|
List Of Military Aircraft Of Nazi Germany
For unbuilt projects, see List of German aircraft projects, 1939–45. For missiles, see List of German guided weapons of World War II. Aero * Aero Ab-101 captured from Czechoslovakia and used as trainer * Aero A.304 captured from Czechoslovakia and used as trainer Albatros *Albatros Al 101 'L 101', two-seat sportsplane, 1930 *Albatros Al 102 'L 102', two-seat sportsplane, 1931 *Albatros Al 103 'L 103', two-seat sportsplane, 1932 Arado * Arado Ar 64 fighter *Arado Ar 65 fighter/trainer *Arado Ar 66 trainer/night fighter * Arado Ar 67 fighter (prototype) *Arado Ar 68 fighter * Arado Ar 69 trainer (prototypes), 1933 * Arado Ar 76 fighter/trainer *Arado Ar 80 fighter (prototype) * Arado Ar 81 dive bomber (prototype), 1936 * Arado Ar 95 patrol/reconnaissance floatplane, 1936 *Arado Ar 96 trainer *Arado Ar 196 ship-borne reconnaissance/patrol floatplane *Arado Ar 197 naval fighter (prototype) *Arado Ar 198 reconnaissance (prototype) *Arado Ar 199 seaplane trainer (prototypes) *Arado Ar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of German Aircraft Projects, 1939–45
A ''list'' is any set of items in a row. List or lists may also refer to: People * List (surname) Organizations * List College, an undergraduate division of the Jewish Theological Seminary of America * SC Germania List, German rugby union club Other uses * Angle of list, the leaning to either port or starboard of a ship * List (information), an ordered collection of pieces of information ** List (abstract data type), a method to organize data in computer science * List on Sylt, previously called List, the northernmost village in Germany, on the island of Sylt * ''List'', an alternative term for ''roll'' in flight dynamics * To ''list'' a building, etc., in the UK it means to designate it a listed building that may not be altered without permission * Lists (jousting), the barriers used to designate the tournament area where medieval knights jousted * ''The Book of Lists'', an American series of books with unusual lists See also * The List (other) * Listing (di ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Arado Ar 96
The Arado Ar 96 was a German single-engine, low-wing monoplane of all-metal construction, produced by Arado Flugzeugwerke. It was the ''Luftwaffe''s standard advanced trainer during World War II. Design and development Designed by Walter Blume as the result of a 1936 Reich Air Ministry tender, the prototype, powered by a 179 kW (240 hp) Argus As 10c engine, first flew in 1938. In 1939, an initial batch of Ar 96A aircraft was produced. This was followed by the major production series, the more powerful Ar 96B, fitted with the Argus As 410 engine. In 1943, Arado started development of a new derivative of the Ar 96, using non-strategic metals and wood, to be powered by a Argus As 411 MA engine. The French company SIPA was ordered to build three prototypes and 25 preseries aircraft, but the Allied invasion of France forced the Germans to shift production of the Ar 396 to Czechoslovakia.Nëel June 1977, p. 3Smith & Kay 1972, p. 54 The first Czech-built example flew on 24 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Arado E
Arado may refer to: * Arado Flugzeugwerke, a German aircraft company * Arwad Arwad, the classical Aradus ( ar, أرواد), is a town in Syria on an eponymous island in the Mediterranean Sea. It is the administrative center of the Arwad Subdistrict (''nahiyah''), of which it is the only locality. [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Arado Ar 532
The Arado Ar 232 ''Tausendfüßler'' (German: "Millipede"), sometimes also called '' Tatzelwurm'', was a cargo aircraft, designed and built in small numbers by the German firm Arado Flugzeugwerke during World War II. The design introduced, or brought together, almost all of the features now considered to be standard in modern cargo transport aircraft designs, including a box-like fuselage slung beneath a high wing; a rear loading ramp (that had first appeared on the December 1939-flown Junkers Ju 90 V5 fifth prototype four-engined transport via its ''Trapoklappe''); a high-mounted twin tail for easy access to the hold; and various features for operating from rough fields. Although the ''Luftwaffe'' was interested in replacing or supplementing its fleet of outdated Junkers Ju 52/3m transports, it had an abundance of types in production at the time, and did not purchase large numbers of the Ar 232. Development Even before the prototypes were complete in 1941, the Focke-Wulf Fw 190 p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Arado Ar 440
The Arado Ar 240 was a German twin-engine, multi-role heavy fighter aircraft, developed for the ''Luftwaffe'' during World War II by Arado Flugzeugwerke. Its first flight was in 1940, but problems with the design hampered development, and it remained only marginally stable throughout the prototype phase. The project was eventually cancelled, with the existing airframes used for a variety of test purposes. Design and development The Ar 240 came about as the response to a 1938 request for a much more capable second-generation heavy fighter to replace the Messerschmitt Bf 110, which was becoming outdated. Both Arado and Messerschmitt responded. Messerschmitt's response, the Me 210, was a totally new design, but thanks to Messerschmitt's experience with the ''Zerstörer'' ("Destroyer") concept, it would be able to enter service quickly. Arado's design was considerably more ambitious for the smaller firm, a dream project of Arado's chief designer, Walter Blume, since the mid-1930s. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Arado Ar 396
The Arado Ar 96 was a German single-engine, low-wing monoplane of all-metal construction, produced by Arado Flugzeugwerke. It was the ''Luftwaffe''s standard advanced trainer during World War II. Design and development Designed by Walter Blume as the result of a 1936 Reich Air Ministry tender, the prototype, powered by a 179 kW (240 hp) Argus As 10c engine, first flew in 1938. In 1939, an initial batch of Ar 96A aircraft was produced. This was followed by the major production series, the more powerful Ar 96B, fitted with the Argus As 410 engine. In 1943, Arado started development of a new derivative of the Ar 96, using non-strategic metals and wood, to be powered by a Argus As 411 MA engine. The French company SIPA was ordered to build three prototypes and 25 preseries aircraft, but the Allied invasion of France forced the Germans to shift production of the Ar 396 to Czechoslovakia.Nëel June 1977, p. 3Smith & Kay 1972, p. 54 The first Czech-built example flew on 24 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Arado Ar 240
The Arado Ar 240 was a German twin-engine, multi-role heavy fighter aircraft, developed for the ''Luftwaffe'' during World War II by Arado Flugzeugwerke. Its first flight was in 1940, but problems with the design hampered development, and it remained only marginally stable throughout the prototype phase. The project was eventually cancelled, with the existing airframes used for a variety of test purposes. Design and development The Ar 240 came about as the response to a 1938 request for a much more capable second-generation heavy fighter to replace the Messerschmitt Bf 110, which was becoming outdated. Both Arado and Messerschmitt responded. Messerschmitt's response, the Me 210, was a totally new design, but thanks to Messerschmitt's experience with the ''Zerstörer'' ("Destroyer") concept, it would be able to enter service quickly. Arado's design was considerably more ambitious for the smaller firm, a dream project of Arado's chief designer, Walter Blume, since the mid-1930s. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
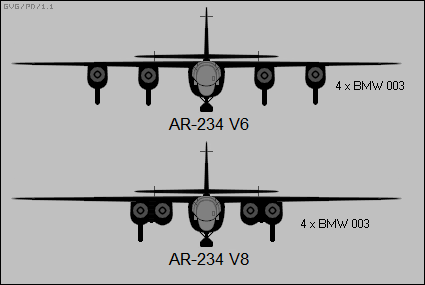
Arado Ar 234
The Arado Ar 234 ''Blitz'' (English: lightning) is a jet-powered bomber designed and produced by the German aircraft manufacturer Arado. It was the world's first operational turbojet-powered bomber, seeing service during the latter half of the Second World War. Development of the Ar 234 can be traced back to the latter half of 1940 and the request to tender from the Ministry of Aviation to produce a jet-powered high-speed reconnaissance aircraft. Arado was the only respondent with their ''E.370'' design. While its range was beneath that of the Ministry's specification, an initial order for two prototypes was promptly issued to the company, designated ''Ar 234''. While both of the prototypes had been mostly completed prior to the end of 1941, the Junkers Jumo 004 turbojet engines were not available prior to February 1943. Due to engine unreliability, the maiden flight of the Ar 234 V1 was delayed until 30 July 1943. In addition to the original reconnaissance-orientated ''Ar 23 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Arado Ar 233
The Arado Ar 233 was a 1940s German design for a civil twin-engined amphibian flying boat, developed by Dewoitine in France under the control of Arado Flugzeugwerke.Bridgeman 1988, p. 156 Design and development The Ar 233 was a twin-engined flying-boat with room for ten passengers. It would have been powered by either two BMW 323 or BMW 801 engines. A retractable tricycle landing gear would have allowed amphibious operation. A mockup was completed by Dewoitine in German-occupied France, but the project was abandoned due to the Liberation of France The liberation of France in the Second World War was accomplished through diplomacy, politics and the combined military efforts of the Allied Powers, Free French forces in London and Africa, as well as the French Resistance. Nazi Germany inv ... in 1944. General history of the Aircraft The Arado Ar 233 was intended for civilian use only but, later on in the development process, the Germans wanted to weaponize it and make it suita ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Arado Ar 232
The Arado Ar 232 ''Tausendfüßler'' (German: "Millipede"), sometimes also called '' Tatzelwurm'', was a cargo aircraft, designed and built in small numbers by the German firm Arado Flugzeugwerke during World War II. The design introduced, or brought together, almost all of the features now considered to be standard in modern cargo transport aircraft designs, including a box-like fuselage slung beneath a high wing; a rear loading ramp (that had first appeared on the December 1939-flown Junkers Ju 90 V5 fifth prototype four-engined transport via its ''Trapoklappe''); a high-mounted twin tail for easy access to the hold; and various features for operating from rough fields. Although the ''Luftwaffe'' was interested in replacing or supplementing its fleet of outdated Junkers Ju 52/3m transports, it had an abundance of types in production at the time, and did not purchase large numbers of the Ar 232. Development Even before the prototypes were complete in 1941, the Focke-Wulf Fw 190 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Arado Ar 231
The Arado Ar 231 was a lightweight floatplane, developed during World War II in Germany as a scout plane for submarines by Arado. The need to be stored inside the submarine necessitated compromises in design that made this single-seat seaplane of little practical use. Design and development Designed from the outset for use on U-boat " cruisers", like the Type XI B, the Ar 231 was a light parasol-wing aircraft. The aircraft was powered by a 119 kW (160 hp) Hirth HM 501 inline engine, weighed around 1,000 kg (2,200 lb), and had a 10 m (33 ft) wingspan. The design led to a simple and compact aircraft that could be fitted into a storage cylinder only 2 m (6 ft 7 in) in diameter. For ease of storage, the Ar 231's wings featured detachable sections that two operators could remove in less than six minutes. One unusual feature was an offset wing design, with the right wing root attaching to the wing's tilted center section (elevated above ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Arado Ar 199
The Arado Ar 199 was a floatplane aircraft, built by Arado Flugzeugwerke. It was a low-wing monoplane, designed in 1938 to be launched from a catapult and operated over water. The enclosed cockpit had two side-by-side seats for instructor and student, and a third, rear seat, for a trainee-navigator or radio operator. Two of the 5 prototypes, ''D-IFRB'' and ''D-ISBC'' did serve as trainers and were used for air-sea rescue Air-sea rescue (ASR or A/SR, also known as sea-air rescue), and aeronautical and maritime search and rescue (AMSAR) by the ICAO and International Maritime Organization, IMO, is the coordinated search and rescue (SAR) of the survivors of emergenc ... operations from Northern Norway. Specifications(Ar 199) References ;Notes ;Bibliography * {{RLM aircraft designations 1930s German military trainer aircraft Ar 199 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |