|
List Of Open-source Codecs
This is a listing of open-source codecs—that is, open-source software implementations of audio or video coding formats. Many of the codecs listed implement media formats that are restricted by patents and are hence not open formats. For example, x264 is a widely used open source implementation of the heavily patent encumbered MPEG-4 AVC video compression standard. Video codecs *x264 – H.264/MPEG-4 AVC implementation. x264 is not a codec (encoder/decoder); it is just an encoder (it cannot decode video). *OpenH264 – H.264 baseline profile encoding and decoding *OpenVVC an VVC /H.266 Real Time-Decoder for Mac OS, Windows, Linux and Android and special Version of FFmpeg, which was used for Ateme Satellite Broadcast Test. *x265 – An encoder based on the High Efficiency Video Coding (HEVC/H.265) standard. *Xvid – MPEG-4 Part 2 codec, compatible with DivX * libvpx – VP8 and VP9 implementation; formerly a proprietary codec developed by On2 Technologies, released by G ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Codec
A codec is a device or computer program that encodes or decodes a data stream or signal. ''Codec'' is a portmanteau of coder/decoder. In electronic communications, an endec is a device that acts as both an encoder and a decoder on a signal or data stream, and hence is a type of codec. ''Endec'' is a portmanteau of encoder/decoder. A coder or encoder encodes a data stream or a signal for transmission or storage, possibly in encrypted form, and the decoder function reverses the encoding for playback or editing. Codecs are used in videoconferencing, streaming media, and video editing applications. History In the mid-20th century, a codec was a device that coded analog signals into digital form using pulse-code modulation (PCM). Later, the name was also applied to software for converting between digital signal formats, including companding functions. Examples An audio codec converts analog audio signals into digital signals for transmission or encodes them for storag ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Android (operating System)
Android is a mobile operating system based on a modified version of the Linux kernel and other open-source software, designed primarily for touchscreen mobile devices such as smartphones and tablets. Android is developed by a consortium of developers known as the Open Handset Alliance and commercially sponsored by Google. It was unveiled in November 2007, with the first commercial Android device, the HTC Dream, being launched in September 2008. Most versions of Android are proprietary. The core components are taken from the Android Open Source Project (AOSP), which is free and open-source software (FOSS) primarily licensed under the Apache License. When Android is installed on devices, the ability to modify the otherwise free and open-source software is usually restricted, either by not providing the corresponding source code or by preventing reinstallation through technical measures, thus rendering the installed version proprietary. Most Android devices ship with additio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Intel
Intel Corporation is an American multinational corporation and technology company headquartered in Santa Clara, California, Santa Clara, California. It is the world's largest semiconductor chip manufacturer by revenue, and is one of the developers of the x86 series of instruction sets, the instruction sets found in most personal computers (PCs). Delaware General Corporation Law, Incorporated in Delaware, Intel ranked No. 45 in the 2020 Fortune 500, ''Fortune'' 500 list of the largest United States corporations by total revenue for nearly a decade, from 2007 to 2016 fiscal years. Intel supplies microprocessors for List of computer system manufacturers, computer system manufacturers such as Acer Inc., Acer, Lenovo, HP Inc., HP, and Dell Technologies, Dell. Intel also manufactures motherboard chipsets, network interface controllers and integrated circuits, flash memory, Graphics processing unit, graphics chips, Embedded system, embedded processors and other devices related to com ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
AOMedia Video 1
AOMedia Video 1 (AV1) is an open, royalty-free video coding format initially designed for video transmissions over the Internet. It was developed as a successor to VP9 by the Alliance for Open Media (AOMedia), a consortium founded in 2015 that includes semiconductor firms, video on demand providers, video content producers, software development companies and web browser vendors. The AV1 bitstream specification includes a reference video codec. In 2018, Facebook conducted testing that approximated real-world conditions, and the AV1 reference encoder achieved 34%, 46.2% and 50.3% higher data compression than libvpx-vp9, x264 High profile, and x264 Main profile respectively. Like VP9, but unlike H.264/AVC and HEVC, AV1 has a royalty-free licensing model that does not hinder adoption in open-source projects. AVIF is an image file format that uses AV1 compression algorithms. History The Alliance's motivations for creating AV1 included the high cost and uncertai ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
On2 Technologies
On2 Technologies, formerly known as The Duck Corporation, was a small publicly traded company (on the American Stock Exchange), founded in New York City in 1992 and headquartered in Clifton Park, New York, that designed video codec technology. It created a series of video codecs called TrueMotion (including TrueMotion S, TrueMotion 2, TrueMotion RT 2.0, TrueMotion VP3, 4, 5, 6, 7 and 8). In February 2010, On2 Technologies was acquired by Google for an estimated $124.6 million. On2's VP8 technology became the core of Google's WebM video file format. History While known by the name ''The Duck Corporation'', they developed TrueMotion S, a codec that was used by some games for full motion video (FMV) sequences during the 1990s. The original office of the Duck Corporation was founded in New York City by Daniel B. Miller, Victor Yurkovsky, and Stan Marder. In 1994 Duck opened its first "satellite" engineering office in Colonie, NY under the management of Eric Ameres. Miller ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Libvpx
libvpx is a free software video codec library from Google and the Alliance for Open Media (AOMedia). It serves as the reference software implementation for the VP8 and VP9 video coding formats, and for AV1 a special fork named libaom that was stripped of backwards compatibility. As free software it is published also in source code under the terms of the revised BSD license. It ships with the commandline tools vpxenc/aomenc and vpxdec/aomdec that build on its functionality. History libvpx originates from the video codec company On2 Technologies that sold its first software codec in mid-90s. libvpx was released as free software by Google on May 19, 2010, after the acquisition of On2 Technologies for an estimate of over 120 million US dollars. In June 2010, Google amended the VP8 codec software license to the 3-clause BSD license after some contention over whether the original license was actually open source. Google was criticised for dumping untidy code with bad documen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
MPEG-4 Part 2
MPEG-4 Part 2, MPEG-4 Visual (formally ISO/ IEC 14496-2) is a video compression format developed by the Moving Picture Experts Group (MPEG). It belongs to the MPEG-4 ISO/IEC standards. It uses block-wise motion compensation and a discrete cosine transform (DCT), similar to previous standards such as MPEG-1 Part 2 and H.262/MPEG-2 Part 2. Several popular codecs including DivX, Xvid, and Nero Digital implement this standard. Note that MPEG-4 Part 10 defines a different format from MPEG-4 Part 2 and should not be confused with it. MPEG-4 Part 10 is commonly referred to as H.264 or AVC, and was jointly developed by ITU-T and MPEG. MPEG-4 Part 2 is H.263 compatible in the sense that a basic H.263 bitstream is correctly decoded by an MPEG-4 Video decoder. (MPEG-4 Video decoder is natively capable of decoding a basic form of H.263.) In MPEG-4 Visual, there are two types of video object layers: the video object layer that provides full MPEG-4 functionality, and a reduced functio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Xvid
Xvid (formerly "XviD") is a video codec library following the MPEG-4 video coding standard, specifically MPEG-4 Part 2 Advanced Simple Profile (ASP). It uses ASP features such as b-frames, global and quarter pixel motion compensation, lumi masking, trellis quantization, and H.263, MPEG and custom quantization matrices. Xvid is a primary competitor of the DivX Pro Codec. In contrast with the DivX codec, which is proprietary software developed by DivX, Inc., Xvid is free software distributed under the terms of the GNU General Public License. This also means that unlike the DivX codec, which is only available for a limited number of platforms, Xvid can be used on all platforms and operating systems for which the source code can be compiled. History In January 2001, DivXNetworks founded ''OpenDivX'' as part of Project Mayo which was intended to be a home for open source multimedia projects. OpenDivX was an open-source MPEG-4 video codec based on a stripped-down version o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
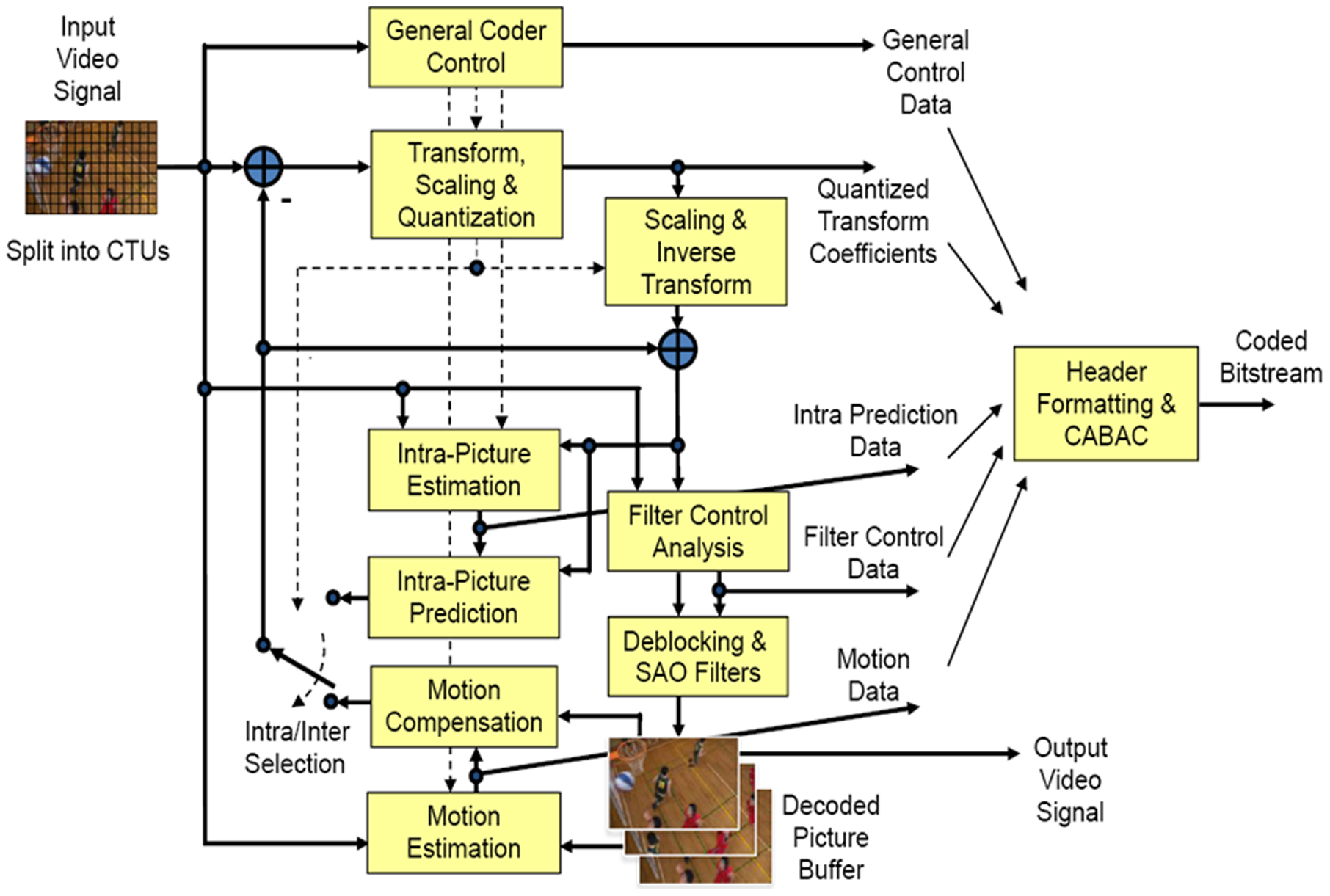
High Efficiency Video Coding
High Efficiency Video Coding (HEVC), also known as H.265 and MPEG-H Part 2, is a video compression standard designed as part of the MPEG-H project as a successor to the widely used Advanced Video Coding (AVC, H.264, or MPEG-4 Part 10). In comparison to AVC, HEVC offers from 25% to 50% better data compression at the same level of video quality, or substantially improved video quality at the same bit rate. It supports resolutions up to 8192×4320, including 8K UHD, and unlike the primarily 8-bit AVC, HEVC's higher fidelity Main 10 profile has been incorporated into nearly all supporting hardware. While AVC uses the integer discrete cosine transform (DCT) with 4×4 and 8×8 block sizes, HEVC uses integer DCT and DST transforms with varied block sizes between 4×4 and 32×32. The High Efficiency Image Format (HEIF) is based on HEVC. , HEVC is used by 43% of video developers, and is the second most widely used video coding format after AVC. Concept In most ways, HEVC is an ex ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
X265
x265 is a software codec for creating digital video streams in the High Efficiency Video Coding (HEVC/H.265) video compression format developed by the Joint Collaborative Team on Video Coding (JCT-VC). It is available as a command-line app or a software library, under the terms of GNU General Public License (GPL) version 2 or later; however, customers may request a commercial license. History x265 builds on source code from x264, an open-source video encoder for the previous MPEG video coding standard, H.264/MPEG-4 AVC. The project has licensed the rights to use the x264 source code. Development on x265 began in March 2013. MulticoreWare made the source code for x265 publicly available on July 23, 2013. The x265 project was initially funded by a small group of charter licensee companies that direct the development requirements and receive commercial licenses to use x265 in their products without having to release their products under the GPL 2 license. In February 2014, x26 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Broadcast
Broadcasting is the distribution (business), distribution of sound, audio or video content to a dispersed audience via any electronic medium (communication), mass communications medium, but typically one using the electromagnetic spectrum (radio waves), in a :wikt:one-to-many, one-to-many model. Broadcasting began with AM radio, which came into popular use around 1920 with the spread of vacuum tube radio transmitters and radio receiver, receivers. Before this, all forms of electronic communication (early radio, telephone, and telegraph) were wikt:one-to-one, one-to-one, with the message intended for a single recipient. The term ''broadcasting'' evolved from its use as the agricultural method of sowing seeds in a field by casting them broadly about. It was later adopted for describing the widespread distribution of information by printed materials or by telegraph. Examples applying it to "one-to-many" radio transmissions of an individual station to multiple listeners appeared as ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |