|
List Of People From Edinburgh
This list contains famous or notable people who were either born, residents, or otherwise closely associated with the City of Edinburgh, Scotland. The entries in each section are listed alphabetically. Architecture Arts Authors Medicine, science and engineering Military Religion Royalty *Charles X of France (1757–1836), in Holyrood Palace during his exile *Henry Stuart, Lord Darnley (1545–1567), King consort of Scotland *Madeleine of Valois (1520–1537), first spouse of King James V of Scotland *Saint Margaret of Scotland (c. 1045–1093), wife of Malcolm Canmore *Mary of Guise (1515–1560), regent of Scotland, and mother of Mary, Queen of Scots *Mary, Queen of Scots (1542–1587), lived in Holyrood Palace *Mynyddog Mwynfawr, Brittonic ruler of kingdom of Gododdin in Hen Ogledd (in reading of ''Y Gododdin'' accepted by most scholars), perhaps with his court at Din Eidyn Scottish Enlightenment Sports Miscellaneous See also *List of Scots References {{D ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
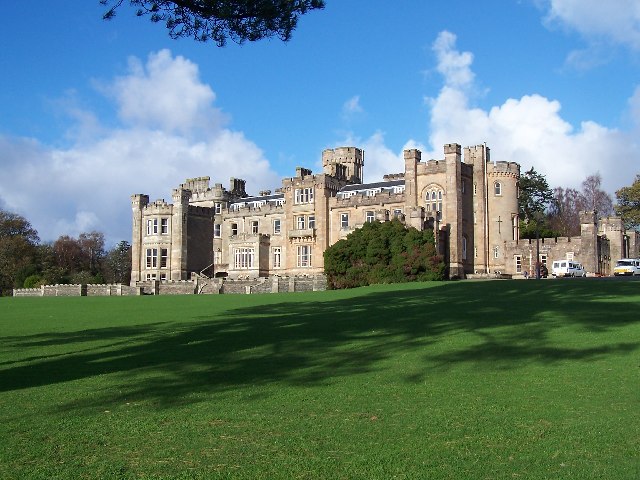
City Of Edinburgh
The City of Edinburgh Council is the local government authority for the city of Edinburgh, capital of Scotland. With a population of in mid-2019, it is the second most populous local authority area in Scotland. In its current form, the council was created in 1996 under the Local Government etc. (Scotland) Act 1994, to replace the City of Edinburgh District Council of the Lothian region, which had, itself, been created in 1975. The history of local government in Edinburgh, however, stretches back much further. Around 1130, David I made the town a royal burgh and a burgh council, based at the Old Tolbooth is recorded continuously from the 14th century. The council is currently based in Edinburgh City Chambers with a main office nearby at Waverley Court. History Before 1368 the city was run from a pretorium (a Latin term for Tolbooth), and later from around 1400 from the Old Tolbooth next to St Giles' Cathedral. A Tolbooth is the main municipal building of a Scottish burgh pr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stewart Henbest Capper
Stewart Henbest Capper (15 December 1859 – 8 January 1925) was a prominent architect in the Arts and Crafts style closely associated with Sir Patrick Geddes with much of his work sadly mislabelled as Geddes’. Due to ill-health he did not achieve much that he might have, and his contemporary Sydney Mitchell completed much of his most public works. His style cleverly mimics medieval and Renaissance details, and, as it sometimes includes either original or faked medieval date-stones, is regularly accepted as being several centuries older than its true age. In later life he is remembered as Professor Capper due to his academic role at McGill University in Canada. This is often remembered more than for his work in Scotland, and much of his due fame has been laid on the shoulders of his clients and those who completed his works. Early life Born in Douglas, Isle of Man, the son of Jasper John Capper (1820-1918), he was raised in Upper Clapton in London until his family moved ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Reginald Francis Joseph Fairlie
Reginald Francis Joseph Fairlie LLD (7 March 1883 – 27 October 1952) was a Scottish architect. He served as a commissioner of RCAHMS and on the Ancient Monuments Board for Scotland. Life see Born at Kincaple, Fife, he was the son of J. Ogilvy Fairlie of Myres (1848–1916) and Jane Mary Fairlie. He was educated at the Oratory School in Birmingham. > He was apprenticed to Robert Lorimer in 1901, and much of his style echoes that of Lorimer. Ian Gordon Lindsay trained under him (1927–30). A faithful Roman Catholic, Fairlie designed many war memorials, churches and restorations of castles. From a long list of commissions, only a handful fall outside the borders of Scotland. He set up office at 14 Randolph Place in 1908. He served in Royal Engineers in World War I. His older brother John Ogilvy Fairlie was killed in action on 25 September 1915. With the death of his father on 28 September 1916, Reginald fell heir to the family estate of Myres. In the early 1920s he designe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Calton Hill
Calton Hill () is a hill in central Edinburgh, Scotland, situated beyond the east end of Princes Street and included in the city's UNESCO World Heritage Site. Views of, and from, the hill are often used in photographs and paintings of the city. Calton Hill is the headquarters of the Scottish Government, which is based at St Andrew's House,Youngson, A.J. (2001): "The Companion Guide to Edinburgh and the borders", Chapter 9 (Calton Hill), Polygon Books, Edinburgh, UK, on the steep southern slope of the hill. The Scottish Parliament Building and other prominent buildings such as Holyrood Palace lie near the foot of the hill. Calton Hill is also the location of several monuments and buildings: the National Monument,The Calton Hill |
Waterloo Hotel
The Waterloo Hotel is a historical hotel located on Waterloo Place in Edinburgh, Scotland. It was the first large scale purpose built hotel in Edinburgh, trading from 1819 to 1898. The Waterloo Hotel, Tavern and Coffee House The category A listed Georgian building was designed by the Scottish architect Archibald Elliot (1761-1823) and constructed between 1815 and 1819. It contained fifty bedrooms, a coffee room, three dining rooms and a large ballroom (). In the 1970s, long after the hotel ceased trading, the ballroom was demolished to accommodate an extension, but the cupola (domed window in the ceiling), which would have filled the ballroom with light, has been preserved and can still be seen on the 8th floor of the building. Notable guests and events * The Waterloo Hotel opened on Saturday 21 August 1819 to commemorate the visit of Prince Leopold of Saxe-Coburg. He was in the first carriage ever to travel down Waterloo Place. * Charles Grey, 2nd Earl Grey (Earl Grey) was give ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Regent Bridge
Regent Bridge is a road bridge in Edinburgh, Scotland, where the A1 road enters the New Town from the east and passes over a hollow near Calton Hill. The bridge was built in the 19th century, in the neoclassical style as the medieval city was modernised and expanded to the north and east. History In the early nineteenth century, the inconvenient access to Edinburgh by the great London road had long been a subject of general regret. To enter the city from the south, the route ran through narrow and inconvenient streets, an approach that was considered unsuited to the general elegance of the place. In 1814, however, a magnificent entrance was commenced from Calton Hill to Princes Street over a deep ravine called Low Calton that was then occupied by old and ill-built streets. To connect Calton Hill with Princes Street, all these streets were swept away, and an elegant arch, called Regent Bridge, was thrown over the hollow, making the descent from Calton Hill into Princes St ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Archibald Elliot
Archibald Elliot (August 1761 – 16 June 1823) was a Scottish architect based in Edinburgh. He had a very distinctive style, typified by square plans, concealed roofs, crenellated walls and square corner towers. All may be said to derive from the earlier local example of Melville Castle by James Playfair. Many of his works have been demolished. Life He was born in Ancrum, Roxburghshire the son of a carrier. After training as a joiner he moved to cabinet design, working then in London, and appears to have then trained as an architect before returning to Scotland to work in Edinburgh. Archibald Elliot ran an architecture practice in London and Edinburgh with his brother James Elliot. Following James's death in 1810, Archibald ran the company on his own. It was later taken over by Archibald's son, Archibald Elliot Junior. He contributed to many significant buildings and streets in Edinburgh, including St Paul's and St George's Church, Rutland Square, the Regent Bridge, Waterlo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alexander Edward
Alexander Edward (10 June 1651 – 16 November 1708) was a priest of the Scottish Episcopal Church who later became a draughtsman, architect and landscape designer. He was a stylistic follower of Sir William Bruce, and planned several gardens in the grand French axial manner. Early life Alexander Edward was the eldest son of Robert Edward, minister at Murroes in Angus, who was related by marriage to the Maule family, and as such enjoyed the patronage of the Maule Earls of Panmure. Alexander's diary records that his family had to hide from Cromwell's Puritan troops in the 1650s, and also that he had a squint. He graduated from the University of St Andrews in 1670.Colvin, p. 283. Edward was not ordained until 1679, and his activities during the 1670s are unknown. At this time, his father was writing a description of Angus, and preparing a map to accompany the book, entitled ''Angusia, Provincia Scotiae''. The work was commissioned by George Maule, 2nd Earl of Panmure, and publis ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Francis William Deas
Francis William Deas (1862 –13 November 1951) was an influential Scottish Arts and Crafts architect and landscape designer in the late 19th century and first half of the 20th century. He was a keen amateur painter, largely of landscapes. His most important work was probably the restoration of Castle Toward. Life He was born in Haslar in Hampshire. He was the son of Margaret Hepburn and Sir David Deas, a naval surgeon. His grandfather was Francis Deas, provost of Falkland in Fife.Dictionary of Scottish Architects:Deas When his father died in 1876 his father’s brother, Sir George Deas took over the role of organising his education and sent him to Charterhouse School then to the University of Edinburgh. From that point onward he remained in Scotland. In 1890 he was articled to Robert Rowand Anderson and also began attending the new Edinburgh College of Art under Prof Frank Worthington Simon where he studied for three years. From 1896-97 he made a study trip undertaking man ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
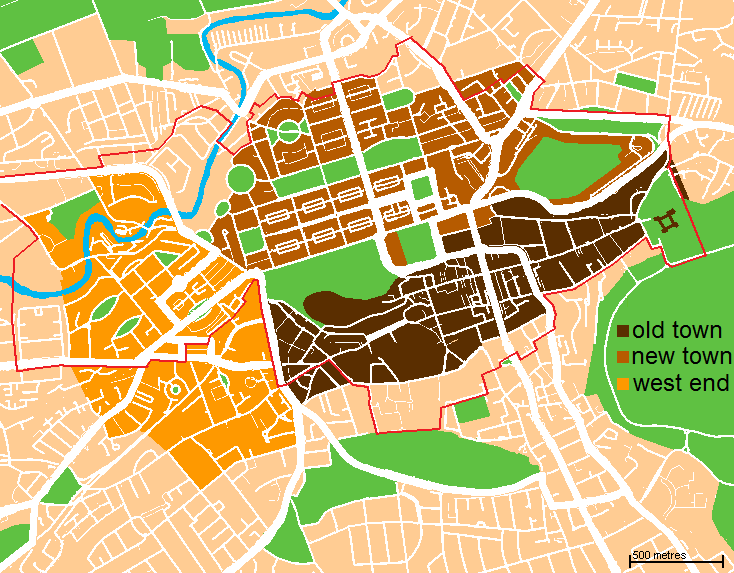
New Town, Edinburgh
The New Town is a central area of Edinburgh, the capital of Scotland. It was built in stages between 1767 and around 1850, and retains much of its original neo-classical and Georgian period architecture. Its best known street is Princes Street, facing Edinburgh Castle and the Old Town across the geological depression of the former Nor Loch. Together with the West End, the New Town was designated a UNESCO World Heritage Site alongside the Old Town in 1995. The area is also famed for the New Town Gardens, a heritage designation since March 2001. Proposal and planning The idea of a New Town was first suggested in the late 17th century when the Duke of Albany and York (later King James VII and II), when resident Royal Commissioner at Holyrood Palace, encouraged the idea of having an extended regality to the north of the city and a North Bridge. He gave the city a grant:That, when they should have occasion to enlarge their city by purchasing ground without the town, or to build ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
James Craig (architect)
James Craig (31 October 1739 – 23 June 1795) was a Scottish architect who worked mostly in lowlands of the country and especially his native city of Edinburgh. He is remembered primarily for his layout of the first Edinburgh New Town. Date of birth James Craig's birth date is traditionally given as 1744, as his baptism is recorded in parish register as Tuesday 13 November 1744. However, more recent research has shown that his birth date was 31 October 1739, as recorded in the registers of George Watson's Hospital, where Craig was educated. As well as his date of birth, the records show he entered the school in 1748, and left in 1755. The 1744 date must therefore be incorrect, as it would mean he started school aged four, and left aged eleven. The baptism year, although not the date, has been shown to be in error, as 13 November fell on a Tuesday in 1739 also. Early life James Craig was the son of William Craig (1695–1762), a merchant, and Mary Thomson (1710–1790), sis ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
David Cousin
David Cousin (19 May 1809 – 14 August 1878) was a Scottish architect, landscape architect and planner, closely associated with early cemetery design and many prominent buildings in Edinburgh. From 1841 to 1872 he operated as Edinburgh’s City Superintendent of Works (also known as the City Architect). Life Cousin was born in North Leith on 19 May 1809, the son of Isabella Paterson (1773-1851) and John Cousin (1781-1862), and was baptised in North Leith Church. Initially he trained under his father as a joiner, but went on to study mathematics with Edward Sang. He trained as an architect under William Henry Playfair, Scotland’s most eminent architect of the time, leaving Playfair's practice in 1831 to set up on his own. During this time he competed, but was unsuccessful, in the competition to design the Scott Monument. He established a partnership with Glaswegian engineer William Gale, and together they won two competitions for the design of the West Church in Greenock ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |


.jpg)