|
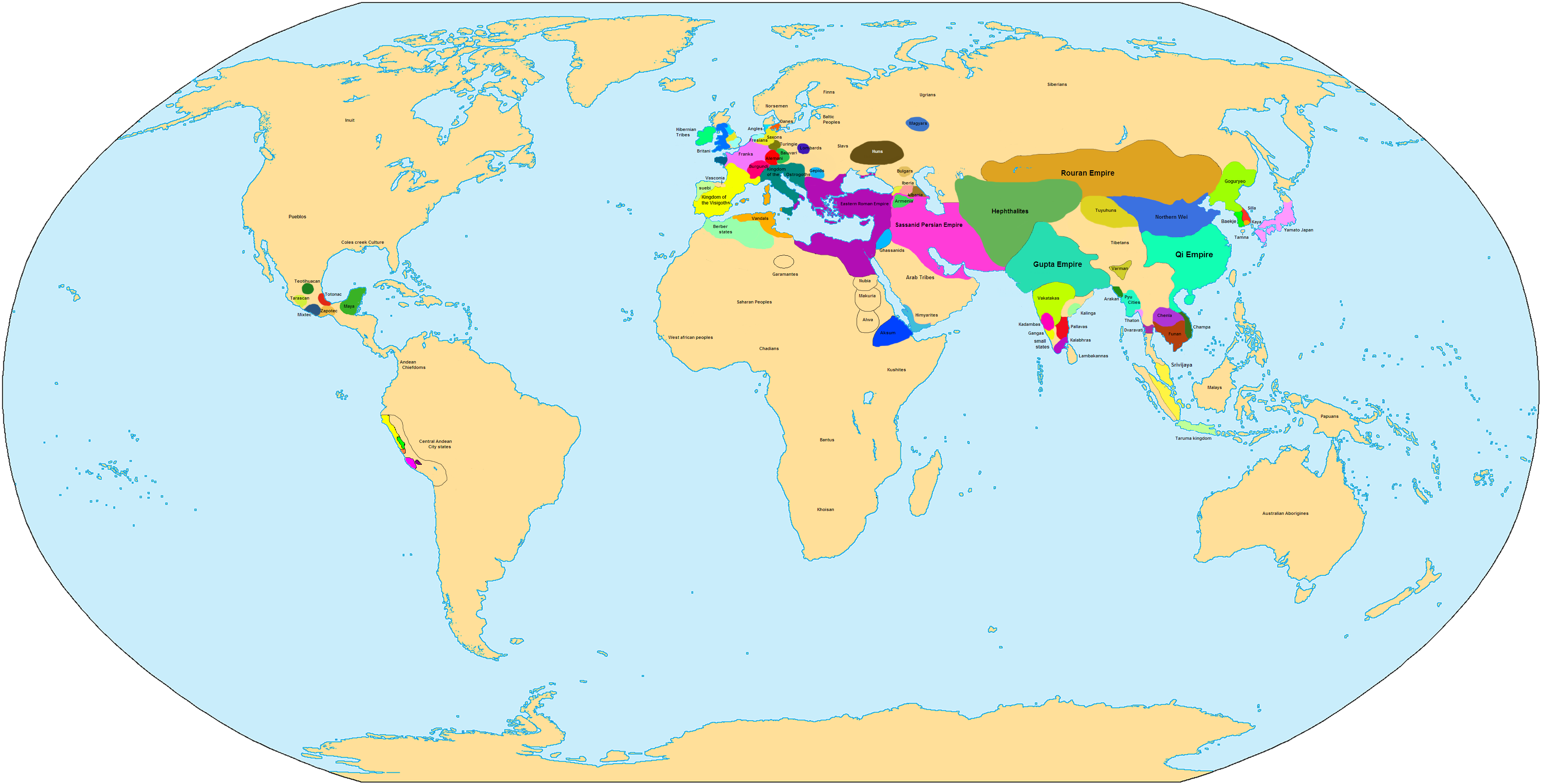
List Of Political Entities In The 5th Century
; Political entities in the 4th century – Political entities in the 6th century – Political entities by year This is a list of political entities in the 5th century (401–500) AD. Political entities See also *List of Bronze Age states *List of Iron Age states * List of Classical Age states *List of states during Late Antiquity *List of states during the Middle Ages Post-classical history (also called the post-classical era) is the period of time that immediately followed the end of ancient history. Depending on the continent, the era generally falls between the years AD 200–600 and AD 1200–1500. The ... References {{DEFAULTSORT:Political Entities In The 5th Century +05 5th century 5th century-related lists ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
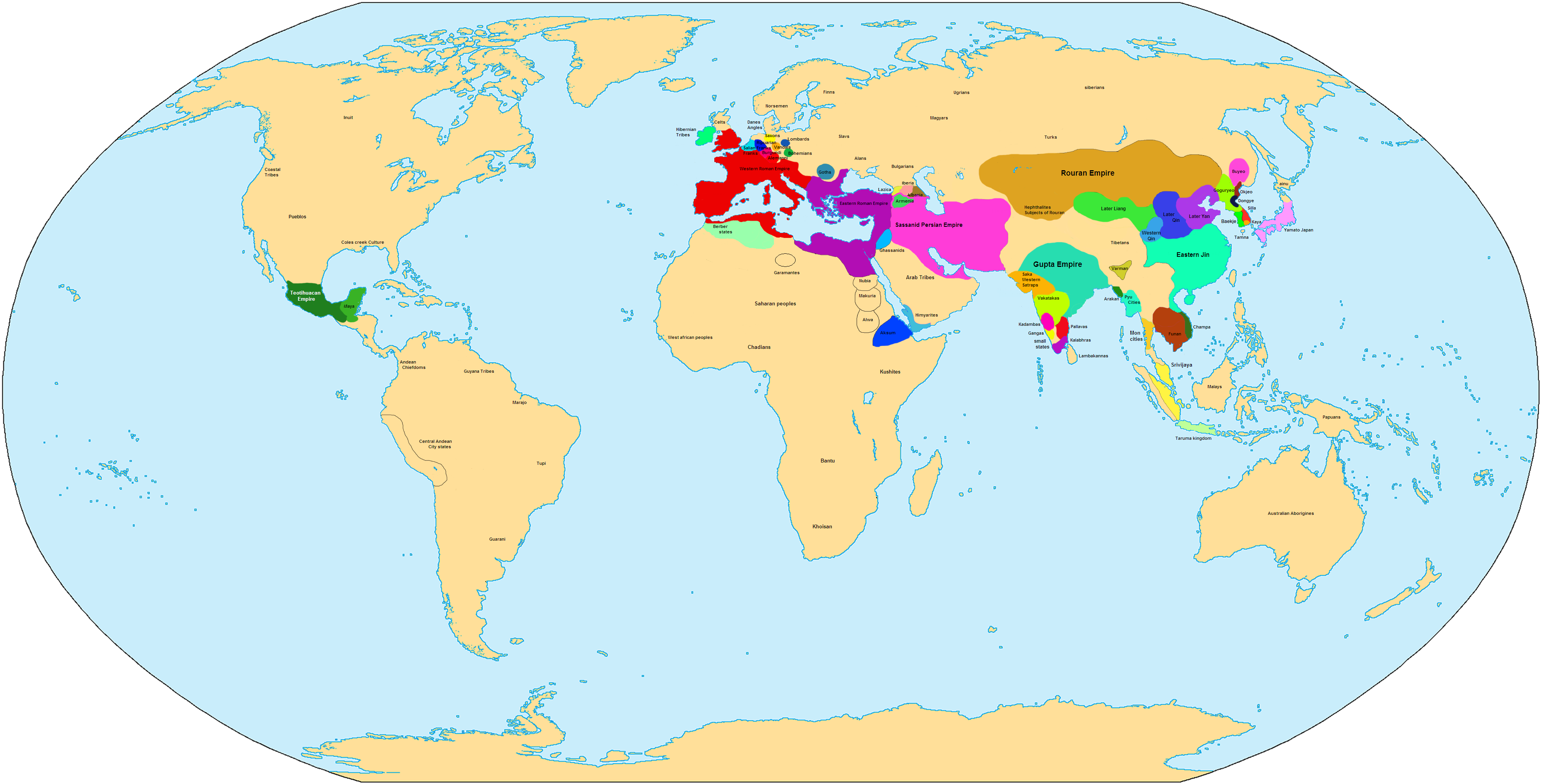
List Of Political Entities In The 4th Century
; Political entities in the 3rd century – Political entities in the 5th century – Political entities by year This is a list of political entities in the 4th century (301–400) AD. Political entities See also * List of Bronze Age states * List of Iron Age states * List of Classical Age states * List of states during Late Antiquity *List of states during the Middle Ages Post-classical history (also called the post-classical era) is the period of time that immediately followed the end of ancient history. Depending on the continent, the era generally falls between the years AD 200–600 and AD 1200–1500. The ... References {{DEFAULTSORT:Political Entities In The 4th Century +04 4th century 4th century-related lists ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Zapotec Civilization
The Zapotec civilization ( "The People"; 700 BC–1521 AD) was an indigenous pre-Columbian civilization that flourished in the Valley of Oaxaca in Mesoamerica. Archaeological evidence shows that their culture originated at least 2,500 years ago. The Zapotec archaeological site at the ancient city of Monte Albán has monumental buildings, ball courts, magnificent tombs and grave goods, including finely worked gold jewelry. Monte Albán was one of the first major cities in Mesoamerica. It was the center of a Zapotec state that dominated much of the territory which today is known as the Mexican state of Oaxaca. History Zapotec civilization originated in the Central Valleys of Oaxaca in the late 6th century BC. The three valleys were divided among three different-sized societies, separated by “no-man’s-land” in the middle. The city of Oaxaca much later developed in that area. Archaeological evidence, such as burned temples and sacrificed war captives, suggests that the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kingdom Of Cait
Cait or Cat was a Pictish kingdom originating c. AD 800 during the Early Middle Ages. It was centered in what is now Caithness in northern Scotland. It was, according to Pictish legend, founded by Caitt (or Cat), one of the seven sons of the ancestor figure Cruithne. The territory of Cait covered not only modern Caithness, but also southeast Sutherland. The place name ''Caithness'' derives from ''Cait'', which is also preserved in the Gaelic name for Sutherland (), in several specific names within that county and in the earliest recorded name for Shetland (, meaning "islands of the Cat people"). Watson (1994) compared this usage with the early Irish (islands of the boars) for Orkney and concluded that these are tribal names based on animals. History See also *Fortriu *Kingdom of Ce *Scotland in the Early Middle Ages Scotland was divided into a series of kingdoms in the early Middle Ages, i.e. between the end of Roman authority in southern and central Britain from ar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Brycheiniog
Brycheiniog was an independent kingdom in South Wales in the Early Middle Ages. It often acted as a buffer state between England to the east and the south Welsh kingdom of Deheubarth to the west. It was conquered and pacified by the Normans between 1088 and 1095, though it remained Welsh in character. It was transformed into the Lordship of Brecknock and later formed the southern and larger part of the historic county of Brecknockshire. To its south was the Kingdom of Morgannwg. The main legacy of the kingdom of Brycheiniog is etymological. It has lent its name to Brecknockshire (Welsh: ''Sir Frycheiniog'', the shire of Brycheiniog) and Brecon (known as ''Aberhonddu'' in Welsh). History Origins Brycheiniog belonged to the Demetae in pre-Roman times. In Welsh tradition, it was given by the Roman governor of Brittania, Magnus Maximus (''Macsen Wledig'' in Welsh), to a Greek named ''Antonius the Black'' (''Anwn Ddu''). Some Welsh legends describe Antonius as Maximus' son, an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bernicia
Bernicia ( ang, Bernice, Bryneich, Beornice; la, Bernicia) was an Anglo-Saxon kingdom established by Anglian settlers of the 6th century in what is now southeastern Scotland and North East England. The Anglian territory of Bernicia was approximately equivalent to the modern English counties of Northumberland, Tyne and Wear, and Durham, as well as the Scottish counties of Berwickshire and East Lothian, stretching from the Forth to the Tees. In the early 7th century, it merged with its southern neighbour, Deira, to form the kingdom of Northumbria, and its borders subsequently expanded considerably. Brittonic ''Bryneich'' Etymologies Bernicia occurs in Old Welsh poetry as ''Bryneich'' or ''Brynaich'' and in the 9th-century ''Historia Brittonum'', (§ 61) as ''Berneich'' or ''Birneich''. This was most likely the name of the native Brittonic kingdom , whose name was then adopted by the Anglian settlers who rendered it in Old English as ''Bernice'' or ''Beornice'' . The coun ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Airgíalla
Airgíalla (Modern Irish: Oirialla, English: Oriel, Latin: ''Ergallia'') was a medieval Irish over-kingdom and the collective name for the confederation of tribes that formed it. The confederation consisted of nine minor kingdoms, all independent of each other but paying nominal suzerainty to an overking, usually from the most powerful dynasty. Airgíalla at its peak roughly matched the modern dioceses of Armagh and Clogher, spanning parts of counties Armagh, Monaghan, Louth, Fermanagh, Tyrone and Londonderry. Its main towns were Armagh and Clogher. The name's usage survives as a cultural area of folk tradition in South East Ulster and adjoining areas of County Louth. According to legend, Airgíalla was founded by the Three Collas, who are said to have conquered what is now central Ulster from the Ulaid. The decisive victory was the battle of Achadh Leithdheirg, said to have been fought around the year 331. However, this tale is thought to be mostly fiction, and the actu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kings Of Ailech
The Kings of Ailech were the over-kings of the medieval Irish province of Ailech in north-western Ireland. It encompassed the territories of the Cenél nEógain and Cenél Conaill. After the battle of Cloítech in 789 its kings were exclusively from the Cenél nEógain. The royal fort for Ailech was the Grianan of Aileach,Seán Duffy (2014); "Brian Boru and the Battle of Clontarf", page 21. Gill & Macmillan. . a hillfort on top of Greenan Mountain in modern-day County Donegal, Republic of Ireland. Early kings (5th–8th centuries) Earlier Kings of Cenél nEógain and Ailech included: * Eógan mac Néill Noigallach (died 465) * Muiredach mac Eógain (died c. 489) * Muirchertach mac Muiredaig (died 534) * Forggus mac Muirchertaig (died 566) * Domnall Ilchelgach mac Muirchertaig (died 566) * Báetán mac Muirchertaig (died 572) * Eochaid mac Domnaill (died 572) * Colcu mac Domnaill (died 580) * Colmán Rímid mac Báetáin (died 604) * Áed Uaridnach mac Domnaill (died 612) * ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Paeonia (kingdom)
In antiquity, Paeonia or Paionia ( grc, Παιονία, Paionía) was the land and kingdom of the Paeonians or Paionians ( grc, Παίονες, Paíones). The exact original boundaries of Paeonia, like the early history of its inhabitants, are obscure, but it is known that it roughly corresponds to most of present-day North Macedonia and north-central parts of Greek Macedonia (i.e. probably the Greek municipalities of Paionia xcluding the village of Evropos">Evropos.html" ;"title="xcluding the village of Evropos">xcluding the village of Evropos Almopia, Sintiki, Irakleia, Serres, Irakleia, and Serres), and a small part of south-western Bulgaria. Ancient authors placed it south of Kingdom of Dardania, Dardania (an area corresponding to modern-day Kosovo and northern North Macedonia), west of the Thracian mountains, and east of the southernmost Illyrians. It was separated from Dardania by the mountains through which the Vardar river passes from the field of Scupi (modern Skop ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gepids
The Gepids, ( la, Gepidae, Gipedae, grc, Γήπαιδες) were an East Germanic tribe who lived in the area of modern Romania, Hungary and Serbia, roughly between the Tisza, Sava and Carpathian Mountains. They were said to share the religion and language of the Goths and Vandals. They are first mentioned by Roman sources in the third century. In the fourth century, they were among the peoples incorporated into the Hunnic Empire, within which they formed an important part. After the death of Attila, the Gepids under their leader Ardaric, led an alliance of other peoples who had been in the empire, and defeated the sons of Attila and their remaining allies at the Battle of Nedao in 454. The Gepids and their allies subsequently founded kingdoms on the Middle Danube, bordering on the Roman Empire. The Gepid Kingdom was one of the most important and long-lasting of these, centered on Sirmium, and sometimes referred to as Gepidia. It covered a large part of the former Roman provinc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Byzantine Empire
The Byzantine Empire, also referred to as the Eastern Roman Empire or Byzantium, was the continuation of the Roman Empire primarily in its eastern provinces during Late Antiquity and the Middle Ages, when its capital city was Constantinople. It survived the fragmentation and fall of the Western Roman Empire in the 5th century AD and continued to exist for an additional thousand years until the fall of Constantinople to the Ottoman Empire in 1453. During most of its existence, the empire remained the most powerful economic, cultural, and military force in Europe. The terms "Byzantine Empire" and "Eastern Roman Empire" were coined after the end of the realm; its citizens continued to refer to their empire as the Roman Empire, and to themselves as Romans—a term which Greeks continued to use for themselves into Ottoman times. Although the Roman state continued and its traditions were maintained, modern historians prefer to differentiate the Byzantine Empire from Ancient Rome ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nazca
Nazca (; sometimes spelled Nasca; qu, Naska) is a city and system of valleys on the southern coast of Peru. It is also the name of the largest existing town in the Nazca Province. The name is derived from the Nazca culture, which flourished in the area between 100 BC and AD 800. This culture was responsible for the Nazca Lines and the ceremonial city of Cahuachi. They also constructed additional underground aqueducts, named puquios, in a regional system that still functions today. The first puquios are believed to have been built by the preceding Paracas culture. Nazca is the capital of the Nazca Province located in the Ica District of the Ica region of Peru. Earthquake On November 12, 1996, at 11:59 a.m. local time (16:59 GMT) there was an earthquake of magnitude 7.5 with its epicenter at 7.7 km into the sea. The earthquake almost completely destroyed the city of Nazca and its surroundings. Due to its occurrence during the day, there were only 14 fatalities. Ho ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |