|
List Of OMB Circulars
This is a partial list of circulars and bulletins issued by the Office of Management and Budget (OMB) within the Executive Office of the President of the United States. Circulars * Circular A-4: Requires federal agencies to identify why regulation is needed, consider a reasonable number of alternative regulatory approaches, and for each alternative conduct a rigorous and objective benefit-cost analysis * Circular A-11: Preparation, submission, and execution of the budget, revised and reissued periodically * Circular A-16: Creation, maintenance and use of spatial data * Circular A-21: Costs in support of sponsored research, development and training *Circular A-119 relates to federal participation in the development and use of voluntary consensus standards and in conformity assessment activities. It was originally published on 20 October 1993, and was updated on 10 February 1998 * Circular A-123: Management responsibilities for internal controls in federal agencies * Circular A-126 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Government Circular
A government circular is a written statement of government policy. It will often provide information, guidance, rules, and/or background information on legislative or procedural matters. See also *List of circulars {{short description, None This is a list of Circulars, distributed documents. Government publications *Government circular, a written statement of government policy ** Chamberlain Circular, a circular issued in 1886 in the United Kingdom encouragi ... ReferencesCirculars , The White House Government statements Government publications {{gov-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
OMB Circular A-123
OMB Circular A-123 is a US Office of Management and Budget (OMB) Government circular that defines the management responsibilities for internal controls in Federal agencies. It was first issued in 1981 by OMB's Office of Federal Financial Management and underwent numerous updates through 21 December 2004. The Circular is addressed to all federal chief financial officer The chief financial officer (CFO) is an officer of a company or organization that is assigned the primary responsibility for managing the company's finances, including financial planning, management of financial risks, record-keeping, and financ ...s, chief information officers, and program managers. The most current circular update (2016) was signed by then-director Shaun Donovan. The 2004 update to Circular A-123 is a re-examination of the existing internal control requirements for Federal agencies and was initiated in light of the new internal control requirements for publicly traded companies contained in th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
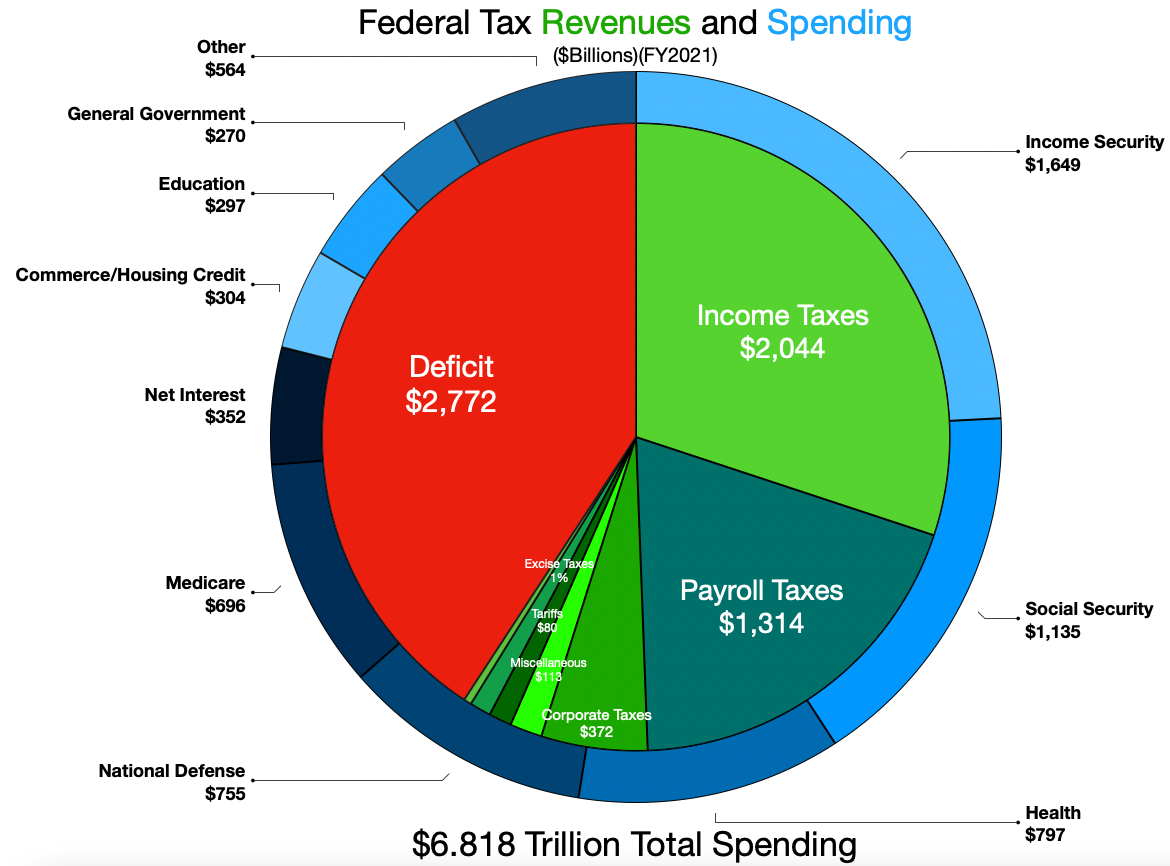
United States Office Of Management And Budget
The Office of Management and Budget (OMB) is the largest office within the Executive Office of the President of the United States (EOP). OMB's most prominent function is to produce the president's budget, but it also examines agency programs, policies, and procedures to see whether they comply with the president's policies and coordinates inter-agency policy initiatives. Shalanda Young became OMB's acting director in March 2021, and was confirmed by the Senate in March 2022. History The Bureau of the Budget, OMB's predecessor, was established in 1921 as a part of the Department of the Treasury by the Budget and Accounting Act of 1921, which President Warren G. Harding signed into law. The Bureau of the Budget was moved to the Executive Office of the President in 1939 and was run by Harold D. Smith during the government's rapid expansion of spending during World War II World War II or the Second World War, often abbreviated as WWII or WW2, was a world war that ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fiscal Year
A fiscal year (or financial year, or sometimes budget year) is used in government accounting, which varies between countries, and for budget purposes. It is also used for financial reporting by businesses and other organizations. Laws in many jurisdictions require company financial reports to be prepared and published on an annual basis but generally not the reporting period to align with the calendar year (1 January to 31 December). Taxation laws generally require accounting records to be maintained and taxes calculated on an annual basis, which usually corresponds to the fiscal year used for government purposes. The calculation of tax on an annual basis is especially relevant for direct taxes, such as income tax. Many annual government fees—such as council tax and license fees, are also levied on a fiscal year basis, but others are charged on an anniversary basis. Some companies, such as Cisco Systems, end their fiscal year on the same day of the week each year: the day ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
OMB A-133 Compliance Supplement
The OMB A-133 Compliance Supplement is a large and extensive United States federal government guide created by the Office of Management and Budget (OMB) and used in auditing federal assistance and federal grant programs, as well as their respective recipients. It is considered to be the most important tool of an auditor for a Single Audit. It was created following amendments in 1996 to the Single Audit Act based on numerous studies performed by the Government Accountability Office, the President's Council on Integrity and Efficiency and the National State Auditors Association (NSAA). It serves to identify existing important compliance requirements that the Federal Government expects to be considered as part of a Single Audit. Without it, auditors would need to research many laws and regulations for each single program of a recipient to determine which compliance requirements are important to the Federal Government. For Single Audits, the Supplement replaces any agency audit guides ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Non-profit Organization
A nonprofit organization (NPO) or non-profit organisation, also known as a non-business entity, not-for-profit organization, or nonprofit institution, is a legal entity organized and operated for a collective, public or social benefit, in contrast with an entity that operates as a business aiming to generate a profit for its owners. A nonprofit is subject to the non-distribution constraint: any revenues that exceed expenses must be committed to the organization's purpose, not taken by private parties. An array of organizations are nonprofit, including some political organizations, schools, business associations, churches, social clubs, and consumer cooperatives. Nonprofit entities may seek approval from governments to be tax-exempt, and some may also qualify to receive tax-deductible contributions, but an entity may incorporate as a nonprofit entity without securing tax-exempt status. Key aspects of nonprofits are accountability, trustworthiness, honesty, and openness to eve ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Local Government In The United States
Local government in the United States refers to governmental jurisdictions below the level of the state. Most states and territories have at least two tiers of local government: counties and municipalities. Louisiana uses the term parish and Alaska uses the term borough for what the U.S. Census Bureau terms county equivalents in those states. Civil townships or towns are used as subdivisions of a county in 20 states, mostly in the Northeast and Midwest. Depending on the state, local governments may operate under their own charters or under general law, or a state may have a mix of chartered and general-law local governments. Generally, in a state having both chartered and general-law local governments, the chartered local governments have more local autonomy and home rule. Municipalities are typically subordinate to a county government, with some exceptions. Certain cities, for example, have consolidated with their county government as consolidated city-counties. In Virginia, citi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
States Of The United States
In the United States, a state is a Federated state, constituent political entity, of which there are 50. Bound together in a political union, each state holds governmental jurisdiction over a separate and defined geographic territory where it shares its sovereignty with the Federal government of the United States, federal government. Due to this shared sovereignty, Americans are Citizenship in the United States, citizens both of the federal republic and of the Domicile (law)#United States, state in which they reside. State citizenship and residency are flexible, and no government approval is required to Freedom of movement under United States law, move between states, except for persons restricted by certain types of court orders (such as paroled convicts and children of divorced spouses who share child custody). State governments of the United States, State governments in the U.S. are allocated power by the people (of each respective state) through their individual State cons ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Value Engineering
Value engineering (VE) is a systematic analysis of the functions of various components and materials to lower the cost of goods, products and services with a tolerable loss of performance or functionality. Value, as defined, is the ratio of function to cost. Value can therefore be manipulated by either improving the function or reducing the cost. It is a primary tenet of value engineering that basic functions be preserved and not be reduced as a consequence of pursuing value improvements. The term "value management" is sometimes used as a synonym of "value engineering", and both promote the planning and delivery of projects with improved performance The reasoning behind value engineering is as follows: if marketers expect a product to become practically or stylistically obsolete within a specific length of time, they can design it to only last for that specific lifetime. The products could be built with higher-grade components, but with value engineering they ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
OMB Circular A-130
OMB Circular A-130, titled Managing Information as a Strategic Resource, is one of many Government circulars produced by the United States Federal Government to establish policy for executive branch departments and agencies. Circular A-130 was first issued in December 1985 to meet information resource management requirements that were included in the Paperwork Reduction Act (PRA) of 1980. Specifically, the PRA assigned responsibility to the OMB Director to develop and maintain a comprehensive set of information resources management policies for use across the Federal government, and to promote the application of information technology to improve the use and dissemination of information in the operation of Federal programs.(See "Background" section of Circular's Transmittal Memorandum No. 2 for brief historical information/ref> The initial release of the Circular provided a policy framework for information resources management (IRM) across the Federal government. Since the time of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
OMB Circular A-126
OMB Circular A-126, revised May 22, 1992, is a Government circular that introduces standards and policies to minimize the cost and improve the management and use of United States Government aircraft. Specifically, OMB Circular A-126 addresses the acquisition, management, usage, cost accounting, and disposal of government aircraft. All policies presented by this circular apply to Executive Agencies, with special policy covering the travel by senior officials or non-Federal travelers on government aircraft that is government-owned, leased, chartered or rented and any related services that apply. The only exceptions are aircraft that is in use by or in support of the President or Vice President of the United States The Office of Management and Budget was created in 1921 under the authority of the Budget and Accounting Act, revised in 1950 as the Budget and Accounting Procedures Act; again in 1970 as Reorganization Plan No. 2; as Executive Order 11541 and . Use and travel on governme ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Internal Control
Internal control, as defined by accounting and auditing, is a process for assuring of an organization's objectives in operational effectiveness and efficiency, reliable financial reporting, and compliance with laws, regulations and policies. A broad concept, internal control involves everything that controls risks to an organization. It is a means by which an organization's resources are directed, monitored, and measured. It plays an important role in detecting and preventing fraud and protecting the organization's resources, both physical (e.g., machinery and property) and intangible (e.g., reputation or intellectual property such as trademarks). At the organizational level, internal control objectives relate to the reliability of financial reporting, timely feedback on the achievement of operational or strategic goals, and compliance with laws and regulations. At the specific transaction level, internal controls refers to the actions taken to achieve a specific objective (e.g., ho ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |

%2C_USA_-_Air_Force_AN0786861.jpg)