|
List Of Quasiparticles
This is a list of quasiparticle In physics, quasiparticles and collective excitations are closely related emergent phenomena arising when a microscopically complicated system such as a solid behaves as if it contained different weakly interacting particles in vacuum. For exa ...s. References {{DEFAULTSORT:Quasiparticles Quasiparticles Physics-related lists it:Quasiparticella#Lista delle quasiparticelle ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Quasiparticle
In physics, quasiparticles and collective excitations are closely related emergent phenomena arising when a microscopically complicated system such as a solid behaves as if it contained different weakly interacting particles in vacuum. For example, as an electron travels through a semiconductor, its motion is disturbed in a complex way by its interactions with other electrons and with atomic nuclei. The electron behaves as though it has a different effective mass travelling unperturbed in vacuum. Such an electron is called an ''electron quasiparticle''. In another example, the aggregate motion of electrons in the valence band of a semiconductor or a hole band in a metal behave as though the material instead contained positively charged quasiparticles called ''electron holes''. Other quasiparticles or collective excitations include the ''phonon'', a quasiparticle derived from the vibrations of atoms in a solid, and the ''plasmons'', a particle derived from plasma oscillation. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Biexciton
In condensed matter physics, biexcitons are created from two free excitons. Formation of biexcitons In quantum information and computation, it is essential to construct coherent combinations of quantum states. The basic quantum operations can be performed on a sequence of pairs of physically distinguishable quantum bits and, therefore, can be illustrated by a simple four-level system. In an optically driven system where the , 0 1 \rangle and , 1 0 \rangle states can be directly excited, direct excitation of the upper , 1 1 \rangle level from the ground state , 0 0 \rangle is usually forbidden and the most efficient alternative is coherent nondegenerate two-photon excitation, using , 0 1 \rangle or , 1 0 \rangle as an intermediate state. Observation of biexcitons Three possibilities of observing biexcitons exist: (a) excitation from the one-exciton band to the biexciton band (pump-probe experiments); (b) two-photon absorption of light from the ground state to the bie ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Orbiton
Orbitons are one of three quasiparticles, along with holons and spinons, that electrons in solids are able to split into during the process of spin–charge separation, when extremely tightly confined at temperatures close to absolute zero. The electron can always be theoretically considered as a bound state of the three, with the spinon carrying the spin of the electron, the orbiton carrying the orbital location and the holon carrying the charge, but in certain conditions they can become deconfined and behave as independent particles. Overview Orbitons can be thought of as energy stored in an orbital occupancy that can move throughout a material, in other words, an orbital-based excitation. An orbiton propagates through a material as a series of orbital excitations and relaxations of the electrons in a material without changes in either the spin of those electrons or the charge at any point in the material. Electrons, being of like charge, repel each other. As a result, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
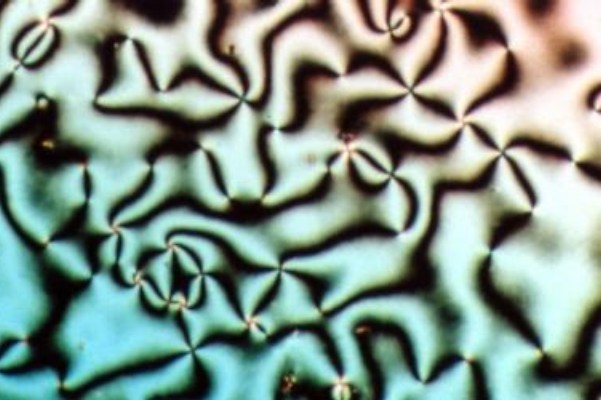
Liquid Crystal
Liquid crystal (LC) is a state of matter whose properties are between those of conventional liquids and those of solid crystals. For example, a liquid crystal may flow like a liquid, but its molecules may be oriented in a crystal-like way. There are many types of LC phases, which can be distinguished by their optical properties (such as textures). The contrasting textures arise due to molecules within one area of material ("domain") being oriented in the same direction but different areas having different orientations. LC materials may not always be in a LC state of matter (just as water may be ice or water vapor). Liquid crystals can be divided into 3 main types: * thermotropic, *lyotropic, and * metallotropic. Thermotropic and lyotropic liquid crystals consist mostly of organic molecules, although a few minerals are also known. Thermotropic LCs exhibit a phase transition into the LC phase as temperature changes. Lyotropic LCs exhibit phase transitions as a function of both ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nematicon
In optics, a nematicon is a spatial soliton in nematic liquid crystals (NLC). The name was invented in 2003 by G. Assanto. and used thereafter Nematicons are generated by a special type of optical nonlinearity present in NLC: the light induced reorientation of the molecular director (''i.e.'' the average molecular orientation). This nonlinearity arises from the fact that the molecular director (i.e., the optic axis of the corresponding uniaxial) tends to align along the electric field of light. Nematicons are easy to generate (with mW optical power or less ) because the NLC dielectric medium exhibits the following properties: * A very large nonlinear response : the effective nonlinearity is typically eight orders of magnitude larger than that of carbon disulfide. This means that much lower optical powers are necessary to obtain the same refractive index variation (increase) or self-focusing to balance out diffraction. * A nonlocal response : the nonlinear response is not ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Majorana Fermion
A Majorana fermion (, uploaded 19 April 2013, retrieved 5 October 2014; and also based on the pronunciation of physicist's name.), also referred to as a Majorana particle, is a fermion that is its own antiparticle. They were hypothesised by Ettore Majorana in 1937. The term is sometimes used in opposition to a Dirac fermion, which describes fermions that are not their own antiparticles. With the exception of neutrinos, all of the Standard Model fermions are known to behave as Dirac fermions at low energy (lower than the electroweak symmetry breaking temperature), and none are Majorana fermions. The nature of the neutrinos is not settled – they may turn out to be either Dirac or Majorana fermions. In condensed matter physics, quasiparticle excitations can appear like bound Majorana fermions. However, instead of a single fundamental particle, they are the collective movement of several individual particles (themselves composite) which are governed by non-Abelian statisti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Coherent Excitation
Coherence, coherency, or coherent may refer to the following: Physics * Coherence (physics), an ideal property of waves that enables stationary (i.e. temporally and spatially constant) interference * Coherence (units of measurement), a derived unit that, for a given system of quantities and for a chosen set of base units, is a product of powers of base units with no other proportionality factor than one * Coherence time, the time over which a propagating wave (especially a laser or maser beam) may be considered coherent; the time interval within which its phase is, on average, predictable Mathematics * Coherence (philosophical gambling strategy), a concept in Bayesian statistics * Coherence (signal processing), a statistic that can be used to examine the relation between two signals or data sets * Coherence (statistics), a property of self-consistency across a set of assessments, or the strength of association between two series * Coherence condition in category theory, a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Magnon
A magnon is a quasiparticle, a collective excitation of the electrons' spin structure in a crystal lattice. In the equivalent wave picture of quantum mechanics, a magnon can be viewed as a quantized spin wave. Magnons carry a fixed amount of energy and lattice momentum, and are spin-1, indicating they obey boson behavior. Brief history The concept of a magnon was introduced in 1930 by Felix Bloch in order to explain the reduction of the spontaneous magnetization in a ferromagnet. At absolute zero temperature (0 K), a Heisenberg ferromagnet reaches the state of lowest energy (so-called ground state), in which all of the atomic spins (and hence magnetic moments) point in the same direction. As the temperature increases, more and more spins deviate randomly from the alignment, increasing the internal energy and reducing the net magnetization. If one views the perfectly magnetized state at zero temperature as the vacuum state of the ferromagnet, the low-temperature state with ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Collective Excitation
In physics, quasiparticles and collective excitations are closely related emergent phenomena arising when a microscopically complicated system such as a solid behaves as if it contained different weakly interacting particles in vacuum. For example, as an electron travels through a semiconductor, its motion is disturbed in a complex way by its interactions with other electrons and with atomic nuclei. The electron behaves as though it has a different effective mass travelling unperturbed in vacuum. Such an electron is called an ''electron quasiparticle''. In another example, the aggregate motion of electrons in the valence band of a semiconductor or a hole band in a metal behave as though the material instead contained positively charged quasiparticles called ''electron holes''. Other quasiparticles or collective excitations include the ''phonon'', a quasiparticle derived from the vibrations of atoms in a solid, and the ''plasmons'', a particle derived from plasma oscillation. T ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Leviton (quasiparticle) .
A leviton, named after Leonid Levitov, is a collective excitation of a single electron within a metal. It has been mostly studied in two-dimensional electron gases alongside quantum point contacts. The main feature is that the excitation produces an electron pulse without the creation of electron holes. The time-dependence of the pulse is described by a Lorentzian distribution created by a pulsed electric potential. Levitons have also been described in graphene Graphene () is an allotrope of carbon consisting of a Single-layer materials, single layer of atoms arranged in a hexagonal lattice nanostructure. References Quasiparticles {{quantum-stub ...[...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Holon (physics)
Holons are one of three quasiparticles, along with spinons and orbitons, that electrons in solids are able to split into during the process of spin–charge separation, when extremely tightly confined at temperatures close to absolute zero. The electron can always be theoretically considered as a bound state of the three, with the spinon carrying the spin of the electron, the orbiton carrying the orbital location and the holon carrying the charge, but in certain conditions they can become deconfined and behave as independent particles. Overview Electrons, being fermions, repel each other due to the Pauli exclusion principle. As a result, in order to move past each other in an extremely crowded environment, they are forced to modify their behavior. Research published in July 2009 by the University of Cambridge and the University of Birmingham in England showed that electrons could jump past each other by quantum tunneling, and in order to do so will separate into two particles, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fracton (subdimensional Particle)
A fracton is an emergent topological quasiparticle excitation which is immobile when in isolation. Many theoretical systems have been proposed in which fractons exist as elementary excitations. Such systems are known as fracton models. Fractons have been identified in various CSS codes as well as in symmetric tensor gauge theories. Gapped fracton models often feature a topological ground state degeneracy that grows exponentially and sub-extensively with system size. Among the gapped phases of fracton models, there is a non-rigorous phenomenological classification into "type I" and "type II". Type I fracton models generally have fracton excitations that are completely immobile, as well as other excitations, including bound states, with restricted mobility. Type II fracton models generally have fracton excitations and no mobile particles of any form. Furthermore, isolated fracton particles in type II models are associated with nonlocal operators with intricate fractal structure. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |