Alismatales (in the clade of monocotyledons). Seagrasses evolved from terrestrial plants which recolonised the ocean 70 to 100 million years ago. The name ''seagrass'' stems from the many species with long and narrow leaves, which grow by rhizome extension and often spread across large "meadows" resembling grassland; many species superficially resemble terrestrial grasses of the family Poaceae. Like all autotrophic plants, seagrasses photosynthesize, in the submerged photic zone, and most occur in shallow and sheltered coastal waters anchored in sand or mud bottoms. Most species undergo submarine pollination and complete their life cycle underwater. While it was previously believed this pollination was carried out without pollinators ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |