|
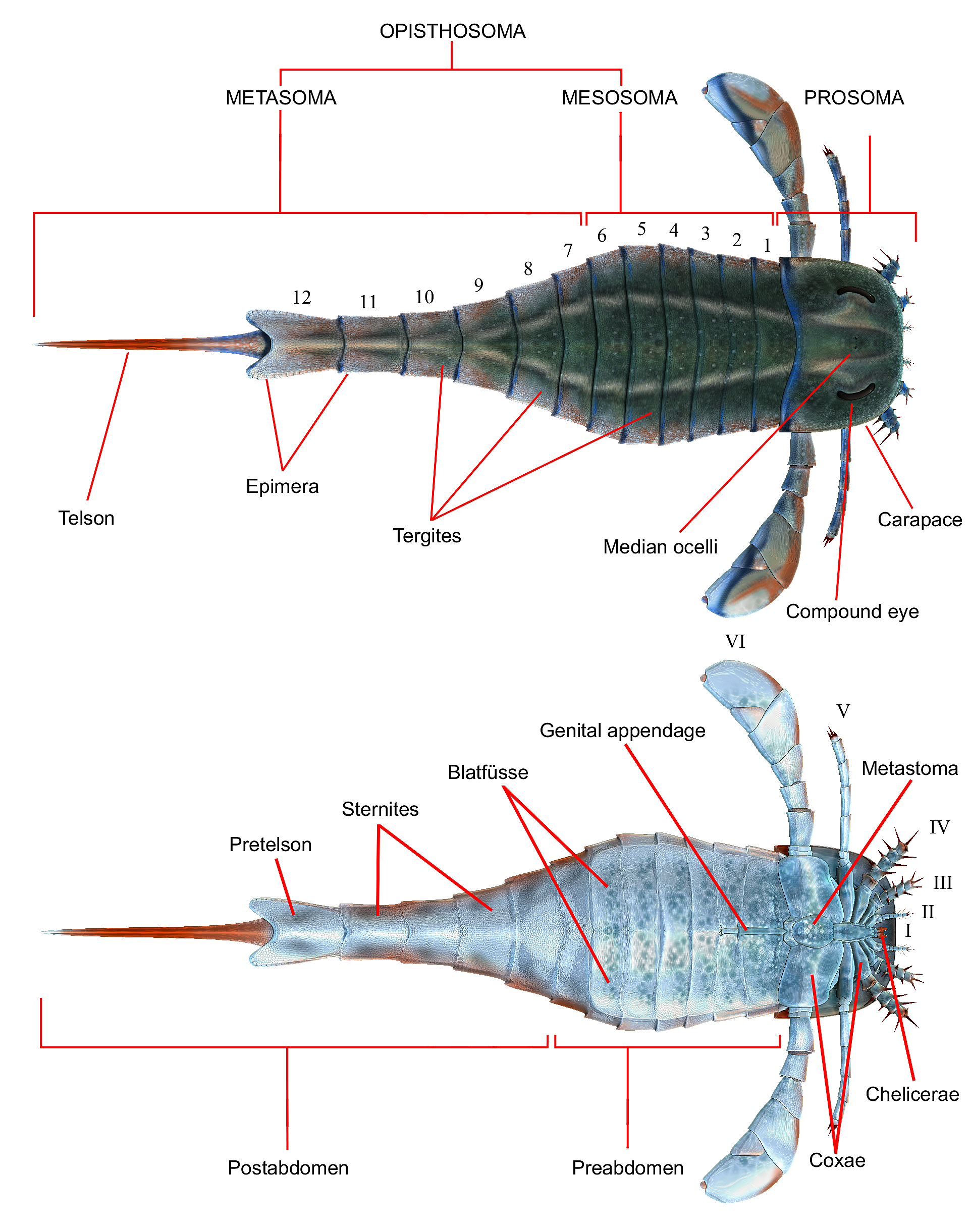
List Of Eurypterids
This list of eurypterid genera is a comprehensive listing of all genera that have ever been included in the order Eurypterida, excluding purely vernacular terms. The list includes all commonly accepted genera, but also genera that are now considered invalid, doubtful ('' nomen dubium''), or were not formally published ('' nomen nudum''), as well as junior synonyms of more established names and genera that are no longer considered eurypterids. The list currently includes 115 names out of which 74 are considered valid eurypterid genera. There are approximately 250 species of eurypterids recognized as valid. Naming conventions and terminology There is no "official" or "canonical" list of eurypterid genera. The closest thing is found contained in the regularly updated ''Summary list'' ''of fossil spiders and their relatives'' in the World Spider Catalog. The vast majority of the content of the list below, including the valid genera, preoccupied names, junior synonyms, taxonomical ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
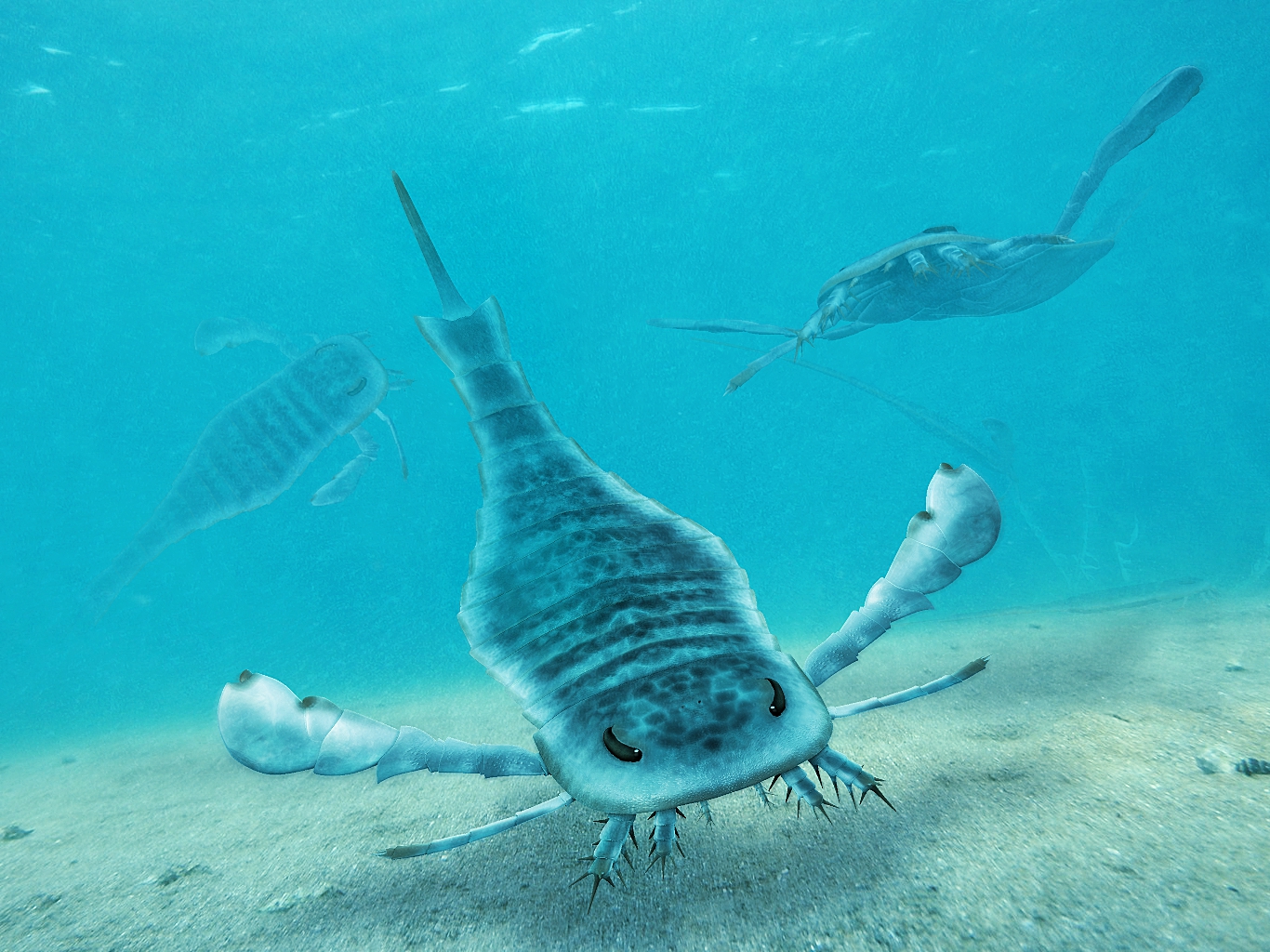
Eurypterus Paleoart
''Eurypterus'' ( ) is an extinct genus of eurypterid, a group of organisms commonly called "sea scorpions". The genus lived during the Silurian period, from around 432 to 418 million years ago. ''Eurypterus'' is by far the most well-studied and well-known eurypterid. ''Eurypterus'' fossil specimens probably represent more than 95% of all known eurypterid specimens. There are fifteen species belonging to the genus ''Eurypterus'', the most common of which is ''E. remipes'', the first eurypterid fossil discovered and the state fossil of New York. Members of ''Eurypterus'' averaged at about in length, but the largest individual discovered was estimated to be long. They all possessed spine-bearing appendages and a large paddle they used for swimming. They were generalist species, equally likely to engage in predation or scavenging. Discovery The first fossil of ''Eurypterus'' was found in 1818 by S. L. Mitchill, a fossil collector. It was recovered from the Bertie Formation ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Devonian
The Devonian ( ) is a geologic period and system of the Paleozoic era, spanning 60.3 million years from the end of the Silurian, million years ago (Mya), to the beginning of the Carboniferous, Mya. It is named after Devon, England, where rocks from this period were first studied. The first significant adaptive radiation of life on dry land occurred during the Devonian. Free-sporing vascular plants began to spread across dry land, forming extensive forests which covered the continents. By the middle of the Devonian, several groups of plants had evolved leaves and true roots, and by the end of the period the first seed-bearing plants appeared. The arthropod groups of myriapods, arachnids and hexapods also became well-established early in this period, after starting their expansion to land at least from the Ordovician period. Fish reached substantial diversity during this time, leading the Devonian to often be dubbed the Age of Fishes. The placoderms began dominating ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1868 In Paleontology
Arthropoda Newly named insects Archosauromorphs Newly named dinosaurs Plesiosaurs New taxa Synapsids Non-mammalian {, class="wikitable sortable" align="center" width="100%" , - ! Name ! Status ! Authors ! Discovery year ! Age ! Unit ! Location ! width="33%" class="unsortable" , Notes ! class="unsortable", Images , - , ''Pristerodon'' , Valid , Huxley , , , , , , rowspan="99", , - References 1860s in paleontology Paleontology Paleontology (), also spelled palaeontology or palæontology, is the scientific study of life that existed prior to, and sometimes including, the start of the Holocene epoch (roughly 11,700 years before present). It includes the study of fossi ... Paleontology 8 Paleontology, 1868 In ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anthraconectes
''Adelophthalmus'' is a genus of eurypterid, an extinct group of aquatic arthropods. Fossils of ''Adelophthalmus'' have been discovered in deposits ranging in age from the Early Devonian to the Early Permian, which makes it the longest lived of all known eurypterid genera, with a total temporal range of over 120 million years. ''Adelopththalmus'' was the final genus of the Eurypterina suborder of eurypterids and consisted the only known genus of swimming eurypterids from the Middle Devonian until its extinction during the Permian, after which the few surviving eurypterids were all walking forms of the suborder Stylonurina. Fossils of ''Adelophthalmus'' have been described from four continents; North America, Europe, Asia and Australia, which indicates that ''Adelophthalmus'' might have had a nearly cosmopolitan (worldwide) distribution, one of few eurypterid genera to achieve one besides potentially ''Pterygotus''. The territorial expansion of ''Adelophthalmus'' had begun early, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Crustacean
Crustaceans (Crustacea, ) form a large, diverse arthropod taxon which includes such animals as decapods, seed shrimp, branchiopods, fish lice, krill, remipedes, isopods, barnacles, copepods, amphipods and mantis shrimp. The crustacean group can be treated as a subphylum under the clade Mandibulata. It is now well accepted that the hexapods emerged deep in the Crustacean group, with the completed group referred to as Pancrustacea. Some crustaceans (Remipedia, Cephalocarida, Branchiopoda) are more closely related to insects and the other hexapods than they are to certain other crustaceans. The 67,000 described species range in size from '' Stygotantulus stocki'' at , to the Japanese spider crab with a leg span of up to and a mass of . Like other arthropods, crustaceans have an exoskeleton, which they moult to grow. They are distinguished from other groups of arthropods, such as insects, myriapods and chelicerates, by the possession of biramous (two-parted) limbs, and by th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1936 In Paleontology
Plants Ferns and fern allies Flowering plants Arthropods Insects Archosauromorphs Newly named dinosaurs Data courtesy of George Olshevsky's dinosaur genera list. Pterosaurs New taxa Synapsids Non-mammalian References {{DEFAULTSORT:1936 In Paleontology 1930s in paleontology Paleontology 6 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Angustidontus
''Angustidontus'' is a genus of predatory pelagic crustaceans from the Late Devonian and Early Carboniferous periods, classified as part of the subclass Eumalacostraca. Fossils of the genus have been recovered in relative abundance from Canada, Germany, the Czech Republic, Poland, Belarus, Ukraine and large parts of the United States, including Oklahoma, Ohio, Indiana, Kentucky, Montana, Utah, Nevada. The major eumalacostracan lineages had already diverged from each other during the Devonian, but their early evolutionary history remains relatively unknown due to a poor fossil record, making fossils of ''Angustidontus'' and other early eumalacostracans important for scientific study. Historically of uncertain classification, studies on the paleobiology of ''Angustidontus'' have allowed researchers to place it between the eumalacostracan orders Amphionidacea and Decapoda. Description ''Angustidontus'' was a predatory angustidontid crustacean, measuring about 6 centimeters in le ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alloeurypterus
''Eurypterus'' ( ) is an extinct genus of eurypterid, a group of organisms commonly called "sea scorpions". The genus lived during the Silurian period, from around 432 to 418 million years ago. ''Eurypterus'' is by far the most well-studied and well-known eurypterid. ''Eurypterus'' fossil specimens probably represent more than 95% of all known eurypterid specimens. There are fifteen species belonging to the genus ''Eurypterus'', the most common of which is ''E. remipes'', the first eurypterid fossil discovered and the state fossil of New York. Members of ''Eurypterus'' averaged at about in length, but the largest individual discovered was estimated to be long. They all possessed spine-bearing appendages and a large paddle they used for swimming. They were generalist species, equally likely to engage in predation or scavenging. Discovery The first fossil of ''Eurypterus'' was found in 1818 by S. L. Mitchill, a fossil collector. It was recovered from the Bertie Formation of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1974 In Paleontology
Bryophytes Plants Angiosperms Archosauromorphs General research * ''Massospondylus'' gastroliths are documented.Raath (1974). Sanders, Manley, and Carpenter (2001), "Table 12.1" page 167. Newly named dinosaurs Data courtesy of George Olshevsky's dinosaur genera list. Newly named birds Newly named pterosaurs References {{Reflist * Raath, M.A. (1974). Fossil vertebrate studies in Rhodesia: further evidence of gastroliths in Prosauropod dinosaurs. Arnoldia Rhodesia. 7 (5): 1–7. * Sanders F, Manley K, Carpenter K. Gastroliths from the Lower Cretaceous sauropod Cedarosaurus weiskopfae. In: Tanke D.H, Carpenter K, editors. Mesozoic vertebrate life: new research inspired by the paleontology of Philip J. Currie. Indiana University Press; Bloomington, IN: 2001. pp. 166–180. Paleontology Paleontology (), also spelled palaeontology or palæontology, is the scientific study of life that existed prior to, and sometimes including, the start of the Holocene ep ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alkenopterus
''Alkenopterus'' is a genus of prehistoric eurypterid classified as part of the family Onychopterellidae. The genus contains two species, ''A. brevitelson'' and ''A. burglahrensis'', both from the Devonian of Germany. Description Like the other onychopterellids, ''Alkenopterus'' was a small eurypterid. The largest species was ''A. brevitelson'', being long. The other species, ''A. burglahrensis'', represents in fact the smallest species of eurypterid known as far, only measuring . The prosoma (head) was large, with a subquadrate (almost square) to semielliptic (nearly elliptic), horseshoe-like outline. It was anteriorly surrounded by a broad and flat marginal rim that reached its Posterior (anatomy), posterior corners. The carapace (the exoskeleton part covering the prosoma) was rounded in the front. Its surface was somewhat inflated, being distinguished several narrow grooves and ridges, most of them wrinkle-like. The prominent Lateral (anatomy), lateral Compound eye, eyes we ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cosmopolitan Distribution
In biogeography, cosmopolitan distribution is the term for the range of a taxon that extends across all or most of the world in appropriate habitats. Such a taxon, usually a species, is said to exhibit cosmopolitanism or cosmopolitism. The extreme opposite of a cosmopolitan species is an endemic one, being found only in a single geographical location. Qualification The caveat “in appropriate habitat” is used to qualify the term "cosmopolitan distribution", excluding in most instances polar regions, extreme altitudes, oceans, deserts, or small, isolated islands. For example, the housefly is highly cosmopolitan, yet is neither oceanic nor polar in its distribution. Related terms and concepts The term pandemism also is in use, but not all authors are consistent in the sense in which they use the term; some speak of pandemism mainly in referring to diseases and pandemics, and some as a term intermediate between endemism and cosmopolitanism, in effect regarding pandemism as ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Permian
The Permian ( ) is a geologic period and stratigraphic system which spans 47 million years from the end of the Carboniferous Period million years ago (Mya), to the beginning of the Triassic Period 251.9 Mya. It is the last period of the Paleozoic Era; the following Triassic Period belongs to the Mesozoic Era. The concept of the Permian was introduced in 1841 by geologist Sir Roderick Murchison, who named it after the region of Perm in Russia. The Permian witnessed the diversification of the two groups of amniotes, the synapsids and the sauropsids ( reptiles). The world at the time was dominated by the supercontinent Pangaea, which had formed due to the collision of Euramerica and Gondwana during the Carboniferous. Pangaea was surrounded by the superocean Panthalassa. The Carboniferous rainforest collapse left behind vast regions of desert within the continental interior. Amniotes, which could better cope with these drier conditions, rose to dominance in place of their am ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |