|
List Of Polish Language Authors
Notable Polish novelists, poets, playwrights, historians and philosophers, listed in chronological order by year of birth: * (''ca.''1465–after 1529) Biernat of Lublin * (1482–1537) Andrzej Krzycki * (1503–1572) Andrzej Frycz Modrzewski * (1505–1569) Mikołaj Rej * (ca. 1525–1573) Piotr z Goniądza * (1530–1584) Jan Kochanowski * (1566–1636) Fabian Birkowski * (1580–1653) Szymon Okolski * (1651–1701) Anna Stanisławska * (1694–1774) Przybysław Dyjamentowski * (1720–1784) Franciszek Bohomolec * (1733–1798) Adam Naruszewicz * (1734–1823) Adam Kazimierz Czartoryski * (1735–1801) Ignacy Krasicki * (1746–1835) Izabela Fleming Czartoryska * (1750–1812) Hugo Kołłątaj * (1755–1826) Stanisław Staszic * (1757–1829) Wojciech Bogusławski * (1757–1841) Julian Ursyn Niemcewicz * (1761–1815) Jan Potocki * (1762–1808) Franciszek Ksawery Dmochowski * (1765–1809) Cyprian Godebski * (1768–1854) Maria Wirtemberska * (1770–1861) Adam Jerzy Czar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Poland
Poland, officially the Republic of Poland, is a country in Central Europe. It is divided into 16 administrative provinces called voivodeships, covering an area of . Poland has a population of over 38 million and is the fifth-most populous member state of the European Union. Warsaw is the nation's capital and largest metropolis. Other major cities include Kraków, Wrocław, Łódź, Poznań, Gdańsk, and Szczecin. Poland has a temperate transitional climate and its territory traverses the Central European Plain, extending from Baltic Sea in the north to Sudeten and Carpathian Mountains in the south. The longest Polish river is the Vistula, and Poland's highest point is Mount Rysy, situated in the Tatra mountain range of the Carpathians. The country is bordered by Lithuania and Russia to the northeast, Belarus and Ukraine to the east, Slovakia and the Czech Republic to the south, and Germany to the west. It also shares maritime boundaries with Denmark and Sweden. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
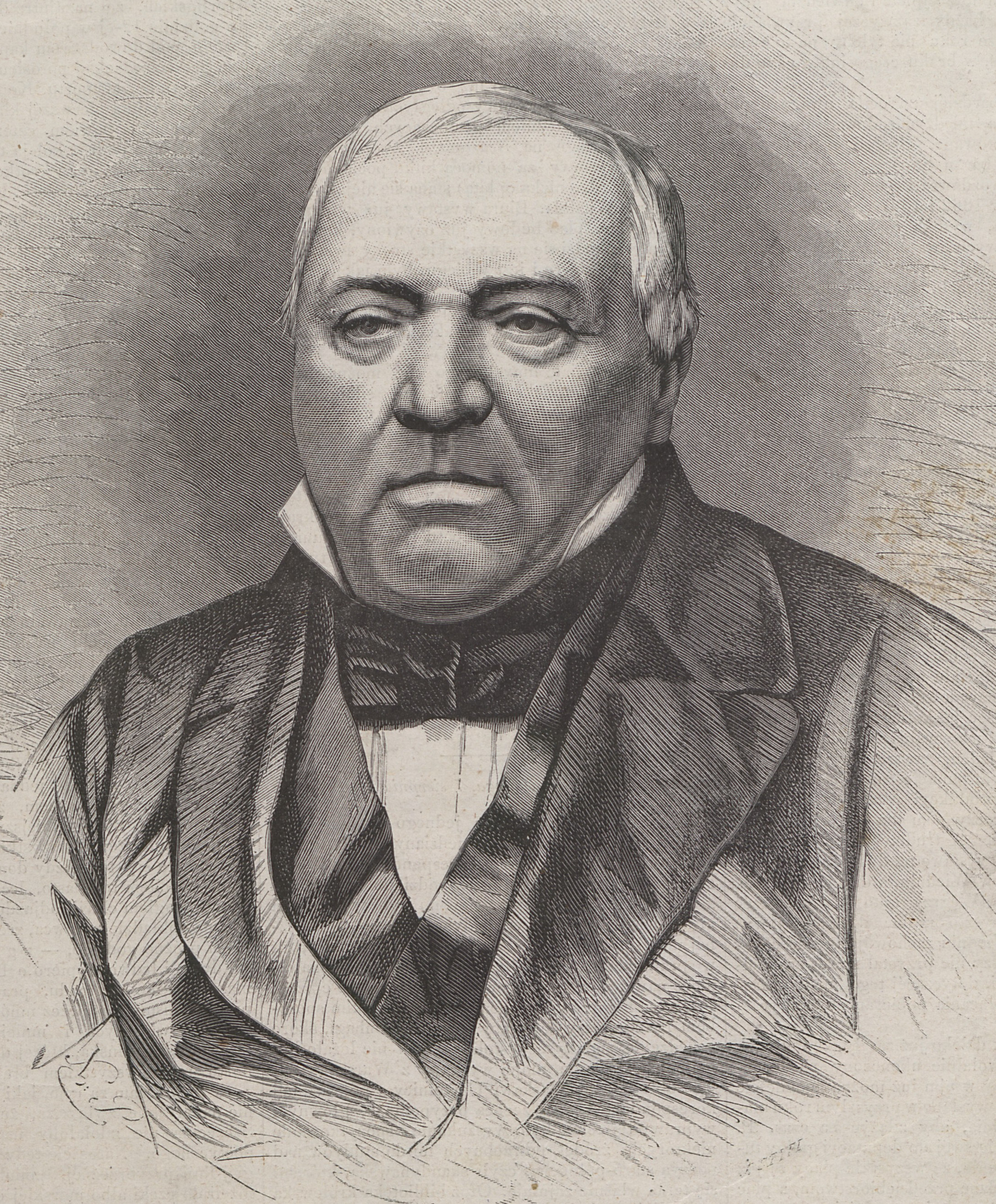
Stanisław Staszic
Stanisław Wawrzyniec Staszic (baptised 6 November 1755 – 20 January 1826) was a leading figure in the Polish Enlightenment: a Catholic priest, philosopher, geologist, writer, poet, translator and statesman. A physiocrat, monist, pan-Slavist (after 1815) and laissez-fairist, he supported many reforms in Poland. He is particularly remembered for his political writings during the " Great (Four-Year) Sejm" (1788–92) and for his large support towards the Constitution of 3 May 1791, adopted by that Sejm. He co-founded the Warsaw Society of Friends of Learning (precursor to the Polish Academy of Sciences), of which he became president. He served as a member of the State Council of the Duchy of Warsaw and as minister of trade and industry in Congress Poland. Staszic is seen as the father of Polish geology, statistics, sociology, Tatra Mountains studies and exploration, mining and industry. Life Early life Stanisław Staszic was born into a burgher family in the town of Pi� ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Adam Mickiewicz
Adam Bernard Mickiewicz (; 24 December 179826 November 1855) was a Polish poet, dramatist, essayist, publicist, translator and political activist. He is regarded as national poet in Poland, Lithuania and Belarus. A principal figure in Polish Romanticism, he is one of Poland's "Three Bards" ( pl, Trzej Wieszcze) and is widely regarded as Poland's greatest poet. He is also considered one of the greatest Slavic and European poets and has been dubbed a "Slavic bard". A leading Romantic dramatist, he has been compared in Poland and Europe to Byron and Goethe. He is known chiefly for the poetic drama ''Dziady'' (''Forefathers' Eve'') and the national epic poem '' Pan Tadeusz''. His other influential works include '' Konrad Wallenrod'' and '' Grażyna''. All these served as inspiration for uprisings against the three imperial powers that had partitioned the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth out of existence. Mickiewicz was born in the Russian-partitioned territories of the former G ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
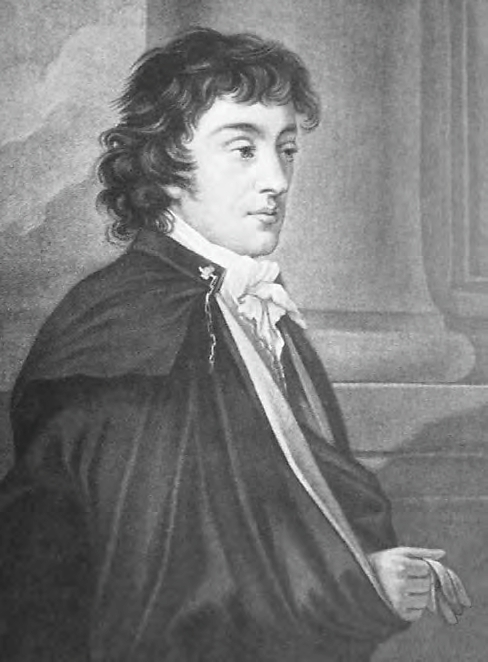
Aleksander Fredro
Aleksander Fredro (20 June 1793 – 15 July 1876) was a Polish poet, playwright and author active during Polish Romanticism in the period of partitions by neighboring empires. His works including plays written in the octosyllabic verse ('' Zemsta'') and in prose (''Damy i Huzary'') as well as fables, belong to the canon of Polish literature. Fredro was harshly criticized by some of his contemporaries for light-hearted humor or even alleged immorality (Seweryn Goszczyński, 1835) which led to years of his literary silence. Many of Fredro's dozens of plays were published and popularized only after his death. His best-known works have been translated into English, French, German, Russian, Czech, Romanian, Hungarian and Slovak. Biography Count Aleksander Fredro, of the Bończa coat of arms, was born in the village of Surochów near Jarosław, then a crown territory of Austria. A landowner's son, he was educated at home. He entered the Polish army at age 16 and saw action in the Napo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kazimierz Brodziński
Kazimierz Brodziński (8 March 1791 in Królówka – 10 October 1835 in Dresden) was an important Polish Romantic poet. Life He was born in Królówka near Bochnia. He came from the low nobility. He was a student at schools in Tarnów, where he also graduated from the grammar school. He served in the army of the Duchy of Warsaw. He took part in the campaign of 1812, during which he was promoted to the rank of lieutenant. During the ''Battle of the Nations'' at Leipzig, he was wounded and taken prisoner by the Prussians. Having returned from captivity in 1814, he settled in Warsaw, where he worked as a clerk. He joined the freemasons, advanced to the fifth degree of initiation; in 1819 he became the secretary of the Great East. From 1818, he was a teacher of Polish literature and of style in schools of various degrees. He also co-operated with ''Pamiętnik Warszawski'', initially as a member of the editorial staff and later as co-editor. In 1823 he became a member of the So ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
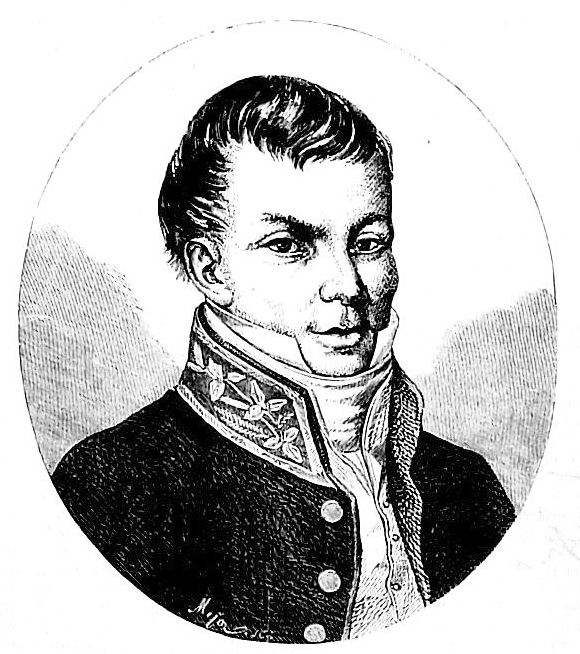
Antoni Gorecki
Antoni Gorecki (1787 – 18 September 1861) was a Polish poet and writer, author of satires and short stories for children. He was born in 1787 in Vilnius, where he finished primary school. In 1802 he started studying at the Faculty of Literature of the University of Vilnius, where he became friends with Joachim Lelewel. In 1805 he graduated and soon afterwards he left Imperial Russia for the Duchy of Warsaw. In 1809 he volunteered for the Polish Army fighting alongside Napoleon Bonaparte in the Napoleonic Wars. Between 1809 and 1812 he took part in most of the battles that took place in the territory of the former Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth. After the Congress of Vienna he remained in exile and travelled across Europe, but finally in 1818 he returned to his hometown. There he published many of his poems, short stories, fables and fairy-tales. Also, he was one of the most notable members of the Towarzystwo Szubrawców (''Scumbags Society'') and one of co-authors of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Joachim Lelewel
Joachim Lelewel (22 March 1786 – 29 May 1861) was a Polish historian, geographer, bibliographer, polyglot and politician. Life Born in Warsaw to a Polonized German family, Lelewel was educated at the Imperial University of Vilna, where in 1814 he became a lecturer in history, with a brief sojourn at Warsaw, 1818–1821, where he joined the Warsaw Society of Friends of Learning. His lectures on Polish history created great enthusiasm, as shown in some lines addressed to him by Adam Mickiewicz that led to Lelewel's removal by the Russians in 1824. Five years later, Lelewel returned to Warsaw, where he was elected a deputy to the Sejm of Congress Poland. He joined the November 1830 Uprising with more enthusiasm than energy, though Tsar Nicholas I identified him as one of the most dangerous rebels. He is considered the author of the motto: "For our freedom and yours". On the suppression of the rebellion, Lelewel made his way in disguise to Germany and subsequently reached Pari ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alojzy Feliński
Alojzy Feliński (1771 – 1820) was a Polish writer. Life Feliński was born in Łuck. In his childhood he met Tadeusz Czacki. He was educated by the Piarists in Dąbrownica, later in Włodzimierz Wołyński. In 1778 he settled in Lublin, where he became a close companion of Kajetan Koźmian. Having resigned from the Bar together with Tadeusz Czacki, in 1779 he entered Parliament in Warsaw, where he became acquainted with many contemporary writers from Jacek Małachowski’s circle of friends. During the Kościuszko Insurrection, Feliński was Tadeusz Kościuszko’s secretary for French correspondence as well as the law and order commissar in Wołyń. After the defeat of the Insurrection he stayed at the Tarnowskis’ in Dzików, in 1795 he returned to Wołyń to manage his estate. In 1809 the author became a member of the ''Society of the Friends of Science''. In 1815 he went to live in Warsaw and joined the circle of classicists. In 1818 he moved to Krzemieniec, where ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Adam Jerzy Czartoryski
Adam Jerzy Czartoryski (; lt, Аdomas Jurgis Čartoriskis; 14 January 177015 July 1861), in English known as Adam George Czartoryski, was a Polish nobleman, statesman, diplomat and author. The son of a wealthy prince, he began his political career as a foreign minister to the Russian Tsar Alexander I after Poland was partitioned by Russia, Prussia and Austria. He later became a leader of the Polish government in exile and a bitter opponent of Alexander's successor, Tsar Nicholas I. In exile, he advocated for the reestablishment of a sovereign Polish state, which also stimulated early Balkan and Belgian nationalism, and intensified their desire for independence. Czartoryski was a dedicated patron of arts and greatly contributed to the Czartoryski Collection. In 1798, he purchased one of Poland's most important national treasures – Leonardo da Vinci's ''Lady with an Ermine'', which he brought as a gift for his mother from Italy. Early life and education Czartoryski was b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Maria Wirtemberska
Princess Maria Czartoryska (formerly Duchess Louis of Württemberg; 15 March 1768, Warsaw – 21 October 1854, Paris), was a Polish noble, writer, musician and philanthropist. Life Maria Anna was a daughter of Prince Adam Kazimierz Czartoryski and Countess Isabella von Flemming. She spent her childhood in the Blue Palace in Warsaw and Powązki. In 1782 she moved with her parents to Puławy. Since 1784 to 1793 Maria was married to Duke Louis of Württemberg, who became the Hetman of the Lithuanian Army in the 1792 war against Russia. Maria divorced him when his betrayal of the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth became known. Maria's only son, Duke Adam of Württemberg, remained with his father and was raised in an atmosphere prejudiced against his mother and Poland. Following her divorce, Maria lived mostly in Warsaw, and since 1798 to 1804 spent winters in Vienna and summers at Puławy. Between 1808-1816 she hosted her literary salon in Warsaw (Blue Saturdays). Her guests ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
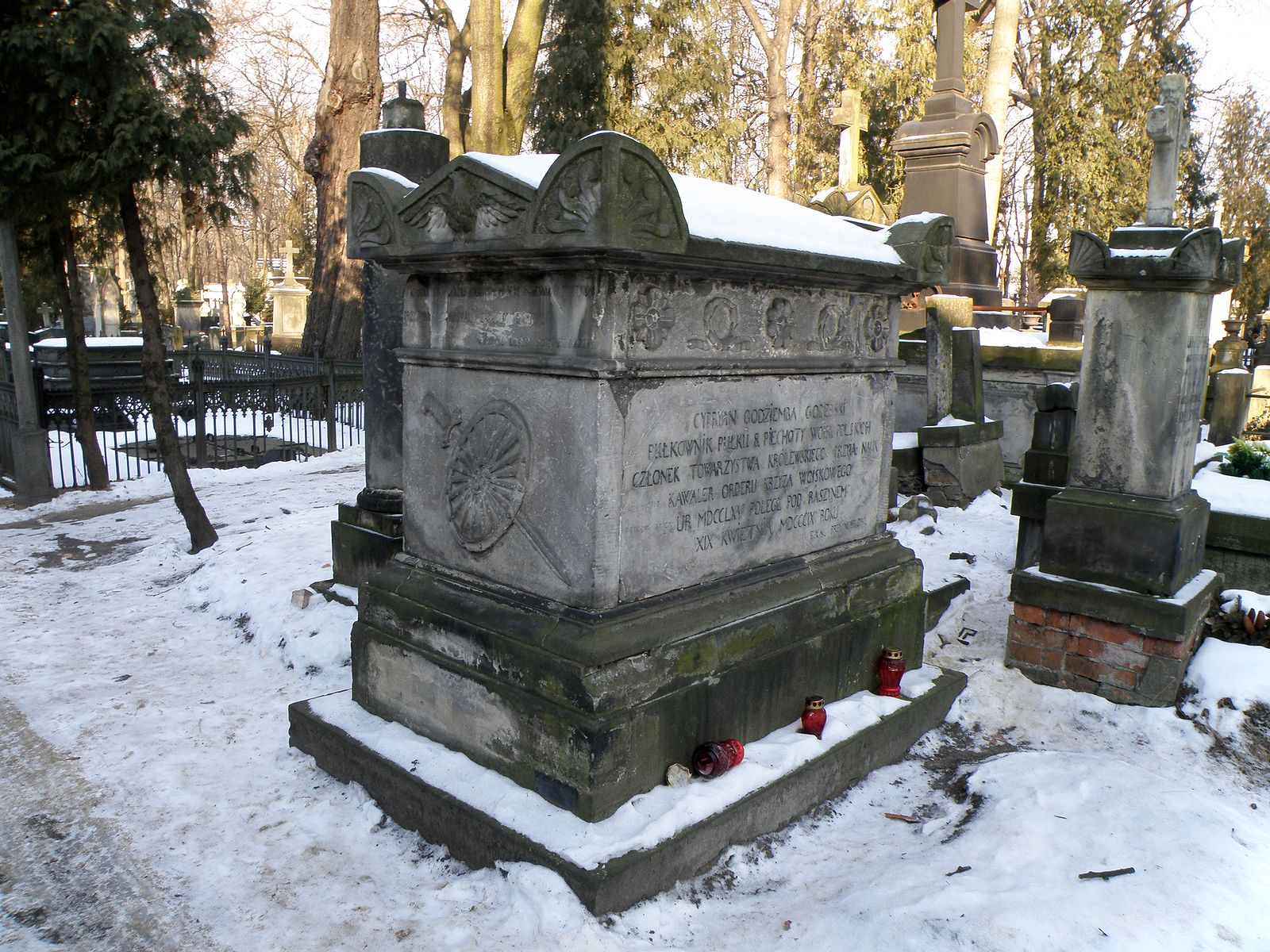
Cyprian Godebski (poet)
Cyprian Godebski (1765 – 19 April 1809) was a Polish poet, novelist and father of writer Franciszek Ksawery. He was an outstanding poet of the so-called "Legions Poetry". Life Godebski served in the Polish Legions from 1798 until 1801. From 1803 to 1806 he became, together with Ksawery Kossecki, publisher and editor of the "Zabawy Przyjemne i Pozyteczne" almanac. From 1805 he was a member of the Friends of Science Society. In 1806 Godebski joined the Polish Army of the Duchy of Warsaw; he had become disillusioned with the policy of Napoleon towards Poland. He died in the Battle of Raszyn The first Battle of Raszyn was fought on 19 April 1809 between armies of the Austrian Empire under Archduke Ferdinand Karl Joseph of Austria-Este and the Duchy of Warsaw under Józef Antoni Poniatowski, as part of the War of the Fifth Coalitio ... in 1809. [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Franciszek Salezy Dmochowski
Franciszek Salezy Dmochowski (1801–1871) was a Polish writer, poet, translator, critic, journalist and publisher. He studied at the University of Warsaw. He took part in the distribution of illegal ''bibuła'' press and publications in partitioned Poland. Son of Franciszek Ksawery Dmochowski Franciszek Ksawery Dmochowski (1762–1818) was a Polish Romantic novelist, poet, translator, publisher, critic, and satirist. Father of Franciszek Salezy Dmochowski. Biography Dmochowski was born in Oprawczyki in Podlaskie Voivodeship on 2 .... References 1801 births 1871 deaths Polish male writers {{Poland-writer-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |