|
List Of Supernovae
This is a list of supernovae that are of historical significance. These include supernovae that were observed prior to the availability of photography, and individual events that have been the subject of a scientific paper that contributed to supernova theory. An alternative, complete and updated list can be found in thOpen Supernova Catalog List ''In most entries, the year when the supernova was seen is part of the designation (1st column).'' See also * List of most distant supernovae * List of supernova candidates * List of supernova remnants * Lists of astronomical objects References Further reading * External linksList of all known supernovaeaThe Open Supernova CatalogIAU Supernovaeon thTransient Name Server (TNS) at IAU |
Crab Nebula
The Crab Nebula (catalogue designations Messier object, M1, New General Catalogue, NGC 1952, Taurus (constellation), Taurus A) is a supernova remnant and pulsar wind nebula in the constellation of Taurus (constellation), Taurus. The common name comes from William Parsons, 3rd Earl of Rosse, who observed the object in 1842 using a telescope and produced a drawing that looked somewhat like a crab. The nebula was discovered by English astronomer John Bevis in 1731, and it corresponds with SN 1054, a bright supernova recorded by Chinese astronomy, Chinese astronomers in 1054. The nebula was the first astronomical object identified that corresponds with a historical supernova explosion. At an apparent magnitude of 8.4, comparable to that of Titan (moon), Saturn's moon Titan, it is not visible to the naked eye but can be made out using binoculars under favourable conditions. The nebula lies in the Perseus Arm of the Milky Way galaxy, at a distance of about from Earth. It has a diame ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cassiopeia (constellation)
Cassiopeia () is a constellation in the northern sky named after the vain queen Cassiopeia, mother of Andromeda, in Greek mythology, who boasted about her unrivaled beauty. Cassiopeia was one of the 48 constellations listed by the 2nd-century Greek astronomer Ptolemy, and it remains one of the 88 modern constellations today. It is easily recognizable due to its distinctive ' W' shape, formed by five bright stars. Cassiopeia is located in the northern sky and from latitudes above 34°N it is visible year-round. In the (sub)tropics it can be seen at its clearest from September to early November, and at low southern, tropical, latitudes of less than 25°S it can be seen, seasonally, low in the North. At magnitude 2.2, Alpha Cassiopeiae, or Schedar, is generally the brightest star in Cassiopeia, though it is occasionally outshone by the variable Gamma Cassiopeiae, which has reached magnitude 1.6. The constellation hosts some of the most luminous stars known, including the yello ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
NGC 5253
NGC 5253 is an irregular galaxy in the constellation Centaurus. It was discovered by William Herschel on 15 March 1787. Properties NGC 5253 is located within the M83 Subgroup of the Centaurus A/M83 Group, a relatively nearby galaxy group that includes the radio galaxy Centaurus A and the spiral galaxy M83 (the Southern Pinwheel Galaxy). NGC 5253 is considered a dwarf starburst galaxy and also a blue compact galaxy. Supernova 1972E, the second-brightest recent supernova visible from Earth (peak visual magnitude of 8.5, fainter only than SN 1987A in the 20th century), occurred in this galaxy. Another supernova, SN 1895b, also has been recorded in the galaxy. Contents NGC 5253 contains a giant dust cloud hiding a cluster (believed to be a super star cluster) of more than one million stars, among them up to 7,000 O-type stars. The cluster is 3 million years old and has a total luminosity of more than one billion suns. It is the site of efficient star formation, with a rate at le ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Harvard University
Harvard University is a private Ivy League research university in Cambridge, Massachusetts. Founded in 1636 as Harvard College and named for its first benefactor, the Puritan clergyman John Harvard, it is the oldest institution of higher learning in the United States and one of the most prestigious and highly ranked universities in the world. The university is composed of ten academic faculties plus Harvard Radcliffe Institute. The Faculty of Arts and Sciences offers study in a wide range of undergraduate and graduate academic disciplines, and other faculties offer only graduate degrees, including professional degrees. Harvard has three main campuses: the Cambridge campus centered on Harvard Yard; an adjoining campus immediately across Charles River in the Allston neighborhood of Boston; and the medical campus in Boston's Longwood Medical Area. Harvard's endowment is valued at $50.9 billion, making it the wealthiest academic institution in the world. Endowment inco ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Central Bureau For Astronomical Telegrams
The Central Bureau for Astronomical Telegrams (CBAT) is the official international clearing house for information relating to transient astronomical events. The CBAT collects and distributes information on comets, natural satellites, novae, supernovae and other transient astronomical events. CBAT also establishes priority of discovery (who gets credit for it) and assigns initial designations and names to new objects. On behalf of the International Astronomical Union (IAU), the CBAT distributes ''IAU Circulars''. From the 1920s to 1992, CBAT sent telegrams in urgent cases, although most circulars were sent via regular mail; when telegrams were dropped, the name "telegram" was kept for historical reasons, and they continued as the ''Central Bureau Electronic Telegrams''. Since the mid-1980s the ''IAU Circulars'' and the related '' Minor Planet Circulars'' have been available electronically. The CBAT is a non-profit organization, but charges for its ''IAU Circulars'' and electronic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
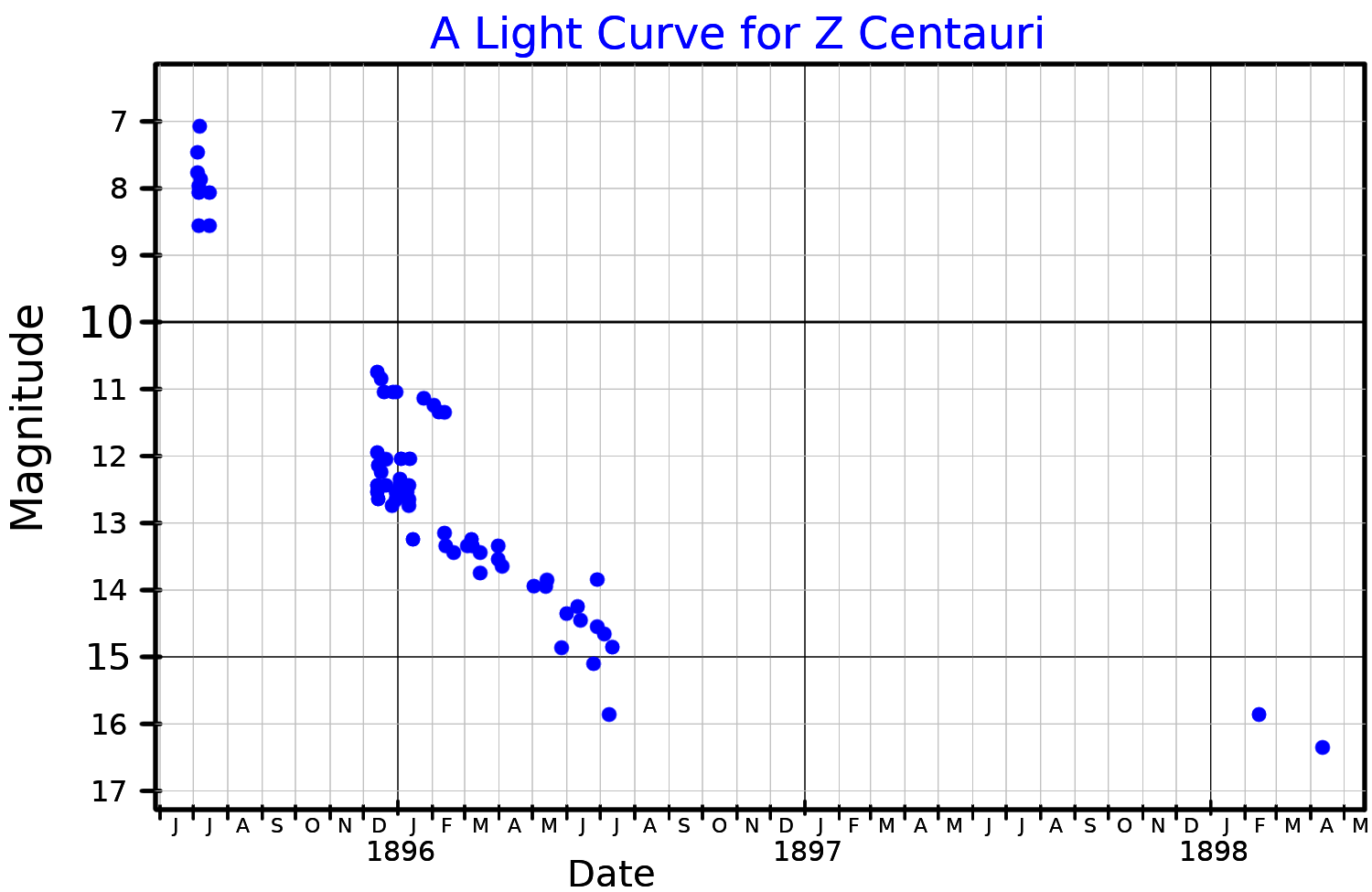
SN 1895B
SN 1895B was a supernova event in the irregular dwarf galaxy NGC 5253, positioned east and north of the galactic center. It is among the closest known extragalactic supernova events. The supernova was discovered by Williamina Fleming on December 12, 1895 after noticing an unusual spectrum on a photographic plate taken July 18, 1895, and was initially given the variable star designation Z Centauri. The light curve is consistent with an event that began ~15 days before the discovery plate was taken, and this indicates the supernova reached a peak visual magnitude of up to 8.49. After the light faded, the remnant has remained undetected at any wavelength, including X-ray and radio. This suggests the expanding remnant is meeting a low density of surrounding interstellar material, which would be consistent with certain double white dwarf merger scenarios. The remnant is expected to reach peak radio emission around the year 2195, and it may become detectable at that time. Reference ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Andromeda Galaxy
The Andromeda Galaxy (IPA: ), also known as Messier 31, M31, or NGC 224 and originally the Andromeda Nebula, is a barred spiral galaxy with the diameter of about approximately from Earth and the nearest large galaxy to the Milky Way. The galaxy's name stems from the area of Earth's sky in which it appears, the constellation of Andromeda, which itself is named after the princess who was the wife of Perseus in Greek mythology. The virial mass of the Andromeda Galaxy is of the same order of magnitude as that of the Milky Way, at . The mass of either galaxy is difficult to estimate with any accuracy, but it was long thought that the Andromeda Galaxy is more massive than the Milky Way by a margin of some 25% to 50%. This has been called into question by a 2018 study that cited a lower estimate on the mass of the Andromeda Galaxy, combined with preliminary reports on a 2019 study estimating a higher mass of the Milky Way. The Andromeda Galaxy has a diameter of about , making it the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Andromeda (constellation)
Andromeda is one of the 48 constellations listed by the 2nd-century Greco-Roman astronomer Ptolemy, and one of the 88 modern constellations. Located in the northern celestial hemisphere, it is named for Andromeda, daughter of Cassiopeia, in the Greek myth, who was chained to a rock to be eaten by the sea monster Cetus. Andromeda is most prominent during autumn evenings in the Northern Hemisphere, along with several other constellations named for characters in the Perseus myth. Because of its northern declination, Andromeda is visible only north of 40° south latitude; for observers farther south, it lies below the horizon. It is one of the largest constellations, with an area of 722 square degrees. This is over 1,400 times the size of the full moon, 55% of the size of the largest constellation, Hydra, and over 10 times the size of the smallest constellation, Crux. Its brightest star, Alpha Andromedae, is a binary star that has also been counted as a part of Pegasus, while ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
SN 1885A
SN 1885A (also S Andromedae) was a supernova in the Andromeda Galaxy, the only one seen in that galaxy so far by astronomers. It was the first supernova ever seen outside the Milky Way, though it was not appreciated at the time how far away it was. It is also known as "Supernova 1885". Discovery The supernova appears to have been seen first on August 17, 1885, by French astronomer Ludovic Gully during a public stargazing event. Gully thought it was scattered moonlight in his telescope and did not follow up on this observation. Irish amateur astronomer Isaac Ward in Belfast claimed to have seen the object on August 19, 1885, but did not immediately publish its existence. The independent detection of the supernova by Ernst Hartwig at Dorpat (Tartu) Observatory in Estonia on August 20, 1885, however, was communicated in a telegram on August 31, 1885, once Hartwig had verified in more ideal circumstances that the feature was not caused by reflected moonlight. The telegram prompte ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cassiopeia A
Cassiopeia A (Cas A) () is a supernova remnant (SNR) in the constellation Cassiopeia and the brightest extrasolar radio source in the sky at frequencies above 1 GHz. The supernova occurred approximately away within the Milky Way; given the width of the Orion Arm, it lies in the next-nearest arm outwards, the Perseus Arm, about 30 degrees from the Galactic anticenter. The expanding cloud of material left over from the supernova now appears approximately across from Earth's perspective. It has been seen in wavelengths of visible light with amateur telescopes down to 234 mm (9.25 in) with filters. It is estimated that light from the supernova itself first reached Earth near the 1690s, although there are no definitively corresponding records from then. Cas A is circumpolar at and above mid-Northern latitudes which had extensive records and basic telescopes. Its likely omission in records is probably due to interstellar dust absorbing optical wavelengt ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Johannes Kepler
Johannes Kepler (; ; 27 December 1571 – 15 November 1630) was a German astronomer, mathematician, astrologer, natural philosopher and writer on music. He is a key figure in the 17th-century Scientific Revolution, best known for his laws of planetary motion, and his books ''Astronomia nova'', ''Harmonice Mundi'', and ''Epitome Astronomiae Copernicanae''. These works also provided one of the foundations for Newton's theory of universal gravitation. Kepler was a mathematics teacher at a seminary school in Graz, where he became an associate of Prince Hans Ulrich von Eggenberg. Later he became an assistant to the astronomer Tycho Brahe in Prague, and eventually the imperial mathematician to Emperor Rudolf II and his two successors Matthias and Ferdinand II. He also taught mathematics in Linz, and was an adviser to General Wallenstein. Additionally, he did fundamental work in the field of optics, invented an improved version of the refracting (or Keplerian) telescope, an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |