|
List Of Rulers Of Assam
The History of Assam is the history of a confluence of people from the east, west, south and the north; the confluence of the Austroasiatic, Tibeto-Burman (Sino-Tibetan), Tai and Indo-Aryan cultures. Although invaded over the centuries, it was never a vassal or a colony to an external power until the third Burmese invasion in 1821 and subsequently the British ingress into Assam in 1824 during the First Anglo-Burmese War. Later documented rulers, and dynasties who are deemed to have ruled a portion of Assam are included in this list. File:Major kingdoms of Assam.png, 260px, Major kingdoms of Assam rect 50 50 650 120 Kamarupa Kingdom rect 45 240 160 310 Kamata Kingdom rect 165 240 300 310 Bhuyan chieftains rect 305 240 415 310 Ahom Kingdom rect 425 240 540 310 Chutiya Kingdom rect 550 240 660 310 Kachari Kingdom rect 4 425 80 495 Koch Bihar rect 120 425 190 495 Koch Hajo rect 125 660 640 760 History of Assam Ancient Kingdoms (c. 1200 BCE – 500 CE) Sonitpura ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
History Of Assam
File:Major kingdoms of Assam.png, upright=1.3, Major kingdoms of Assam rect 50 50 650 120 Kamarupa Kingdom rect 45 240 160 310 Kamata Kingdom rect 165 240 300 310 Bhuyan chieftains rect 305 240 415 310 Ahom Kingdom rect 425 240 540 310 Chutiya Kingdom rect 550 240 660 310 Kachari Kingdom rect 4 425 80 495 Koch Bihar rect 120 425 190 495 Koch Hajo rect 125 660 640 760 History of Assam The history of Assam is the history of a confluence of people from the east, west, south and the north; the confluence of the Austroasiatic, Tibeto-Burman (Sino-Tibetan), Tai and Indo-Aryan cultures. Although invaded over the centuries, it was never a vassal or a colony to an external power until the third Burmese invasion in 1821, and, subsequently, the British ingress into Assam in 1824 during the First Anglo-Burmese War. The Assamese history has been derived from multiple sources. The Ahom kingdom of medieval Assam maintained chronicles, called Buranjis, written in the Ahom and the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pragjyotisha Kingdom
Pragjyotisha is a mythological kingdom that is mentioned in a multitude of Hindu Epics. It came to be associated with the historical Kamarupa after Bhaskaravarman of the Varman dynasty by drawing his lineage from Naraka/Bhagadatta of the legendary Pragjyotisha to bring his peripheral kingdom closer to mainland traditions at a time when he was emerging as a powerful king with interests in North India."Considering the historical content of the seventh century Kāmarūpa, especially during the reign of Bhāskarvarman when the Varmans was ascending to one of the important powers in north India, it appears that they projected Kāmarūpa on a larger geopolitical map by combining it with Prājyotisa, the Epic kingdom. In other words, Prājyotisa was retrieved from the ancient Epic past by the aspirant local kingship to overcome this peripherality. An elusive mythical space was brought into the actual geography of Kāmarūpa" The identification with the mythical Naraka/Bhagadatta lineag ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
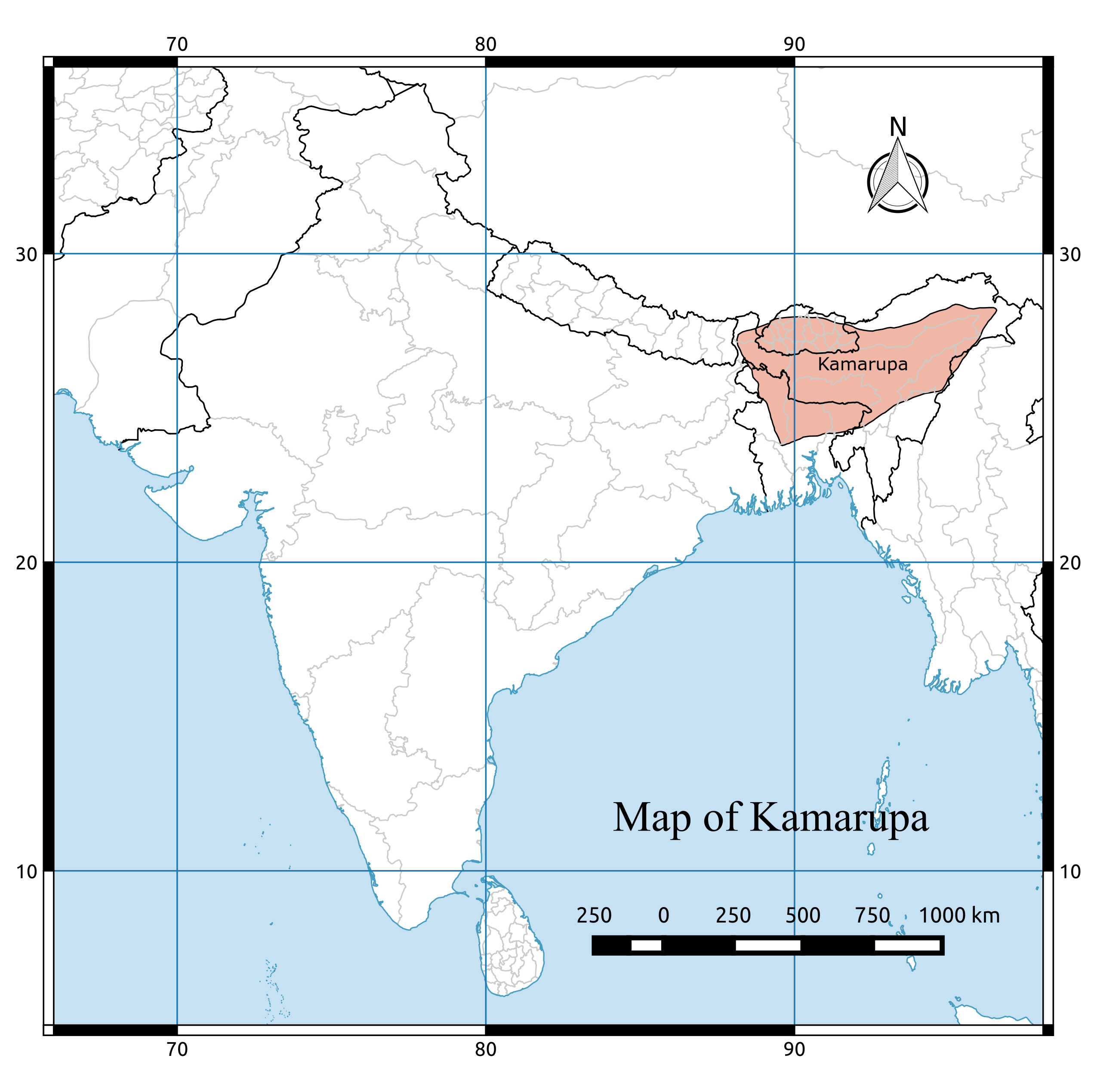
Kamarupa Map
Kamarupa (; also called Pragjyotisha or Pragjyotisha-Kamarupa), an early state during the Classical period on the Indian subcontinent, was (along with Davaka) the first historical kingdom of Assam. Though Kamarupa prevailed from 350 to 1140 CE, Davaka was absorbed by Kamarupa in the 5th century CE."As regards the eastern limits of the kingdom, Davaka was absorbed within Kamarupa under Kalyanavarman and the outlying regions were brought under subjugation by Mahendravarman." Ruled by three dynasties from their capitals in present-day Guwahati, North Guwahati and Tezpur, Kamarupa at its height covered the entire Brahmaputra Valley, North Bengal, Bhutan and northern part of Bangladesh, and at times portions of what is now West Bengal, Bihar and Sylhet. Though the historical kingdom disappeared by the 12th century to be replaced by smaller political entities, the notion of Kamarupa persisted and ancient and medieval chroniclers continued to call a part of this kingdom Kamru ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vajradatta
Vajradatta ( sa, वज्रदत्त) was son and successor of the king Bhagadatta, third in line to throne of Naraka dynasty of Pragjyotisha Kingdom. Vajradatta had studied four vedas along with Angas, and the Nitishastras of Brihaspati and Shukra. Vajradatta is mentioned in epics as powerful as Indra, speedy like Vajra and who pleased the performer of hundred sacrifices, who is Indra again, in battle. He said to possess bolt-like lustre and conquered enemies like Indra. Role in Mahabharata The Aswamedha Parva of Mahabharata gives account of Vajradatta. He was not able to accompany his father Bhagadatta in Mahabharata war, as he was child then. King Yudhishthira organised Aswamedha Parva, and Arjuna was appointed as guard of the Aswamedha horse. Horse after traversing different countries reached east to Pragjyotisha, then ruled by the Vajradatta. Vajradatta made an attempt to hold the horse to avenge his fathers humiliation in Mahabharata war in hands of Arjuna. He was d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bhagadatta
Bhagadatta ( sa, भगदत्त) was the son of Narakasura, and the king of Pragjyotisha. Bhagadatta was born from a limb of the asura called Bāṣkala. He was a renowned warrior, and was known to be a great friend of Indra. When Arjuna embarked on a conquest to help his brother Yudhishthira perform the Rajasuya Yagya, Bhagadatta was one of the first kings to be conquered by him. He was particularly skilled in the use of elephants in warfare. Riding on his elephant Supratik, he fought valiantly in the battle of Kurukshetra on behalf of the Kauravas. At this time he was very old. He was so old, in fact, that he tied his wrinkled eyelids with a silken handkerchief so that they could cover his eyes in battle. He was succeeded by his son Vajradatta. He fought for the Kaurava in the ''Mahabharata'' war. He was the leader of a great army of Kiratas and Chinas in the war. Life In the Battle of Kurukshetra, Bhagadatta fought on the side of the Kauravas. He had long history of enmit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Naraka
Naraka ( sa, नरक) is the realm of hell in Indian religions. According to some schools of Hinduism, Sikhism, Jainism and Buddhism, ''Naraka'' is a place of torment. The word ''Neraka'' (modification of ''Naraka'') in Indonesian and Malaysian has also been used to describe the Islamic concept of Hell. Alternatively, the "hellish beings" that are said to reside in this underworld are often referred to as ''Narakas''. These beings are also termed in Sanskrit as ''Narakiyas'' ( sa, नारकीय, ), ''Narakarnavas'' ( sa, नरकार्णव, ) and ''Narakavasis'' ( sa, नरकवासी, ). Hinduism Naraka is a realm in the Vedas, a place where souls are sent for the expiation of their sins. It is mentioned primarily in the Dharmashastras, Itihasas, and the Puranas, but also described in the Vedic samhitas, the Aranyakas and the Upanishads. Some Upanishads speak of 'darkness' instead of hell. A summary of the Upanishads and the Bhagavad Gita mentions hell ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Narakasura
Naraka, also known as Narakasura (), is an asura king in Hindu mythology. In Assamese tradition, he is regarded as the legendary progenitor of all three dynasties of Pragjyotisha-Kamarupa, and the founding ruler of the legendary Bhauma dynasty of Pragjyotisha. Though the myths about Naraka are first mentioned in the Mahabharata, later texts embellish them. According to later post-Vedic texts such as the Brahma Purana and Vishnu Purana, he was the son of Bhudevi, fathered either by the Varaha incarnation of Vishnu or Hiranyaksha. He is claimed as one who established Pragjyotisha. He was killed by Krishna and Satyabhama. His son Bhagadatta—of Mahabharata fame—succeeded him. The 10th/11th-century Kalika Purana embellishes the myths further and he is claimed to have come from Mithila and said to have established the kingdom of Pragjyotisha after overthrowing the last of the Kirata kings, Ghatakasura, of the Danava dynasty. It was foretold that he would be destroyed by a lat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kirata
The Kirāta ( sa, किरात) is a generic term in Sanskrit literature for people who had territory in the mountains, particularly in the Himalayas and Northeast India and who are believed to have been Sino-Tibetan in origin. The meaning of 'Kirata' referred by scholars as people with the lion's character, or mountain dwellers. Historical mention and mythology The ''Kirata''s often mentioned along with Cinas (Chinese), and slightly different from the Nishadas, are first mentioned in the Yajurveda (''Shukla'' XXX.16; ''Krisha'' III.4,12,1), and in the Atharvaveda (X.4,14). According to Suniti Kumar Chatterji, the name ''Kirata'' seems to be used for any non-Aryan hill-folk, however Manu's Dharmashastra (X.44) calls them "degraded Kshatriyas", which Chatterji infers to be a term for people who were advanced in military or civilization to some degree and not complete barbarians. It is speculated that the term is a Sanskritization of a Tibeto-Burman ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Banasura
Bana, also referred to as Banasura (), is an asura king in Hindu mythology, ruling from the city of Śoṇitapura. He is described to be the son of Mahabali. His tale of battling Krishna is described in the Bhagavata Purana. Legend A mighty asura, Bana once ruled over a large kingdom, Śoṇitapura. His influence was so strong and fierce that all the kings – and even some of the devas – shuddered in front of him. Banasura used to worship a rasalingam given to him by Vishvakarman, on instruction from Vishnu. As an ardent devotee of Shiva, he used his thousand arms to play the mridangam when Shiva was performing the tandavam dance. When Shiva offered Banasura a boon, the latter requested Shiva to be his city's guardian: therefore, Banasura became invincible. As time passed, he became even more cruel and arrogant. One day, Usha saw a young man in her dream, made love to him, and fell in love with him. Chitralekha, a friend of Usha a talented artist, helped Usha to identif ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
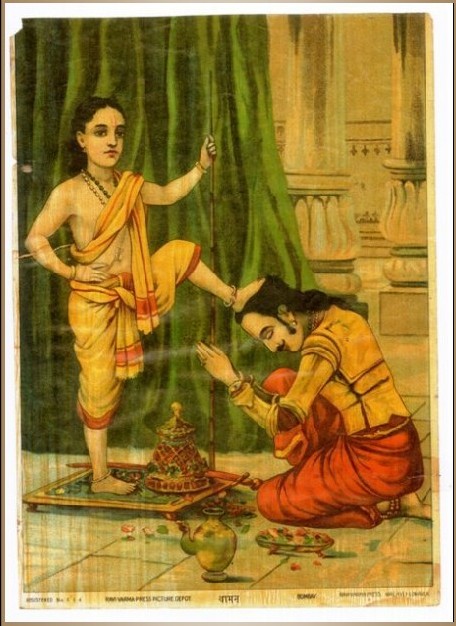
Mahabali
Mahabali (IAST: Mahābalī), also known as Bali, Indrasenan, or Māveli, is a daitya king featured in Hinduism. He is the grandson of Prahlada, and a descendant of the sage Kashyapa. There are many versions of his legend, in ancient texts such as the ''Shatapatha Brahmana'', ''Ramayana'', ''Mahabharata'', and several ''Puranas''. According to Hindu literature, he was banished beneath the earth into the ''patala'' (netherworld) by the Vamana avatar of Vishnu. In Hinduism, Mahabali is considered one of the Chiranjivi, a group of eight immortals. It is believed that he will become the King of Svarga (heaven) in the next ''yuga''. In Kerala, King Mahabali is considered to be the noblest and most prosperous ruler, who transformed his kingdom into a heavenly place. His legend is a major part of the annual festival Onam in the state of Kerala, and Balipratipada (the fourth day of Deepavali and first day of Kartika month) festival in North India and Tulunadu. Hinduism Mahabali is de ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Virochana
Virochana () is an asura king in Hinduism. He is the grandson of Hiranyakashipu, the son of Prahlada (according to the Atharvaveda (VIII.10.22), and the father of Bali. Legend Being the son of Prahlada, a staunch devotee of Vishnu, Virochana is raised to be religious, performing rites and rituals with care. He is stated to be kind towards Brahmins. In the Mahabharata, Vidura recounts the tale of Virochana and Sudhanva, the son of Sage Angiras. During the svayamvara of a beautiful princess called Kesini, the asura prince was asked to state if Brahmins were superior to the daityas. Being a daitya himself, Virochana replied that the daityas were superior, due to the worlds being under their suzerainty. Kesini invites Sudhanva to join them the following morning, washing his feet according to custom. Virochana offered to share his own golden seat with the Brahmin, but the latter turned down this offer, stating that Prahlada always chose to seat himself beneath him. The daitya and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Prahlad
Prahlada () is an asura king in Hindu mythology. He is known for his staunch devotion towards the preserver deity, Vishnu. He appears in the narrative of Narasimha, the man-lion avatar of Vishnu, who rescues Prahlada by slaying his wicked father, Hiranyakashipu. Prahlada is described as a saintly boy, known for his innocence and bhakti to Vishnu. Despite the abusive nature of his father, Hiranyakashipu, he continues to worship Vishnu. He is considered to be a ''mahājana'', or great devotee, by followers of Vaishnava traditions. A treatise is accredited to him in the Bhagavata Purana, in which Prahlada describes the process of his loving worship towards Vishnu. The majority of stories in the Puranas regarding him are based on the activities of Prahlada as a young boy, and he is usually depicted as such in paintings and illustrations. Legend Prahlada was born to Kayadhu and Hiranyakashipu, an evil daitya king who had been granted a boon that he could not be killed off by ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |