|
List Of Russian Weaponry
The following is a list of modern Russian small arms and light weapons which were in service in 2016: Handguns Revolvers Pistols Special purpose Submachine guns Special purpose Shotguns Rifles Bolt-action Semi-automatic Selective-fire Special purpose Anti-materiel rifles Machine guns Squad automatic weapons (SAWs) General-purpose Heavy Hand grenades Fragmentation Anti-tank Grenade launchers Stand-alone Attached Automatic grenade launchers Rocket launchers General purpose Incendiary and thermobaric Special purpose Recoilless rifles Mortars Anti-tank guided missiles Man-portable air defense system Landmines See also * List of equipment of the Russian Ground Forces * List of Russian weaponry makers References {{DEFAULTSORT:Russian small arms and light weapons Weapons of Russia Lists of weapons Firearms of Russia, Russian and Soviet milita ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
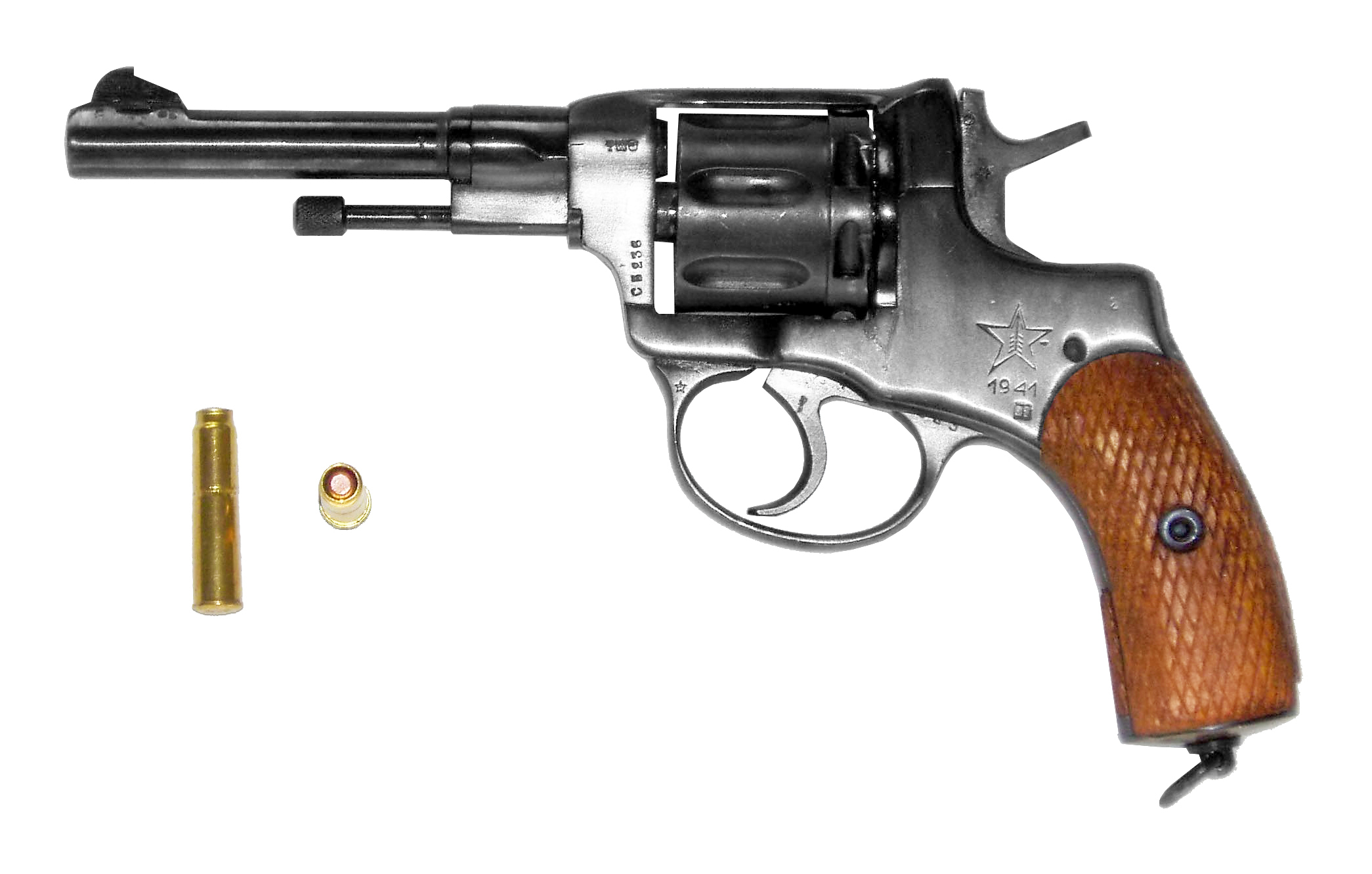
Nagant M1895
The Nagant M1895 Revolver is a seven-shot, gas-seal revolver designed and produced by Belgian industrialist Léon Nagant for the Russian Empire. The Nagant M1895 was chambered for a proprietary cartridge, 7.62×38mmR, and featured an unusual "gas-seal" system, in which the cylinder moved forward when the gun was cocked, to close the gap between the cylinder and the barrel, providing a boost to the muzzle velocity of the bullet and allowing the weapon to be suppressed (an unusual characteristic for a revolver). In fact, a 38mm long shell covers the whole bullet for this very purpose as well. This way, early Nagant users would avoid dealing with gases of black powder. Its design would inspire the Pieper M1893 carbine and Steyr 1893 revolver. Russian M1895 Léon Nagant and his brother Émile were well known in the Russian Tsar's court and military administration because of the part they had played in the design of the Russian service rifle, the Mosin–Nagant Model 1891. The Nag ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
SR-1 Vektor
The SR-1 Vektor also known as the Gyurza (''Гюрза'', Russian for " blunt-nosed viper") or Serdyukov SPS is a 9×21mm Gyurza semi-automatic pistol designed for the Russian military. The firearm is currently produced as the SR1M. Design details The operating system is based on the Beretta 92, utilizing a dropping block. The frame is polymer and steel. While the SR-1 does not have a traditional manual safety, it is equipped with a grip safety that disengages the trigger mechanism, as well as a trigger safety to prevent fire when the trigger is not depressed. Additionally the hammer must also be placed into half-cock to engage the sear and enable double action firing. Users * – Armed Forces of the Kyrgyz RepublicАлександр Ким. Это — спецназ! Отдельная бригада специального назначения Минобороны отметила десятую годовщину своего существования // газета «� ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
MP-443 Grach 06
The MP-443 ''Grach'' (russian: MП-443 Грач, lit=rook) or "PYa", for "''Pistolet Yarygina'' ("Yarygin Pistol"), following traditional Russian naming procedure (russian: Пистолет Ярыгина), is the Russian standard military-issue side arm. The development was headed by the designer . It was developed under designation "'' Grach''" in response to Russian military trials, which began in 1993. In 2003, it was adopted as a standard sidearm for all branches of Russian military and law enforcement, alongside the Makarov PM, GSh-18, and SPS. Design details The PYa is a high-capacity, double-action, short-recoil semi-automatic pistol. Barrel/slide locking is a simplified Colt– Browning design, similar to that found in many modern pistols (for example the SIG Sauer and Glock families of pistols); the breech end of the barrel is rectangular in shape, rather than rounded, and fits into matching locking grooves within the slide, near the ejection port. The slide stop leve ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
MP-446 Viking
The MP-446 Viking is a 9×19mm Parabellum, 9mm Semi-automatic pistol, semi-automatic handgun originating from Russia. Overview It was created by the Izhevsk Mechanical Plant. It weighs at around when unloaded, and has a Magazine (firearms), magazine capacity of 18 rounds. The pistol is a sport/civilian version of MP-443 Grach, Yarygin PYa (MP-443) pistol which has been used by Russian military since 2003. MP-446 is short recoil operation, recoil-operated, locked breech pistol. The key differences between MP-446 and MP-443 are the frame material (polyamide rather than steel) and barrel construction: the barrel of the MP-446 was intentionally weakened to prevent safe use of high-powered armour-piercing military rounds (i.e. Russian 9×19mm Parabellum, 9x19mm 7N21 type, 9x19mm NATO) or civilian "Overpressure ammunition, +P" or "+P+" cartridges. Variants * MP-446 "Viking" (export variant) - with 18-round magazineГалина Валеева. Ещё раз о пистолете � ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
MP-443 Grach
The MP-443 ''Grach'' (russian: MП-443 Грач, lit=rook) or "PYa", for "''Pistolet Yarygina'' ("Yarygin Pistol"), following traditional Russian naming procedure (russian: Пистолет Ярыгина), is the Russian standard military-issue side arm. The development was headed by the designer . It was developed under designation "'' Grach''" in response to Russian military trials, which began in 1993. In 2003, it was adopted as a standard sidearm for all branches of Russian military and law enforcement, alongside the Makarov PM, GSh-18, and SPS. Design details The PYa is a high-capacity, double-action, short-recoil semi-automatic pistol. Barrel/slide locking is a simplified Colt– Browning design, similar to that found in many modern pistols (for example the SIG Sauer and Glock families of pistols); the breech end of the barrel is rectangular in shape, rather than rounded, and fits into matching locking grooves within the slide, near the ejection port. The slide stop leve ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
GSh-18 06
The GSh-18 (Cyrillic: Г Ш-18) is a 9 mm semi-automatic pistol developed by the KBP Instrument Design Bureau in Tula during the 1990s. The pistol's name is derived from its designers—Gryazev and Shipunov—and its magazine capacity of 18 rounds. Design details The GSh-18 is a rotating-barrel, short recoil, locked-breech pistol with 10 locking lugs spaced equally around the barrel, the large locking surface area resulting in a strong lockup, making it suitable for high-velocity ammunition loads. The GSh-18 may be employed using standard 9×19mm Parabellum rounds, but was designed for the high velocity, Russian armour-piercing 9×19mm 7N31 round. The pistol incorporates a pre-set striker. The slide and working parts are steel, and the weapon has a polymer frame. Two different designs of grip have been observed. The magazine capacity is 18 rounds, and an additional round may be carried in the chamber. The magazine release is reversible for left-handed shooters and the ejector d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
GSh-18
The GSh-18 (Cyrillic: Г Ш-18) is a 9 mm semi-automatic pistol developed by the KBP Instrument Design Bureau in Tula during the 1990s. The pistol's name is derived from its designers—Gryazev and Shipunov—and its magazine capacity of 18 rounds. Design details The GSh-18 is a rotating-barrel, short recoil, locked-breech pistol with 10 locking lugs spaced equally around the barrel, the large locking surface area resulting in a strong lockup, making it suitable for high-velocity ammunition loads. The GSh-18 may be employed using standard 9×19mm Parabellum rounds, but was designed for the high velocity, Russian armour-piercing 9×19mm 7N31 round. The pistol incorporates a pre-set striker. The slide and working parts are steel, and the weapon has a polymer frame. Two different designs of grip have been observed. The magazine capacity is 18 rounds, and an additional round may be carried in the chamber. The magazine release is reversible for left-handed shooters and the ejector d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
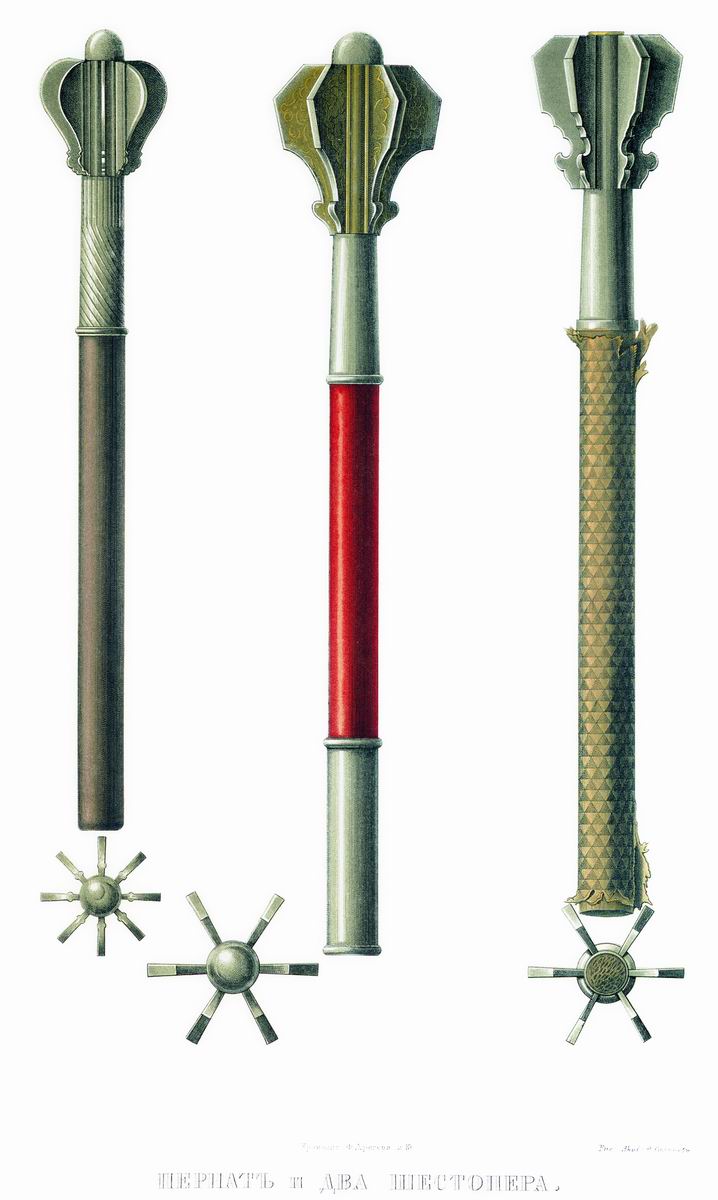
Pernach OTs-33
A pernach (russian: перна́ч, uk, перна́ч or , pl, piernacz) is a type of flanged mace originating in the 12th century in the region of Kievan Rus' and later widely used throughout Europe. The name comes from the Slavic word ''перо'' (''pero'') meaning feather, referring to a type of pernach resembling an arrow with feathering. Among a variety of similar weapons developed in 12th-century Persian- and Turkic-dominated areas, the pernach became pre-eminent, being capable of penetrating plate armour and plate mail. A pernach or shestoper ( uk, шестопeр, "six-feathered") was often carried as a ceremonial mace of rank by certain Eastern European military commanders, including Polish magnates, Ukrainian Cossack colonels and sotniks (cf. centurion). In Ukraine it symbolized the authority of Colonels (polkovnyk, regional leaders or military officers) [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Russian Ministry Of Internal Affairs
The Ministry of Internal Affairs of the Russian Federation (MVD; russian: Министерство внутренних дел (МВД), ''Ministerstvo vnutrennikh del'') is the interior ministry of Russia. The MVD is responsible for law enforcement in Russia through its agencies the Police of Russia, Migration Affairs, Drugs Control, Traffic Safety, the Centre for Combating Extremism, and the Investigative Department. The MVD is headquartered in Zhitnaya Street 16 in Yakimanka, Moscow. The MVD claims ancestry from the Ministry of Internal Affairs of the Russian Empire founded in 1802 by Tsar Alexander I which became the interior ministry of the Russian Republic, the Russian Soviet Federative Socialist Republic, and the Soviet Union. The MVD was dissolved and reformed several times during the Stalin era until being established as the Ministry of Internal Affairs of the USSR in 1946. The current MVD was formed in 1990 from the Russian branch of the MVD of the USSR shortly be ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
OMON
OMON (russian: ОМОН – Отряд Мобильный Особого Назначения , translit = Otryad Mobil'nyy Osobogo Naznacheniya , translation = Special Purpose Mobile Unit, , previously ru , Отряд Милиции Особого Назначения , translit = Otryad Militsii Osobogo Naznacheniya , translation = Special Purpose Unit of the Militia) is a system of special police units within the National Guard of Russia. It previously operated within the structures of the Soviet and Russian Ministries of Internal Affairs (MVD). Originating as the special forces unit of the Soviet Militsiya in 1988, it has played major roles in several armed conflicts during and following the 1991 dissolution of the Soviet Union. OMON is much larger and better known than SOBR, another special-police branch of the National Guard of Russia. In modern contexts, OMON serves as a riot police group, or as a gendarmerie-like paramilitary force. OMON units also exist in Belar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stechkin APS
The Stechkin or APS (''Avtomaticheskiy Pistolet Stechkina'' = ''Автоматический Пистолет Стечкина'') is a Soviet selective fire machine pistol chambered in 9×18mm Makarov and 9×19mm Parabellum introduced into service in 1951 for use with artillery and mortar crews, tank crews and aircraft personnel, where a cumbersome assault rifle was deemed unnecessary. Seeing service in a number of wars such as the Vietnam War, Russo-Ukrainian War and Syrian Civil War. The APS was praised for its innovative concept and good controllability for its size. However, the high cost of the weapon, complex and time-consuming machining, combined with a limited effective range, large size and weight for a pistol, and fragile buttstock have been mentioned as a reason to phase it out of active service in favour of assault rifles such as the AKS-74U. The pistol bears the name of its developer, Igor Stechkin. Adoption and service Submachine guns such as the PPSh-41 or the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |