|
List Of Stock Used By Swiss Federal Railways
The followling is an incomplete list of locomotives and multiple units used by the Swiss Federal Railways. Steam locomotives Steam railcars Electric locomotives Electric trainsets Electric railcars Diesel locomotives Diesel trainsets Battery-electric railcars Heavy shunters Light shunters Notes :1 Designations have changed over time :2 Numbers have changed over time :3 Numbers not continuous :4 Changes within one series :5 Not used any more, not yet used, or defined, but never used :6 Details have changed over time, this is the latest information :7 Today Zentralbahn :8 Classic Rail sold four of these locomotives to MThB :9 These locomotives were bought by the SBB-CFF-FFS Swiss Federal Railways (german: link=no, Schweizerische Bundesbahnen, ''SBB''; french: link=no, Chemins de fer fédéraux suisses, ''CFF''; it, Ferrovie federali svizzere, ''FFS'') is the national railway company of Switzerland. It is usuall ... and leased to BLS Lötschbe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Swiss Federal Railways
Swiss Federal Railways (german: link=no, Schweizerische Bundesbahnen, ''SBB''; french: link=no, Chemins de fer fédéraux suisses, ''CFF''; it, Ferrovie federali svizzere, ''FFS'') is the national railway company of Switzerland. It is usually referred to by the initials of its German, French, and Italian names, either as SBB CFF FFS, or used separately. The Romansh version of its name, ''Viafiers federalas svizras'', is not officially used. The official English abbreviation is "SBB", instead of the English acronym such as "SFR", which stands for ''Swiss Federal Railways'' itself. The company, founded in 1902, is headquartered in Bern. It used to be a government institution, but since 1999 it has been a special stock corporation whose shares are held by the Swiss Confederation and the Swiss cantons. It is currently the largest rail and transport company of Switzerland, and operates on most standard gauge lines of the Swiss network. It also heavily collaborates with ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
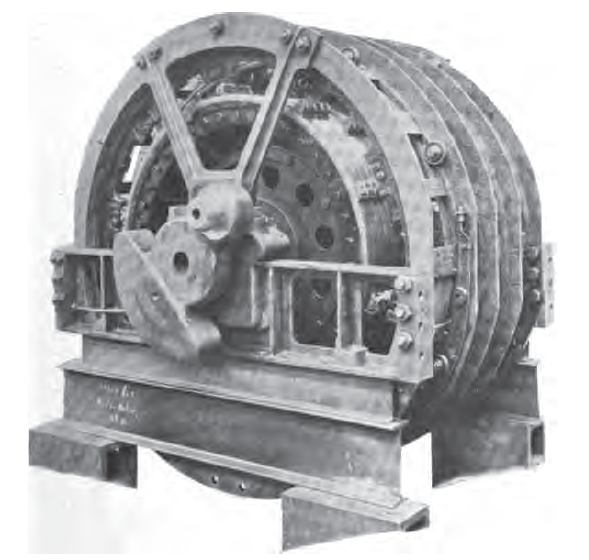
Midi E 3301
Midi E 3301 was a prototype electric locomotive of Class E 3300 designed for the Chemins de fer du Midi, France. Because of poor performance, it was refused by the Compagnie du Midi and was re-deployed to Swiss railways. On 1 May 1919, it was classified Fb 2/5 11001 and, in 1920, it became experimental locomotive Be 2/5 11001 of the Swiss Federal Railways (SBB). Overview Many lines of the Midi network being mountain lines, the company began an electrification programme in 1909. The system chosen was single phase alternating current at 12 kV and 16⅔ Hz. Six prototype locomotives were ordered for the Perpignan - Villefranche-de-Conflent line. They were: * E 3001 from Thomson and General Electric * E 3101 from AEG and Henschel * E 3201 from Westinghouse, later SNCF 1C1 3900 * E 3301 from Brown-Boveri and SLM Winterthur * E 3401 from Ateliers du Nord et de l'Est * E 3501 from Schneider The E 3301 locomotive was expected to perform the following tasks: * ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
SBB-CFF-FFS Ae 6/6
The Ae 6/6 is a heavy electric locomotive used by the Swiss Federal Railways (SBB-CFF-FFS). It is sometimes also referred to as ''canton locomotive'' ("Kantonslokomotive"), because the first 25 locomotives were named after the cantons, and carried the canton's coat of arms on the side and chrome embellishments (a single raised stripe on each side and three raised stripes on each end), and the Swiss coat of arms on the front, between the chrome stripes. These adornments made them internationally famous. The other 95 locomotives received the names of capital cities of Swiss cantons, and other towns and cities, but without the chrome embellishments. The namings were held as ceremonies in the respective cities. A less appealing moniker is ''Schienenwolf'' ("railroad plough") as the three axle bogie construction stresses heavily the tracks. Originally designed for heavy services on the Gotthard route, as many Swiss locomotives were, the Ae 6/6 was one of the classic ''Gotthard loco ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
SBB-CFF-FFS Ae 4/7
The Ae 4/7 was a universal locomotive of the Swiss Federal Railways, employing the so-called Buchli drive. Thanks to this drive construction, invented by Jakob Buchli, it was one of the longest-lasting locomotives. It was in regular use for 7 decades, from the 1920s into the 1990s, hauling freight and passenger trains all over Switzerland. History In the 1920s stronger locomotives were needed for the Swiss plateau (which has grades up to 12‰). The existing locomotives with three driven axles were a bit weak for their services. Because the Buchli drive already proved to be reliable on the , two prototypes of the Ae 4/7 were ordered in 1925. Subsequently, in total 127 were built between 1927 and 1934. While the mechanical part was built by the Swiss Locomotive and Machine Works, the electrical equipment was built in three varieties, because these parts were built by three different manufacturers, Brown, Boveri & Cie. (BBC) (10901–10916, 10932–10938, 10952–10972, 11003–1 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
SBB-CFF-FFS Ae 4/6
The Swiss locomotive class Ae 4/6 was a class of electric locomotives. They were intended as a powerful locomotive for the steep gradients of the Gotthard Railway, but smaller than the huge 'double locomotives' which had previously been tested there. They were built from 1941, during World War II, and although Switzerland remained neutral through this, material shortages led to some quality problems with these locomotives. Origins The SBB Ae 4/6 was needed for service on the steep gradients of the Gotthard Railway. Electric locomotives were needed, rather than steam, both because of Switzerland's dependence on imported coal, and also because of the ventilation problems in long tunnels. Existing electric types, such as the SBB-CFF-FFS Ce 6/8 I, Ce 6/8I, SBB-CFF-FFS Ce 6/8 II, Ce 6/8II 'crocodiles' and the SBB-CFF-FFS Be 4/6 12303-12342, Be 4/6 of the early 1920s had been powerful enough for the gradients, but their use of a coupling rod drive limited their speed. A new express pa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
SBB-CFF-FFS Ae 3/6 III
Swiss Federal Railways (german: link=no, Schweizerische Bundesbahnen, ''SBB''; french: link=no, Chemins de fer fédéraux suisses, ''CFF''; it, Ferrovie federali svizzere, ''FFS'') is the national railway company of Switzerland. It is usually referred to by the initials of its German, French, and Italian names, either as SBB CFF FFS, or used separately. The Romansh version of its name, ''Viafiers federalas svizras'', is not officially used. The official English abbreviation is "SBB", instead of the English acronym such as "SFR", which stands for ''Swiss Federal Railways'' itself. The company, founded in 1902, is headquartered in Bern. It used to be a government institution, but since 1999 it has been a special stock corporation whose shares are held by the Swiss Confederation and the Swiss cantons. It is currently the largest rail and transport company of Switzerland, and operates on most standard gauge lines of the Swiss network. It also heavily collaborates wit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
SBB-CFF-FFS Ae 3/6 II
Swiss Federal Railways (german: link=no, Schweizerische Bundesbahnen, ''SBB''; french: link=no, Chemins de fer fédéraux suisses, ''CFF''; it, Ferrovie federali svizzere, ''FFS'') is the national railway company of Switzerland. It is usually referred to by the initials of its German, French, and Italian names, either as SBB CFF FFS, or used separately. The Romansh version of its name, ''Viafiers federalas svizras'', is not officially used. The official English abbreviation is "SBB", instead of the English acronym such as "SFR", which stands for ''Swiss Federal Railways'' itself. The company, founded in 1902, is headquartered in Bern. It used to be a government institution, but since 1999 it has been a special stock corporation whose shares are held by the Swiss Confederation and the Swiss cantons. It is currently the largest rail and transport company of Switzerland, and operates on most standard gauge lines of the Swiss network. It also heavily collaborates wit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
SBB-CFF-FFS Ae 3/6 I
Swiss Federal Railways (german: link=no, Schweizerische Bundesbahnen, ''SBB''; french: link=no, Chemins de fer fédéraux suisses, ''CFF''; it, Ferrovie federali svizzere, ''FFS'') is the national railway company of Switzerland. It is usually referred to by the initials of its German, French, and Italian names, either as SBB CFF FFS, or used separately. The Romansh version of its name, ''Viafiers federalas svizras'', is not officially used. The official English abbreviation is "SBB", instead of the English acronym such as "SFR", which stands for ''Swiss Federal Railways'' itself. The company, founded in 1902, is headquartered in Bern. It used to be a government institution, but since 1999 it has been a special stock corporation whose shares are held by the Swiss Confederation and the Swiss cantons. It is currently the largest rail and transport company of Switzerland, and operates on most standard gauge lines of the Swiss network. It also heavily collaborates wit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
SBB-CFF-FFS Ae 3/5
The Ae 3/5 was a Swiss electric locomotive, operating out of Lausanne from 1926 to 1957, then out of Berne from 1957 to 1982. The examples were withdrawn from service starting in 1977, with one since classified as an historic vehicle. History The first units were delivered without security devices; these were added later. The symmetrical drive system of the locomotives are roughly equal to that of the Be 4/7. At the end of the Second World War, the maximum speed was reduced to 75 km/h. After repairs, they were again allowed proceed at speeds of 90 km/h. In 1957, the brake system was modified and traction brakes were installed. The locomotives were equipped with remote control ability (from a control car) between 1963 and 1966; it was not possible to control the locomotives from the units themselves. Up to two units of this type could be controlled from a control car. Once upgraded to remote units, the locomotives hauled automobile trains along the Gotthard railway ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
SBB-CFF-FFS Ce 6/8 I
The ''Ce 6/8 I 14201 was one of four test locomotives ordered by the Schweizerischen Bundesbahnen (Swiss Federal Railways) (SBB) in June 1917. For gaining experience for ordering electrical locomotives this locomotive should – as its three siblings Be 3/5 12201, Be 4/6 12301 and Be 4/6 12302 – have been used for services on the Gotthardbahn (Gotthard railway). The development of freight locomotives subsequently took a completely different way which was not conceivable at the ordering date (see Ce 6/8II). The Ce 6/8I came into service only after the first Ce 6/8II. History In November 1913 the executive board of the Schweizerischen Bundesbahnen (Swiss Federal Railways) (SBB) decided to electrify Gotthardbahn (Gotthard railway) from Erstfeld to Biasca. Due to World War One, the SBB had to reduce schedules more and more because of the shortage of coal. Therefore, – in the autumn of 1918 – on Sundays only milk trains were running. That's why the SBB forced – b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
SBB-CFF-FFS Ce 6/6
The Ce 6/6 was an electric locomotive operated by Schweizerischen Bundesbahnen (Swiss Federal Railways) (SBB). Originally ordered from Siemens-Schuckert by Malmbanen in Sweden as Fc 2x3 / 3 in 1912, the locomotive was not delivered due to World War I and was instead bought by SBB in 1919. Description The sole Ce 6/6 was a double locomotive consisting of two identical halves permanently connected. Each engine had a drivers cab, with a large electric motor mounted behind driving three axles. Originally allocated the service number 12200, it was renumbered 14101 in 1920. Service The locomotive was used to pull good trains between Bern and Thun. It was retired early in 1937 due to the high maintenance costs inherent in running a unique engine. Röthenbachsäge The Ce 6/6 was known as ''Röthenbachsäge'', named after the sawmill near Röthenbach im Emmental Röthenbach im Emmental is a municipality in the administrative district of Emmental in the canton of Bern in Switzerland. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
SBB-CFF-FFS Ce 4/4
Swiss Federal Railways (german: link=no, Schweizerische Bundesbahnen, ''SBB''; french: link=no, Chemins de fer fédéraux suisses, ''CFF''; it, Ferrovie federali svizzere, ''FFS'') is the national railway company of Switzerland. It is usually referred to by the initials of its German, French, and Italian names, either as SBB CFF FFS, or used separately. The Romansh language, Romansh version of its name, ''Viafiers federalas svizras'', is not officially used. The official English abbreviation is "SBB", instead of the English acronym such as "SFR", which stands for ''Swiss Federal Railways'' itself. The company, founded in 1902, is headquartered in Bern. It used to be a state-owned enterprise, government institution, but since 1999 it has been a special stock corporation whose shares are held by the Swiss Confederation and the Cantons of Switzerland, Swiss cantons. It is currently the largest rail and transport company of Switzerland, and operates on most standard gau ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |





.jpg)