|
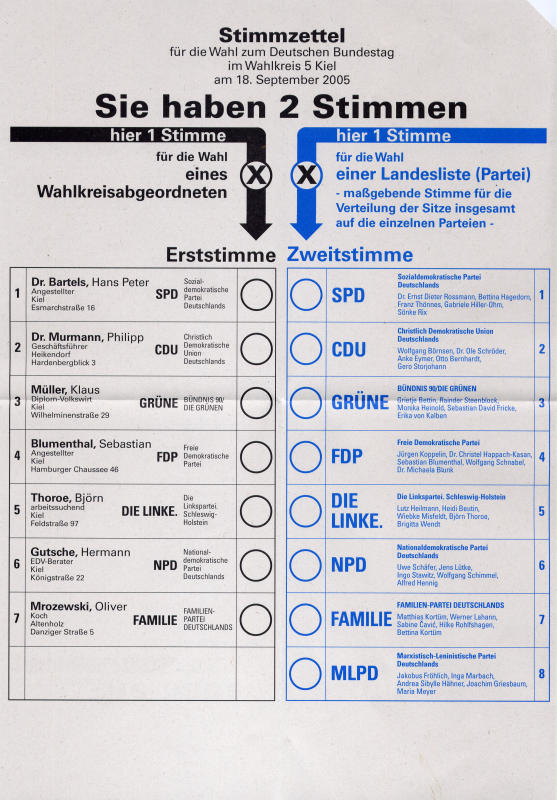
List System
A party-list system is a type of electoral system that formally involves political parties in the electoral process, usually to facilitate multi-winner elections. In party-list systems, parties put forward a list of candidates, the party-list who stand for election on one ticket. Voters can usually vote directly for the party-list, but in other systems voters may vote for directly individuals candidates within or across party lists (such systems are referred to as open list and panachage), besides or instead of voting directly for parties (mixed electoral systems). Most commonly, party-list systems refer to party-list proportional representation, but there are other electoral systems using party-lists including the general ticket (party block voting) and mixed electoral systems. Not only are not all party-list systems proportional, not all proportional systems are party-list systems. Candidates who won their seats from a party-list are called list MPs. Types party-list systems ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Electoral System
An electoral system or voting system is a set of rules that determine how elections and Referendum, referendums are conducted and how their results are determined. Electoral systems are used in politics to elect governments, while non-political elections may take place in business, Nonprofit organization, non-profit organisations and informal organisations. These rules govern all aspects of the voting process: when elections occur, suffrage, who is allowed to vote, who can stand as a candidate, voting method, how ballots are marked and cast, how the ballots are counted, how votes translate into the election outcome, limits on campaign finance, campaign spending, and other factors that can affect the result. Political electoral systems are defined by constitutions and electoral laws, are typically conducted by election commissions, and can use multiple types of elections for different offices. Some electoral systems elect a single winner to a unique position, such as prime ministe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Plurality Voting
Plurality voting refers to electoral systems in which a candidate, or candidates, who poll more than any other counterpart (that is, receive a plurality), are elected. In systems based on single-member districts, it elects just one member per district and may also be referred to as first-past-the-post (FPTP), single-member plurality (SMP/SMDP), single-choice voting (an imprecise term as non-plurality voting systems may also use a single choice), simple plurality or relative majority (as opposed to an ''absolute majorit''y, where more than half of votes is needed, this is called ''majority voting''). A system which elects multiple winners elected at once with the plurality rule, such as one based on multi-seat districts, is referred to as plurality block voting. Plurality voting is distinguished from ''majority voting'', in which a winning candidate must receive an absolute majority of votes: more than half of all votes (more than all other candidates combined if each voter ha ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Electoral District
An electoral district, also known as an election district, legislative district, voting district, constituency, riding, ward, division, or (election) precinct is a subdivision of a larger state (a country, administrative region, or other polity) created to provide its population with representation in the larger state's legislative body. That body, or the state's constitution or a body established for that purpose, determines each district's boundaries and whether each will be represented by a single member or multiple members. Generally, only voters (''constituents'') who reside within the district are permitted to vote in an election held there. District representatives may be elected by a first-past-the-post system, a proportional representative system, or another voting method. They may be selected by a direct election under universal suffrage, an indirect election, or another form of suffrage. Terminology The names for electoral districts vary across countries and, oc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Outline Of Democracy
The following outline is provided as an overview of and topical guide to democracy. Democracy – form of government which allows people to participate equally—either directly or through elected representatives—in the proposal, development, and creation of laws.Larry Jay Diamond, Marc F. Plattner (2006)Electoral systems and democracyp.168. Johns Hopkins University Press, 2006. Nature of democracy Democracy can be described as a(n): * Institution – structure or mechanism of social order and cooperation governing the behavior of a set of individuals within a given human community. Institutions are identified with a social purpose and permanence, transcending individual human lives and intentions, and with the making and enforcing of rules governing cooperative human behavior. ** Government – the legislators, administrators, and arbitrators in the bureaucracy who control a state at a given time and to the system of government by which they are organize ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Comparison Of Electoral Systems
Electoral systems are the rules for conducting elections, a main component of which is the algorithm for determining the winner (or several winners) from the ballots cast. This article discusses methods and results of comparing different electoral systems, both those which elect a unique candidate in a 'single-winner' election and those which elect a group of representatives in a multiwinner election. There are 4 main types of reasoning which have been used to try to determine the best voting method: # Argument by example # Adherence to logical criteria # Results of simulated elections # Results of real elections Expert opinions on single-winner voting methods In 2010, a panel of 22 experts on voting procedures were asked: "What is the best voting rule for your town to use to elect the mayor?". One member abstained. Approval voting was used to decide between 18 single-winner voting methods. The ranking (with number ''N'' of approvers from a maximum of 21) of the various syst ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Electoral Systems By Country
This is a list of electoral systems by country in alphabetical order. An electoral system is used to elect national legislatures and heads of state. Maps Electoral systems by country Key Type of system type of representation: single winner (single office, e.g. FPTP, TRS), majoritarian (body elected in winner-take-all districts e.g. FPTP, TRS, block voting), proportional (body elected by STV/party-list PR), mixed (combination of majoritarian+proportional), semi-proportional (e.g. SNTV, LV), indirect (by legislature(s) and/or electoral college), no election (chosen by a single person, or other rules e.g. hereditary) ; Seats per district: Most elections are split into a number of electoral districts. In some elections, there is one person elected per district. In others, there are many people elected per district. Electoral districts can have different names, see list of electoral districts by nation. ; Total number of seats: the number of representatives elected to the b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Election
An election is a formal group decision-making process by which a population chooses an individual or multiple individuals to hold public office. Elections have been the usual mechanism by which modern representative democracy has operated since the 17th century. Elections may fill offices in the legislature, sometimes in the executive and judiciary, and for regional and local government. This process is also used in many other private and business organisations, from clubs to voluntary associations and corporations. The global use of elections as a tool for selecting representatives in modern representative democracies is in contrast with the practice in the democratic archetype, ancient Athens, where the elections were considered an oligarchic institution and most political offices were filled using sortition, also known as allotment, by which officeholders were chosen by lot. Electoral reform describes the process of introducing fair electoral systems wher ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Double Simultaneous Vote
Double simultaneous vote (DSV) is an electoral system in which multiple offices – such as the president and members of a legislature – are elected through a single vote cast for a party. It can be combined with other electoral systems; in Uruguay DSV is used to elect the president and members of the Senate and Chamber of Representatives, with the presidential election also using the two-round system; if no party/presidential candidate receives a majority of the vote, a second round is held for the presidential election. The initial republican constitutions of several countries in the Commonwealth of Nations, such as Kenya, Guyana and Zambia, provided for presidential elections by double simultaneous vote. Occasionally, as in Tanganyika, a variant was used whereby the candidate who won a majority of ''constituencies'' (as opposed to a plurality of votes) would be elected. Some Latin American countries used a DSV variant known as ''Ley de Lemas ''Ley de Lemas'' is a form of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mixed Ballot Transferable Vote
The mixed ballot transferable vote (MBTV) refers to a type of vote linkage-based mixed-member electoral system where a group of members are elected on local (lower) tier, for example in single-member districts (SMDs). Other members are elected on a compensatory national (upper) tier from a list and voters cast a single ballot where they may indicate their preferences separately.https://doi.org/10.13140/RG.2.2.15129.34407 Electoral incentives and the equal value of ballots in vote transfer systems with positive winner compensation This article is primarily about systems using mixed ballots, for the dual vote, hybrid versions of parallel voting and MSV used in Hungary and formerly used in Italy for national elections see Scorporo. Overview Unused votes from the lower tier are counted on the upper tier in a compensatory way using a (partial, positive) vote transfer mechanism. This tied, preferential nature of the dual ballot makes it different from mixed-member proportional (seat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ley De Lemas
''Ley de Lemas'' is a form of the double simultaneous vote (DSV) electoral system which is, or has been, used in elections in Argentina, Uruguay, and Honduras. It is an unusual variant of open list proportional representation, and works as follows: *Each political party (or coalition, if permitted) is formally termed a ''lema''. *Each ''lema'' might have several ''sublemas'' (candidates or lists of candidates). The actual composition of these ''sublemas'' can vary: it can be simply a pair of candidates (for election to the posts of governor and vice-governor, for example), or an ordered list of candidates to fill the seats in a legislative body. *Each party can present several ''sublemas'' to the main election. *The winning party is the one which receives the most votes after the votes won by each of its ''sublemas'' have been added together. Within this party, the winning ''sublema'' is the one which, individually, won the most votes. Once the number of votes received by each ''l ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Localized List
A localized list or local list is a technique used under systems of party-list proportional representation to determine which party candidates are elected from the party list. Local lists differ from open lists or closed lists. As with open lists, local lists allow the electorate to vote for individual candidates, but that preference is expressed through local or district level election processes. Closed lists do not allow voters to express such a preference. Voters vote only for the party. Voting in local list systems takes place at the district level, where each party is represented by a single candidate. In this, the system resembles first-past-the-post or other single-winner systems. However, the candidate with the largest number of votes in a district is not necessarily the one that is elected. This is because of the proportionality requirement of the system. To ensure that each party receives a proportional share of seats relative to its share of the popular vote, the firs ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |