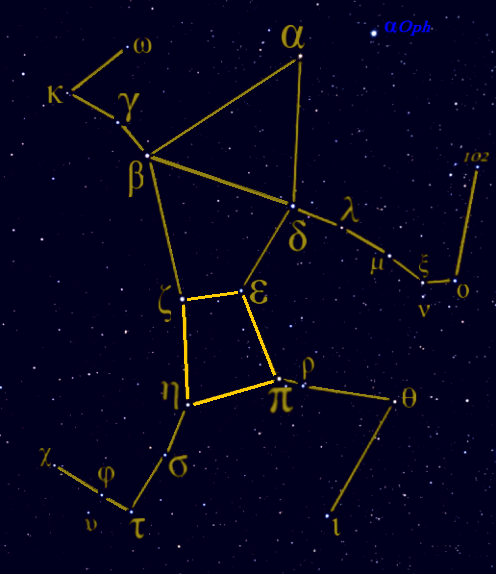
|
List Of Stars In Hercules ...
This is the list of notable stars in the constellation Hercules, sorted by decreasing brightness. See also *List of stars by constellation References * * * * {{Stars of Hercules *List Hercules Hercules (, ) is the Roman equivalent of the Greek divine hero Heracles, son of Jupiter and the mortal Alcmena. In classical mythology, Hercules is famous for his strength and for his numerous far-ranging adventures. The Romans adapted the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Star
A star is an astronomical object comprising a luminous spheroid of plasma (physics), plasma held together by its gravity. The List of nearest stars and brown dwarfs, nearest star to Earth is the Sun. Many other stars are visible to the naked eye at night sky, night, but their immense distances from Earth make them appear as fixed stars, fixed points of light. The most prominent stars have been categorised into constellations and asterism (astronomy), asterisms, and many of the brightest stars have proper names. Astronomers have assembled star catalogues that identify the known stars and provide standardized stellar designations. The observable universe contains an estimated to stars. Only about 4,000 of these stars are visible to the naked eye, all within the Milky Way galaxy. A star's life star formation, begins with the gravitational collapse of a gaseous nebula of material composed primarily of hydrogen, along with helium and trace amounts of heavier elements. Its stellar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Beta Herculis
Beta Herculis (β Herculis, abbreviated Beta Her, β Her), formally named Kornephoros , or Rutilicus, is a binary star and the brightest star in the northern constellation of Hercules at a base apparent visual magnitude of 2.81. This is a suspected variable star with an apparent magnitude that may rise as high as 2.76. Based upon parallax measurements, it is located at a distance of from the Sun. Although Beta Herculis appears to the naked eye to be a single star, in July 1899 the American astronomer W. W. Campbell discovered from spectroscopic measurements that its radial velocity varies, and concluded that it has a companion. Properties At Palomar Observatory, Antoine Labeyrie and others used speckle interferometry with the Hale Telescope to resolve the system in 1977. The Hipparcos satellite observed the orbital motion of the primary relative to other stars, and an orbit was computed in 2005 using spectroscopic data together with these measur ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
109 Herculis
109 Herculis is a single star in the northern constellation of Hercules. It is visible to the naked eye as a faint, orange-hued point of light with an apparent visual magnitude of 3.84. The star is located around distant, based on parallax. It is moving closer to the Earth with a heliocentric radial velocity of −58 km/s, and may come as close as away in around 328,000 years. This is an aging giant star with a stellar classification of K2IIIab. It is a red clump giant, meaning it on the horizontal branch and is generating energy through helium fusion at its core. The star is roughly six billion years old with slightly more mass than the Sun. With the supply of hydrogen at its core exhausted, it has expanded to nearly 12 times the Sun's radius. The star is radiating 57 times the luminosity of the Sun from its swollen photosphere at an effective temperature of 4,569 K. This star, together with 93 Her, 95 Her, and 102 Her, were consist Cerberus In ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gamma Cassiopeiae Variable
A Gamma Cassiopeiae variable (γ Cassiopeiae variable) is a type of variable star, named for its prototype γ Cassiopeiae. Variability γ Cassiopeiae variables show irregular changes in brightness on a timescale of decades. These typically have amplitudes of the order of a magnitude. For example, γ Cassiopeiae is usually about magnitude 2.5 and has varied between magnitudes 1.6 and 3.0. The variations are associated with changes in the spectrum between normal absorption spectra and Be star spectra, often also including shell star characteristics. Pleione and γ Cassiopeiae itself are both variable stars that have intermittent shell episodes where strong shell features appear in the spectrum and the brightness increases or decreases significantly. At other times the shell is not detectable in the spectrum, and even the emission lines may disappear. The General Catalogue of Variable Stars (GCVS) categorises γ Cassiopeiae stars as eruptive variables and describes them as r ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Omicron Herculis
Omicron Herculis, Latinized from o Herculis, is a star in the constellation Hercules. It used to be called Masym ("the wrist"), but this name was transferred to Lambda Herculis. Properties Omicron Herculis is a B9.5III star approximately 106 pc from the Earth. It has an apparent magnitude of 3.83. The star radiates with a bluish-white hue, and has a luminosity approximately 355 times as bright as the Sun. Omicron Herculis is 3.49 solar masses. Stellar evolutionary caclulations show that it has just left the main sequence. Omicron Herculis is an eruptive variable of the Gamma Cassiopeiae class, which are rapidly rotating B-class stars with mass outflow. It has a projected rotational velocity of 194 km/s. Some sources list Omicron Herculis as being both spectroscopic and an interferometric binary star with a separation of about 60 milliarcseconds, although the companion star has not been confirmed. Omicron Hercules is notable for residing close to the coord ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Beta Cephei Variable
Beta Cephei variables, also known as Beta Canis Majoris stars, are variable stars that exhibit small rapid variations in their brightness due to pulsations of the stars' surfaces, thought due to the unusual properties of iron at temperatures of 200,000 K in their interiors. These stars are usually hot blue-white stars of spectral class B and should not be confused with Cepheid variables, which are named after Delta Cephei and are luminous supergiant stars. Properties Beta Cephei variables are main-sequence stars of masses between about 7 and 20 M_\odot (that is, 7–20 times as massive as the Sun). Among their number are some of the brightest stars in the sky, such as Beta Crucis and Beta Centauri; Spica is also classified as a Beta Cephei variable but mysteriously stopped pulsating in 1970. Typically, they change in brightness by 0.01 to 0.3 magnitudes with periods of 0.1 to 0.3 days (2.4–7.2 hours). The prototype of these variable stars, Beta Cephei, shows variation in apparen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Iota Herculis
Iota Herculis (ι Herculis, ι Her) is a fourth-magnitude variable star system in the constellation Hercules, consisting of at least four stars all about away. The brightest is a β Cephei variable, a pulsating star. Visibility Iota Herculis is dim enough that in cities with a lot of light pollution it is unlikely to be visible with the naked eye. In rural areas it will usually be visible, and for much of the Northern Hemisphere the star is circumpolar and visible year around. Pole star As a visible star, the proximity of Iota Herculis to the precessional path the Earth's North Pole traces across the celestial sphere makes it a pole star, a title currently held by Polaris. In 10,000 BCE it was the pole star, and in the future it will be again. While Polaris is only 0.5° off the precessional path Iota Herculis is 4° off. Properties Iota Herculis is a B-type subgiant star that is at the end of its hydrogen fusion stage. With a stellar classification B3IV, it ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gamma Herculis
Gamma Herculis, Latinized from γ Herculis, is a magnitude 3.74 binary star system in the northern constellation of Hercules. Properties This is known to be a spectroscopic binary system, although there is no information about the secondary component. Based upon parallax measurements, this system is located at a distance of about from the Earth. The spectrum of the primary star matches a stellar classification of A9III, which indicates this is a giant star that has exhausted the hydrogen at its core and evolved away from the main sequence. The effective temperature is about 7,031 K, giving the star a white hue characteristic of A-type stars. It is rotating rapidly with a projected rotational velocity of . The interferometry-measured angular diameter of this star is , which, at its estimated distance, equates to a physical radius of about six times the radius of the Sun. Observations by German astronomer Ernst Zinner in 1929 gave indications that this may be a varia ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Xi Herculis
Xi Herculis is a solitary star located within the northern constellation of Hercules. The star is visible to the naked eye with an apparent visual magnitude of 3.70. Based upon an annual parallax shift of 23.84 mas as seen from Earth, it is located 137 light years from the Sun. At that distance, the visual magnitude of the star is diminished by an extinction factor of 0.05 due to interstellar dust. It is a suspected member of the Sirius stream of co-moving stars. This is an evolved G-type giant star with a stellar classification of G8 III. It is a red clump star, which means it is on the horizontal branch and generating energy through the thermonuclear fusion of hydrogen at its core. The star is emitting X-rays with a luminosity of in the 0.3–10 keV band. It has twice the mass of the Sun but, at the age of two and a half billion years, it has expanded to 10 times the Sun's radius. The star is radiating 51 times the solar luminosity from its photo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eta Herculis
Eta Herculis (η Her, η Herculis) is a fourth-magnitude star in the constellation Hercules. Properties Eta Herculis is a G-type star. With a stellar classification G7.5IIIb, it is considerably larger than the Sun, having a mass that is 2.3 times solar and a radius 9.8 times. Though it only shines with an apparent magnitude of 3.48, it is part of the "Keystone" asterism, visible overhead in the mid-summer night sky to northern observers, allowing it to be easily recognized. Eta Herculis is 50 times more luminous than the Sun. The Hipparcos satellite mission estimated its distance at roughly 34.4 parsecs from Earth, or 112 light years away. If one follows the line connecting Eta Herculis with Zeta Herculis one comes across one of the earliest and most stunning globular clusters in the nighttime sky, M13, discovered in 1714 by Edmond Halley. Eta Herculis is a double star once thought to be part of a binary star system A star system or stellar system i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mu Herculis
Mu Herculis (μ Herculis) is a nearby quadruple star system about 27.1 light years from Earth in the constellation Hercules (constellation), Hercules. Its main star, Mu Herculis A is fairly similar to the Sun although more highly stellar evolution, evolved with a stellar classification of G5 IV. Since 1943, the stellar spectrum, spectrum of this star has served as one of the stable anchor points by which other stars are classified. Its mass is about 1.1 times that of the Sun, and it is beginning to expand to become a giant. Etymology In the catalogue of stars in the ''Calendarium of Al Achsasi Al Mouakket'', this star was designated ''Marfak Al Jathih Al Aisr'', which was translated into Latin as ''Cubitum Sinistrum Ingeniculi'', meaning ''the left elbow of kneeling man''. In Chinese astronomy, Chinese, (), the ''Heavenly Market enclosure, Left Wall of Heavenly Market Enclosure'', refers to an asterism which represents eleven old states in China, mar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alpha Herculis
Alpha Herculis (α Herculis, abbreviated Alpha Her, α Her), also designated 64 Herculis, is a multiple star system in the constellation of Hercules. Appearing as a single point of light to the naked eye, it is resolvable into a number of components through a telescope. It has a combined apparent magnitude of 3.08, although the brightest component is variable in brightness. Based on parallax measurements obtained during the Hipparcos mission, it is approximately 360 light-years (110 parsecs) distant from the Sun. System Alpha Herculis is a triple star system. The primary (brightest) of the three stars, designated α1 Herculis or α Herculis A, is a pulsating variable star on the asymptotic giant branch (AGB), and is the second nearest AGB star after Mira. The primary star forms a visual binary pair with a second star, which is itself a spectroscopic binary. Alpha Herculis also forms the A and B components of a wider system designated WDS J17146+1423, with ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |