|
List Of Stars In Phoenix ...
This is the list of stars in the constellation Phoenix. See also *List of stars by constellation References * * * * * * {{Stars of Phoenix *List Phoenix Phoenix most often refers to: * Phoenix (mythology), a legendary bird from ancient Greek folklore * Phoenix, Arizona, a city in the United States Phoenix may also refer to: Mythology Greek mythological figures * Phoenix (son of Amyntor), a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Star
A star is an astronomical object comprising a luminous spheroid of plasma (physics), plasma held together by its gravity. The List of nearest stars and brown dwarfs, nearest star to Earth is the Sun. Many other stars are visible to the naked eye at night sky, night, but their immense distances from Earth make them appear as fixed stars, fixed points of light. The most prominent stars have been categorised into constellations and asterism (astronomy), asterisms, and many of the brightest stars have proper names. Astronomers have assembled star catalogues that identify the known stars and provide standardized stellar designations. The observable universe contains an estimated to stars. Only about 4,000 of these stars are visible to the naked eye, all within the Milky Way galaxy. A star's life star formation, begins with the gravitational collapse of a gaseous nebula of material composed primarily of hydrogen, along with helium and trace amounts of heavier elements. Its stellar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Beta Phoenicis
Beta Phoenicis (β Phoenicis, β Phe) is a binary star in the constellation Phoenix. Its apparent magnitude is 3.30, meaning that it can be seen with the naked eye ''(see Bortle scale)''. The distance to Beta Phoenicis is poorly known. The original reduction of the Hipparcos satellite's data yielded a parallax value of 16 milliarcseconds, yet its standard error was larger than the parallax value itself. The new reduction of the Hipparcos data gave 0.12 ± 14.62 milliarcseconds, still unusable. The General Catalogue of Trigonometric Parallaxes, an older catalogue of ground-based parallaxes, lists the parallax as 20 ± 16 milliarcseconds, corresponding to about . Beta Phoenicis is a relatively wide visual binary consisting of two G-type giant stars, both with spectral type In astronomy, stellar classification is the classification of stars based on their spectral characteristics. Electromagnetic radiation from the star is analyzed by splitting it with a prism or ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lambda1 Phoenicis
λ1 Phoenicis, Latinized as Lambda1 Phoenicis, is a double star in the southern constellation of Phoenix. It is visible to the naked eye as a faint, white-hued point of light with a combined apparent visual magnitude of 4.76. The system is located approximately 183 light years away from the Sun based on parallax. It is a member of the Hyades Supercluster. The brighter component is an A-type main-sequence star with a stellar classification of A0Va. It may form a binary system of two roughly equal stars. An infrared excess suggests there is a debris disk A debris disk (American English), or debris disc (Commonwealth English), is a circumstellar disk of dust and debris in orbit around a star. Sometimes these disks contain prominent rings, as seen in the image of Fomalhaut on the right. Debris di ... orbiting from the star with a mean temperature of 95 K. It has one visual companion at an angular separation of about and magnitude 13.7. References ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
HD 222095
HD 222095 is a single star in the southern constellation of Phoenix, near the western constellation border with Grus. It has a white hue and is visible to the naked eye with an apparent visual magnitude of 4.74. The star is located at a distance of is approximately 200 light years based on parallax, and it is drifting further away with a radial velocity of +3.4 km/s. This object is an A-type main-sequence star with a stellar classification of A1/2V. It has a high rate of spin with a projected rotational velocity of 141 to 165 km/s, giving it an equatorial bulge that is 4% larger than the polar radius. The star is 482 million years old with 2.55 times the mass of the Sun and around 2.2 times the Sun's radius. It is radiating 41 times the luminosity of the Sun from its photosphere at an effective temperature The effective temperature of a body such as a star or planet is the temperature of a black body that would emit the same total amount of electroma ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
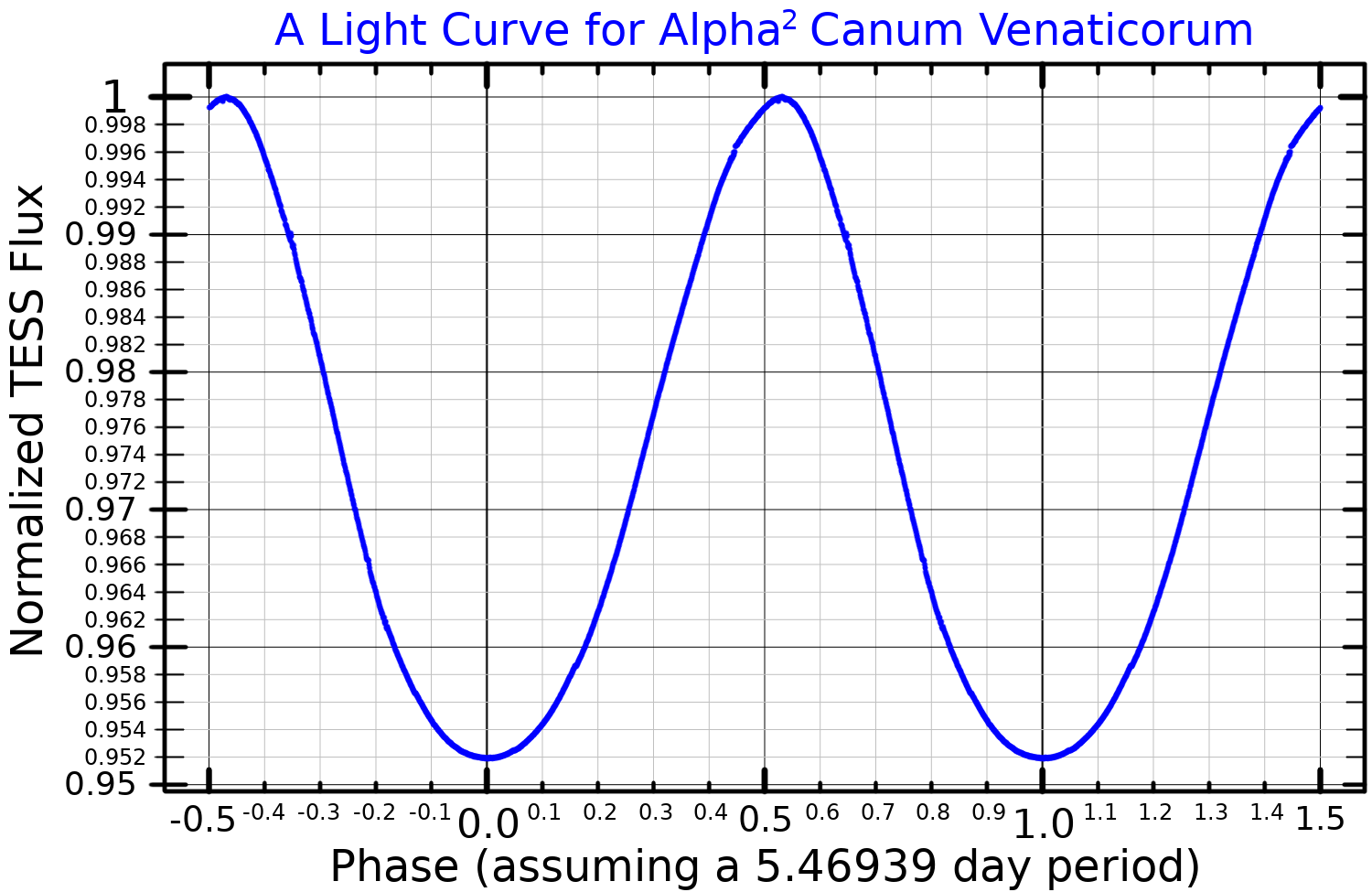
Alpha2 Canum Venaticorum Variable
An Alpha2 Canum Venaticorum variable (or α2 CVn variable) is a type of variable star. These stars are chemically peculiar star, chemically peculiar main sequence stars of stellar classification, spectral class B8p to A7p. They have strong magnetic fields and strong silicon, strontium, or chromium spectral lines. Their brightness typically varies by 0.01 to 0.1 Apparent magnitude, magnitudes over the course of 0.5 to 160 days. In addition to their intensities, the intensities and profiles of the spectral lines of α2 CVn variables also vary, as do their magnetic fields. The periods of these variations are all equal and are believed to equal the period of rotation of the star. It is thought that they are caused by an inhomogeneous distribution of metals in the atmospheres of these stars, so that the surface of the star varies in brightness from point to point. The type-star which this class is named after is Cor_Caroli#α2_Canum_Venaticorum, α² Canum Venaticorum, a star in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Iota Phoenicis
ι Phoenicis, Latinized as Iota Phoenicis, is a binary star system in the southern constellation of Phoenix, near the constellation border with Grus. It is visible to the naked eye as a faint, white-hued star with an apparent visual magnitude that fluctuates around 4.71. This system lies approximately 254 light years from the Sun based on parallax, and it is drifting further away with a radial velocity of +19.4 km/s. The primary component is an Ap star on the main sequence with a stellar classification of A2VpSrCrEu, where the suffix notation indicates abnormal abundances of strontium, chromium, and europium in the stellar atmosphere. It is an Alpha2 Canum Venaticorum variable; its apparent magnitude varies from 4.70 down to 4.75 with a period of 12.5 days. A rotationally-modulated magnetic field has been measured, varying from to . It has an estimated rotation period of , although this is in need of further confirmation. The proper motion companion is a mag ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mu Phoenicis
μ Phoenicis, Latinized as Mu Phoenicis, is a suspected astrometric binary star system in the southern constellation of Phoenix. It is visible to the naked eye as a faint, yellow-hued star with an apparent visual magnitude of 4.59. This system is located approximately 246 light years distant from the Sun based on parallax, and is drifting further away with a radial velocity of +17.4 km/s. The visible component is an aging G-type giant star with a stellar classification of G8III. Having exhausted the supply of hydrogen at its core, this star cooled and expanded off the main sequence. At present it has 13 times the girth of the Sun. It is 1.4 billion years old with 2.5 times the mass of the Sun. It is radiating 97 times the luminosity of the Sun The solar luminosity (), is a unit of radiant flux ( power emitted in the form of photons) conventionally used by astronomers to measure the luminosity of stars, galaxies and other celestial objects in ter ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Semiregular Variable
In astronomy, a semiregular variable star, a type of variable star, is a giant or supergiant of intermediate and late (cooler) spectral type showing considerable periodicity in its light changes, accompanied or sometimes interrupted by various irregularities. Periods lie in the range from 20 to more than 2000 days, while the shapes of the light curves may be rather different and variable with each cycle. The amplitudes may be from several hundredths to several magnitudes (usually 1-2 magnitudes in the V filter). Classification The semiregular variable stars have been sub-divided into four categories for many decades, with a fifth related group defined more recently. The original definitions of the four main groups were formalised in 1958 at the tenth general assembly of the International Astronomical Union (IAU). The General Catalogue of Variable Stars (GCVS) has updated the definitions with some additional information and provided newer reference stars where old examples such ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Psi Phoenicis
Psi Phoenicis (ψ Phoenicis) is a star in the constellation Phoenix (constellation), Phoenix. Its apparent magnitude varies from 4.3 to 4.5 with a period of about 30 days and it is approximately 342 light years away based on parallax. Psi Phoenicis is a red giant in the asymptotic giant branch, asymptotic branch with a spectral type of M4III, indicating it is an evolved star in the last stellar evolution, evolutionary stage before becoming a white dwarf. In 1973 astronomer Olin J. Eggen discovered it is a variable star, varying in magnitude between 4.3 and 4.5 with an approximate period of 30 days. A more recent study identified two possible periods of 43.7 and 48.1 days, with amplitudes of 0.038 and 0.023 magnitudes. The star is classified as a semiregular variable, of no specific subtype. In 2001, Psi Phoenicis was observed by the VLTI, VLT Interferometer with the test instrument VINCI. The observations, in combination with stellar atmospheric models, detected the limb ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eta Phoenicis
Eta Phoenicis (η Phe) is a class A0IV (white subgiant) star in the constellation Phoenix. Its apparent magnitude is 4.36 and it is approximately 246 light years away based on parallax. Eta Phoenicis has two reported companions; in addition to a distant secondary, B, at magnitude 11.5 and separation 20", the primary has a reported companion Ab with an estimated separation of 6.8 AU, a period slightly longer than 10 years, a magnitude of 8.5, and a spectral type around G5V. The primary is surrounded by an orbiting debris disk. References Phoenix (constellation) A-type subgiants Phoenicis, Eta Binary stars 003405 0191 0191 is the UK telephone dialling code used by Newcastle, Durham, Sunderland and other nearby areas in the north east of England. Areas covered Numbering in the 0191 area is officially divided into three distinct areas, each with their own batc ... 004150 Durchmusterung objects {{multi-star-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Zeta Phoenicis
Zeta Phoenicis (ζ Phoenicis, abbreviated Zet Phe, ζ Phe) is a multiple star system in the constellation of Phoenix. It is visible to the naked eye. Based upon parallax measurements made by the Hipparcos spacecraft, it is located some away. Zeta Phoenicis A is itself an Algol-type eclipsing binary star. It consists of two B-type main sequence stars that orbit each other. The larger and brighter (Zeta Phoenicis Aa) is formally named Wurren . When one passes in front of one another, it blocks some of the other star's light. As a result, its apparent magnitude fluctuates between 3.9 and 4.4 with a period of 1.6697739 days (its orbital period). The system most likely contains four stars with two other telescopic components of apparent magnitude 7.2 and 8.2 at angular separations of 0.8 and 6.4 arcseconds from the main pair. The closer (Zeta Phoenicis B) is an A-type main-sequence star with an orbital period around the main pair of about 210 years, as well as an eccentric ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Delta Phoenicis
Delta Phoenicis, Latinized from δ Phoenicis, is a single, yellow-hued star in the southern constellation of Phoenix. With an apparent visual magnitude of 3.93, it is visible to the naked eye. Based upon an annual parallax shift of 22.95 mas as seen from Earth, it is located 142 light years from the Sun. The star is moving closer to the Sun with a radial velocity of −7 km/s. This is a G-type giant star with a stellar classification of G8.5 IIIb. It is a red clump star, which means it has reached the stage of its evolution where it is generating energy through helium fusion at its core. The measured angular diameter of this star, after correction for limb darkening, is . At its estimated distance, this yields a physical size of about 10.5 times the radius of the Sun.. The radius (R*) is given by: :\begin 2\cdot R_* & = \frac \\ & \approx 21\cdot R_ \end It is around 3.7 billion years old with 1.46 times the mass of the Sun. The star is radiating ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |