|
Litberg
The Litberg is, at 65 metres above sea level (NN), the highest point in the district of Stade, Germany. It lies about 2.5 kilometres south of Beckdorf in the municipality of Sauensiek. The Litberg is a small hill covered with birch, pine, willow and alder, which was formed from an Ice Age moraine. It forms a protected area on the geest west of the Harburg Hills. Access The hill can best be accessed from the south, from the town of Sauensiek, or from the north, starting from Beckdorf or its subdistrict of Goldbeck. From the east, one can also start from the village of Regesbostel. Views The summit is located in the middle of the forest, so the best views are from the edge of the forest during the ascent and from the 25 m high observation tower, which was built in October 2008 at the summit. In clear conditions you can see the Hamburg TV tower and Köhlbrand Bridge on the horizon. In addition, there are good views over the geest all around the area. History Carl Fri ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hills Of Lower Saxony
This List of mountains and hills in Lower Saxony shows a selection of high or well-known mountains and hills in the German state of Lower Saxony (''in order of height''). Although there is no universally agreed definition of a 'mountain', summits at 2.000 feet (610 metres) or higher may generally be referred to as mountains; those below 2.000 feet as 'hills',Whittow, John (1984). ''Dictionary of Physical Geography''. London: Penguin, 1984. . hence the division of this list. By this definition, it can be seen that all the mountains in Lower Saxony occur in the Harz. Highest points in Lower Saxony's regions The following table lists the highest points in the various landscapes (hill ranges or regions) of Lower Saxony. In the "Landscape" column, major hill ranges are shown in bold. Clicking "List" in the rows of the "List" column links to other hills or mountains in that landscape – some of which are outside Lower Saxony. The table is arranged by height, but may be sorted by oth ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sauensiek
Sauensiek is a municipality in the district of Stade, Lower Saxony, Germany. Location The Litberg, the highest point in the district of Stade, lies within the municipality of Sauensiek. It has a height of 65 metres above sea level and has been designated as a protected area. History Sauensiek belonged - as to its government - to the Prince-Archbishopric of Bremen, established in 1180.Michael Schütz, „Die Konsolidierung des Erzstiftes unter Johann Rode“, in: ''Geschichte des Landes zwischen Elbe und Weser'': 3 vols., Hans-Eckhard Dannenberg and Heinz-Joachim Schulze (eds.) on behalf of the Landschaftsverband der ehemaligen Herzogtümer Bremen und Verden, Stade: Landschaftsverband der ehemaligen Herzogtümer Bremen und Verden, 1995 and 2008, vol. I 'Vor- und Frühgeschichte' (1995; ), vol. II 'Mittelalter (einschl. Kunstgeschichte)' (1995; ), vol. III 'Neuzeit' (2008; ), (=Schriftenreihe des Landschaftsverbandes der ehemaligen Herzogtümer Bremen und Verden; vols. 7–9 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Regesbostel
Regesbostel is a municipality in the district of Harburg, in Lower Saxony, Germany Germany,, officially the Federal Republic of Germany, is a country in Central Europe. It is the second most populous country in Europe after Russia, and the most populous member state of the European Union. Germany is situated betwe .... References Harburg (district) {{Harburg-geo-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Glacial Erratic
A glacial erratic is glacially deposited rock differing from the type of rock native to the area in which it rests. Erratics, which take their name from the Latin word ' ("to wander"), are carried by glacial ice, often over distances of hundreds of kilometres. Erratics can range in size from pebbles to large boulders such as Big Rock () in Alberta. Geologists identify erratics by studying the rocks surrounding the position of the erratic and the composition of the erratic itself. Erratics are significant because: *They can be transported by glaciers, and they are thereby one of a series of indicators which mark the path of prehistoric glacier movement. Their lithographic origin can be traced to the parent bedrock, allowing for confirmation of the ice flow route. *They can be transported by ice rafting. This allows quantification of the extent of glacial flooding resulting from ice dam failure which release the waters stored in proglacial lakes such as Lake Missoula. Erratics ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
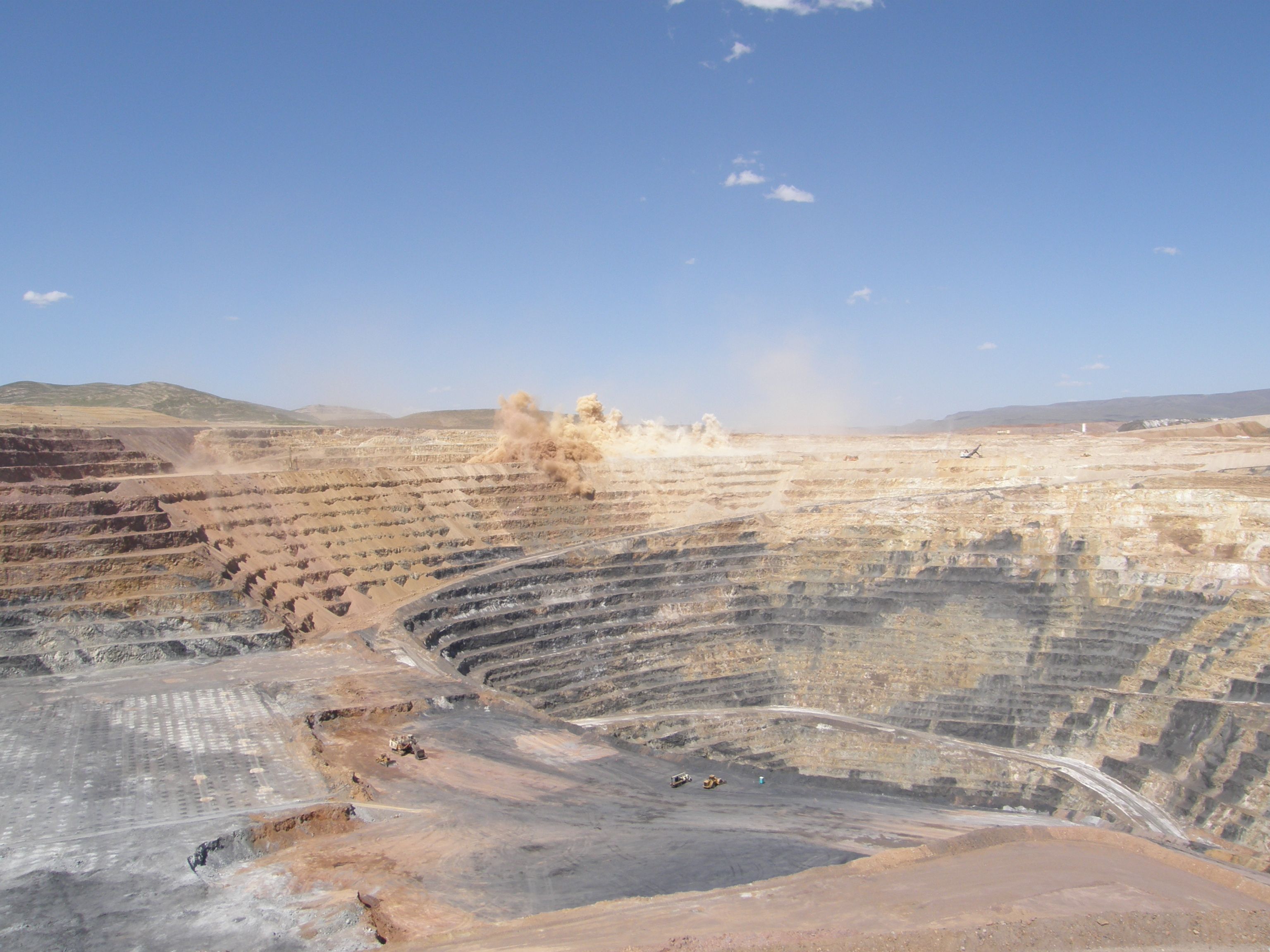
Open-cast Mine
Open-pit mining, also known as open-cast or open-cut mining and in larger contexts mega-mining, is a surface mining technique of extracting rock or minerals from the earth from an open-air pit, sometimes known as a borrow. This form of mining differs from extractive methods that require tunnelling into the earth, such as long wall mining. Open-pit mines are used when deposits of commercially useful ore or rocks are found near the surface. It is applied to ore or rocks found at the surface because the overburden is relatively thin or the material of interest is structurally unsuitable for tunnelling (as would be the case for cinder, sand, and gravel). In contrast, minerals that have been found underground but are difficult to retrieve due to hard rock, can be reached using a form of underground mining. To create an open-pit mine, the miners must determine the information of the ore that is underground. This is done through drilling of probe holes in the ground, then plotting eac ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Deutschmark
The Deutsche Mark (; English: ''German mark''), abbreviated "DM" or "D-Mark" (), was the official currency of West Germany from 1948 until 1990 and later the unified Germany from 1990 until the adoption of the euro in 2002. In English, it was typically called the "Deutschmark" (). One Deutsche Mark was divided into 100 pfennigs. It was first issued under Allied occupation in 1948 to replace the Reichsmark and served as the Federal Republic of Germany's official currency from its founding the following year. On 31 December 1998, the Council of the European Union fixed the irrevocable exchange rate, effective 1 January 1999, for German mark to euros as DM 1.95583 = €1. In 1999, the Deutsche Mark was replaced by the euro; its coins and banknotes remained in circulation, defined in terms of euros, until the introduction of euro notes and coins on 1 January 2002. The Deutsche Mark ceased to be legal tender immediately upon the introduction of the euro—in contrast to the o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
North German Plain
The North German Plain or Northern Lowland (german: Norddeutsches Tiefland) is one of the major geographical regions of Germany. It is the German part of the North European Plain. The region is bounded by the coasts of the North Sea and the Baltic Sea to the north, Germany's Central Uplands (''die Mittelgebirge'') to the south, by the Netherlands to the west and Poland to the east. In the west, the southern boundary of the North German Plain is formed by the Lower Saxon Hills: specifically the ridge of the Teutoburg Forest, the Wiehen Hills, the Weser Hills and the Lower Saxon Börde, which partly separate it from that area of the Plain known as the Westphalian Lowland. Elements of the Rhenish Massif also act a part of the southern boundary of the plain: the Eifel, Bergisches Land and the Sauerland. In the east the North German Plain spreads out beyond the Harz Mountains and Kyffhäuser further to the south as far as the Central Saxon hill country and the foothills of the Ore M ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kingdom Of Hanover
The Kingdom of Hanover (german: Königreich Hannover) was established in October 1814 by the Congress of Vienna, with the restoration of George III to his Hanoverian territories after the Napoleonic era. It succeeded the former Electorate of Hanover (known formally as the Electorate of Brunswick-Lüneburg), and joined 38 other sovereign states in the German Confederation in June 1815. The kingdom was ruled by the House of Hanover, a cadet branch of the House of Welf, in personal union with the United Kingdom of Great Britain and Ireland since 1714. Since its monarch resided in London, a viceroy, usually a younger member of the British Royal Family, handled the administration of the Kingdom of Hanover. The personal union with the United Kingdom ended in 1837 upon the accession of Queen Victoria because semi-Salic law prevented females from inheriting the Hanoverian throne while a dynastic male was still alive. Her uncle Ernest Augustus thus became the ruler of Hanover. His only ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Carl Friedrich Gauss
Johann Carl Friedrich Gauss (; german: Gauß ; la, Carolus Fridericus Gauss; 30 April 177723 February 1855) was a German mathematician and physicist who made significant contributions to many fields in mathematics and science. Sometimes referred to as the ''Princeps mathematicorum'' () and "the greatest mathematician since antiquity", Gauss had an exceptional influence in many fields of mathematics and science, and he is ranked among history's most influential mathematicians. Also available at Retrieved 23 February 2014. Comprehensive biographical article. Biography Early years Johann Carl Friedrich Gauss was born on 30 April 1777 in Brunswick (Braunschweig), in the Duchy of Brunswick-Wolfenbüttel (now part of Lower Saxony, Germany), to poor, working-class parents. His mother was illiterate and never recorded the date of his birth, remembering only that he had been born on a Wednesday, eight days before the Feast of the Ascension (which occurs 39 days after Easter). Ga ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Geest
Geest is a type of landform, slightly raised above the surrounding countryside, that occurs on the plains of Northern Germany, the Northern Netherlands and Denmark. It is a landscape of sandy and gravelly soils formed as a glacial outwash plain and now usually mantled by a heathland vegetation on the glacial deposits left behind after the last ice age during the Pleistocene epoch.Whittow, John (1984). ''Dictionary of Physical Geography''. London: Penguin, p. 214. . The term ''geest'' is a substantivisation of the Low German adjective ''güst'', which means "dry and infertile". It is an Old Drift landscape, characterised by the sandy depositions of the Ice Age. In the depressions between the raised flats are wet meadows and, where drainage is poor, bogs. Geest lands are made up of moraines and sandurs. They are almost always next to flat marshlands, the geest being higher and better protected against flood but, compared to the marsh, with poor soil for agriculture. Where the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Köhlbrand Bridge
The Köhlbrand Bridge (german: Köhlbrandbrücke) is a cable-stayed bridge in Hamburg, Germany,Stahl, F. L., & Gagnon, C. P. (1996)Cable Corrosion in Bridges and Other Structures: Causes and SolutionsASCE Publications. . Retrieved on 16 March 2012 which connects the harbor area on the island of Wilhelmsburg between the Norderelbe and Süderelbe branches of the Elbe river with motorway 7 (exit Waltershof). It bridges the Süderelbe, here called Köhlbrand, before it unites with the Norderelbe again. The bridge was opened on 9 September 1974. See also * List of bridges in Hamburg * List of bridges in Germany This list of bridges in Germany lists bridges of particular historical, scenic, architectural or engineering interest. Road and railway bridges, viaducts, aqueducts and footbridges are included. Historical and architectural interest bridges {{ro ... References External links * Videoof the Köhlbrand Bridge Being Inspected by UAV/drone {{DEFAULTSORT:Kohlbra ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hamburg
(male), (female) en, Hamburger(s), Hamburgian(s) , timezone1 = Central (CET) , utc_offset1 = +1 , timezone1_DST = Central (CEST) , utc_offset1_DST = +2 , postal_code_type = Postal code(s) , postal_code = 20001–21149, 22001–22769 , area_code_type = Area code(s) , area_code = 040 , registration_plate = , blank_name_sec1 = GRP (nominal) , blank_info_sec1 = €123 billion (2019) , blank1_name_sec1 = GRP per capita , blank1_info_sec1 = €67,000 (2019) , blank1_name_sec2 = HDI (2018) , blank1_info_sec2 = 0.976 · 1st of 16 , iso_code = DE-HH , blank_name_sec2 = NUTS Region , blank_info_sec2 = DE6 , website = , footnotes ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |