|
List Of Works By Joseph Priestley
Joseph Priestley (1733–1804) was a British natural philosopher, Dissenting clergyman, political theorist, theologian, and educator. He is best known for his discovery, simultaneously with Antoine Lavoisier, of oxygen gas. A member of marginalized religious groups throughout his life and a proponent of what was called "rational Dissent," Priestley advocated religious toleration and equal rights for Dissenters. He argued for extensive civil rights in works such as the important ''Essay on the First Principles of Government'', believing that individuals could bring about progress and eventually the Millennium; he was the foremost British expounder of providentialism.Tapper, Alan. "Joseph Priestley." ''Dictionary of Literary Biography'' 252: ''British Philosophers 1500–1799''. Eds. Philip B. Dematteis and Peter S. Fosl. Detroit: Gale Group (2002), 314. Priestley also made significant contributions to education, publishing, among other things, ''The Rudiments of English Grammar'', ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Liberal Arts
Liberal arts education (from Latin "free" and "art or principled practice") is the traditional academic course in Western higher education. ''Liberal arts'' takes the term ''art'' in the sense of a learned skill rather than specifically the fine arts. ''Liberal arts education'' can refer to studies in a liberal arts degree course or to a university education more generally. Such a course of study contrasts with those that are principally vocational, professional, or technical. History Before they became known by their Latin variations (, , ), the liberal arts were the continuation of Ancient Greek methods of enquiry that began with a "desire for a universal understanding." Pythagoras argued that there was a mathematical and geometrical harmony to the cosmos or the universe; his followers linked the four arts of astronomy, mathematics, geometry, and music into one area of study to form the "disciplines of the mediaeval quadrivium". In 4th-century B.C.E. Athens, the governmen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
John Palmer (Unitarian, 1742–1786)
John Palmer (1742–1786) was an English Unitarian minister. Life The son of John Palmer, wig-maker, he was born at Norwich. He was a protégé of John Taylor, who began his education, and, on becoming divinity tutor at Warrington Academy, placed Palmer (1756) at school in Congleton, Cheshire, under Edward Harwood. He entered Warrington Academy in 1759; Joseph Priestley was, from 1761, one of his tutors. In his last year he was constant supply (14 May 1763 to 15 August 1764) at Allostock, Cheshire. He then kept a school at Macclesfield, Cheshire. In 1772 he became minister of King Edward Street Chapel, Macclesfield. There was an orthodox secession from his ministry; he consequently resigned in 1779, and moved to Birmingham without regular charge, being in independent circumstances. At Birmingham he renewed his acquaintance with Priestley, and was a member of a fortnightly clerical club which arranged the material for the ''Theological Repository''. In 1782 Priestley recommen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Theological Repository
The ''Theological Repository'' was a periodical founded and edited from 1769 to 1771 by the eighteenth-century British polymath Joseph Priestley. Although ostensibly committed to the open and rational inquiry of theological questions, the journal became a mouthpiece for Dissenting, particularly Unitarian and Arian, doctrines. Priestley promised to print all viewpoints, but only like-minded authors ever submitted articles. He was therefore forced to provide much of the journal's content himself. After only a few years, due to a lack of funds, he was forced to cease publishing the journal. About a decade later, in 1784, Priestley revived the ''Theological Repository'', but he again became responsible for much of the journal's content and again the journal became insolvent after several issues (1784, 1786, 1788). Joseph Johnson, Priestley's close friend and publisher, was responsible for issuing the journal. Dedicated to the Unitarian cause, he bore much of the financial burden o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Priestley
Priestley may refer to: Places * Priestley, West Virginia, US, an unincorporated community * Priestley Glacier, a major valley glacier in Antarctica * Priestley (lunar crater), on the far side of the Moon * Priestley (Martian crater) * 5577 Priestley, an inner main belt asteroid People Arts * Alice Priestley (born 1962), Canadian children's writer and illustrator * Brian Priestley (born 1940), English jazz writer, pianist and arranger * Chris Priestley (born 1958), British children's book author and illustrator * Jason Priestley (born 1969), Canadian-American actor * J. B. Priestley (1894–1984), English writer and broadcaster * Mark Priestley (1976–2008), Australian actor *Rick Priestley (born 1959), British miniature wargame designer and author * Robert Priestley (1901–1986), American set decorator * Tom Priestley (born 1932), sound and film editor Sciences * Henry Priestley (biochemist) (1884–1961), Australian biochemist * Hilary Priestley, British mathema ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Edward Burn
Edward Burn (1762–1837) was an English cleric, known as a Calvinist Methodist preacher and polemical writer. Life Born on 29 November 1762, Burn was educated for the ministry at Trevecca College. He was ordained orders and obtained a curacy in Birmingham, with John Riland, a Wesleyan and first incumbent at St Mary's Chapel; built 1772–4, it was a new, octagonal evangelical foundation, with Mary Weaman as patron. With Riland, Burn reprinted some religious texts. Burn also began to preach in venues used by dissenters. In 1786 John Wesley visited St Mary's and enjoyed a sermon, by one of Burn and Riland. Burn then entered St Edmund Hall, Oxford, and graduated B.A. on 20 February 1790, M.A. on 22 June 1791. He returned to Birmingham to take over at St Mary's. He was known as a preacher for extemporary oratory. He retained this position till his death. He was one of the founders of the Birmingham Association of the Church Missionary Society, and its first secretary. He came ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
An History Of The Corruptions Of Christianity
''An History of the Corruptions of Christianity'', published by Joseph Johnson in 1782, was the fourth part of 18th-century Dissenting minister Joseph Priestley's ''Institutes of Natural and Revealed Religion'' (1772–74). Summary Priestley's major argument in the ''Institutes'' is that the only revealed religious truths that can be accepted are those that also conform to the truth of the natural world. Because his views of religion were deeply tied to his understanding of nature, the text's theism rests on the argument from design. Many of Priestley's arguments descended from 18th-century deism and comparative religion. The ''Institutes'' shocked and appalled many readers, primarily because it challenged basic Christian orthodoxies, such as the divinity of Christ and the miracle of the Virgin Birth. Priestley wanted to return Christianity to its "primitive" or "pure" form by eliminating the "corruptions" which had accumulated over the centuries. The fourth part of the ''Ins ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Institutes Of Natural And Revealed Religion
The ''Institutes of Natural and Revealed Religion'', written by 18th-century English Dissenting minister and polymath Joseph Priestley, is a three-volume work designed for religious education published by Joseph Johnson between 1772 and 1774. Its central argument is that revelation and natural law must coincide. Overview The ''Institutes'', published as part of a series of works on religious education, was "a summary of a half-century of the writing of liberal theologians on a number of issues and was to become a standard exposition of beliefs for generations of Unitarians." Priestley's major argument is that only revealed religious truths which conform to the truth of the natural world should be accepted. Because his views of religion were deeply tied to his understanding of nature, the text's theism rests on the argument from design. Many of Priestley's arguments descended from 18th-century deism and comparative religion. Priestley wanted to return Christianity to its "primi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Phlogiston Theory
The phlogiston theory is a superseded scientific theory that postulated the existence of a fire-like element called phlogiston () contained within combustible bodies and released during combustion. The name comes from the Ancient Greek (''burning up''), from (''flame''). The idea was first proposed in 1667 by Johann Joachim Becher and later put together more formally by Georg Ernst Stahl. Phlogiston theory attempted to explain chemical processes such as combustion and rusting, now collectively known as oxidation. It was challenged by the concomitant weight increase, and was abandoned before the end of the 18th century following experiments by Antoine Lavoisier and others. Phlogiston theory led to experiments which ultimately concluded with the discovery of oxygen. Theory Phlogiston theory states that ''phlogisticated'' substances contain phlogiston and that they ''dephlogisticate'' when burned, releasing stored phlogiston which is absorbed by the air. Growing plants then absor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
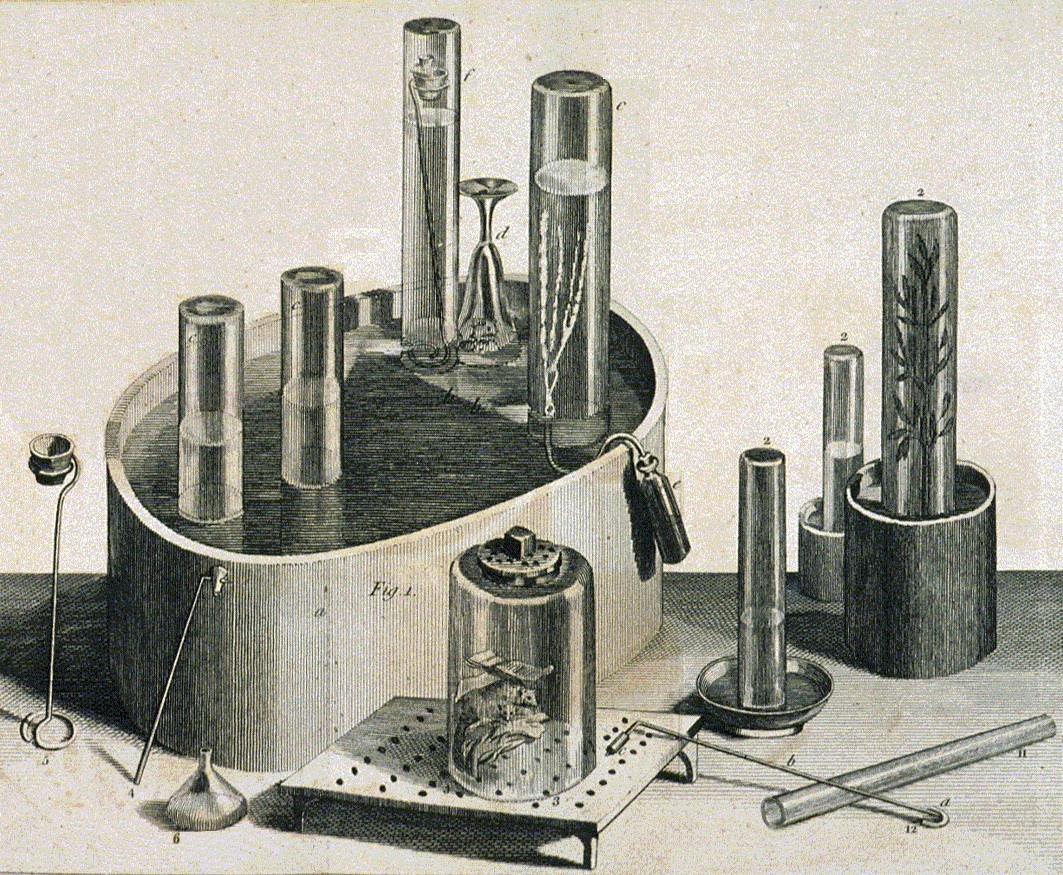
Experiments And Observations On Different Kinds Of Air
''Experiments and Observations on Different Kinds of Air'' (1774–86) is a six-volume work published by 18th-century British polymath Joseph Priestley which reports a series of his experiments on "airs" or gases, most notably his discovery of oxygen gas (which he called "dephlogisticated air"). Airs While working as a companion for Lord Shelburne, Priestley had a great deal of free time to engage in scientific investigations. The Earl even set up a laboratory for him. Priestley's experiments during his years in Calne were almost entirely confined to "airs" and from this work emerged his most important scientific texts: the six volumes of ''Experiments and Observations on Different Kinds of Air''. These experiments helped repudiate the last vestiges of the theory of four elements; as one early biographer writes: "taken collectively, riestleydid more than those of any one of his contemporaries to uproot and destroy the only generalisation by which his immediate predecessors had ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |