|
List Of MeSH Codes (C09)
The following is a partial list of the "C" codes for Medical Subject Headings (MeSH), as defined by the United States National Library of Medicine (NLM). This list continues the information at List of MeSH codes (C08). Codes following these are found at List of MeSH codes (C10). For other MeSH codes, see List of MeSH codes. The source for this content is the set o2006 MeSH Treesfrom the NLM. – otorhinolaryngologic diseases – ciliary motility disorders – kartagener syndrome – ear diseases – cholesteatoma, middle ear – ear deformities, acquired – ear neoplasms – earache – hearing disorders * – hearing loss * – deafness * – hearing loss, bilateral * – hearing loss, conductive * – hearing loss, functional * – hearing loss, high-frequency * – hearing loss, mixed conductive-sensorineural * – hearing loss, sensorineural * – hearing loss, central * – hearing loss, noise-induced * – presbycusis * – usher syndromes * ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Medical Subject Headings
Medical Subject Headings (MeSH) is a comprehensive controlled vocabulary for the purpose of indexing journal articles and books in the life sciences. It serves as a thesaurus that facilitates searching. Created and updated by the United States National Library of Medicine (NLM), it is used by the MEDLINE/PubMed article database and by NLM's catalog of book holdings. MeSH is also used by ClinicalTrials.gov registry to classify which diseases are studied by trials registered in ClinicalTrials. MeSH was introduced in the 1960s, with the NLM's own index catalogue and the subject headings of the Quarterly Cumulative Index Medicus (1940 edition) as precursors. The yearly printed version of MeSH was discontinued in 2007; MeSH is now available only online. It can be browsed and downloaded free of charge through PubMed. Originally in English, MeSH has been translated into numerous other languages and allows retrieval of documents from different origins. Structure MeSH vocabulary is divi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hearing Loss, Conductive
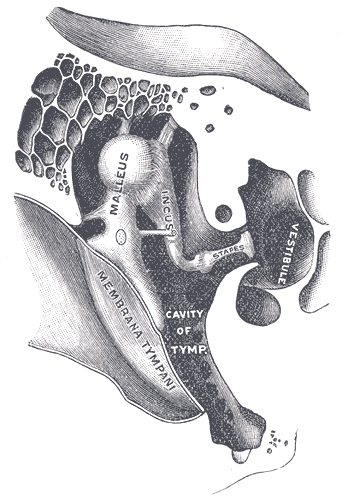
Conductive hearing loss (CHL) occurs when there is a problem transferring sound waves anywhere along the pathway through the outer ear, tympanic membrane (eardrum), or middle ear (ossicles). If a conductive hearing loss occurs in conjunction with a sensorineural hearing loss, it is referred to as a mixed hearing loss. Depending upon the severity and nature of the conductive loss, this type of hearing impairment can often be treated with surgical intervention or pharmaceuticals to partially or, in some cases, fully restore hearing acuity to within normal range. However, cases of permanent or chronic conductive hearing loss may require other treatment modalities such as hearing aid devices to improve detection of sound and speech perception. Causes Common causes of conductive hearing loss include: External ear * Cerumen (earwax) or foreign body in the external auditory canal * Otitis externa, infection or irritation of the outer ear * Exostoses, abnormal growth of bone wi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
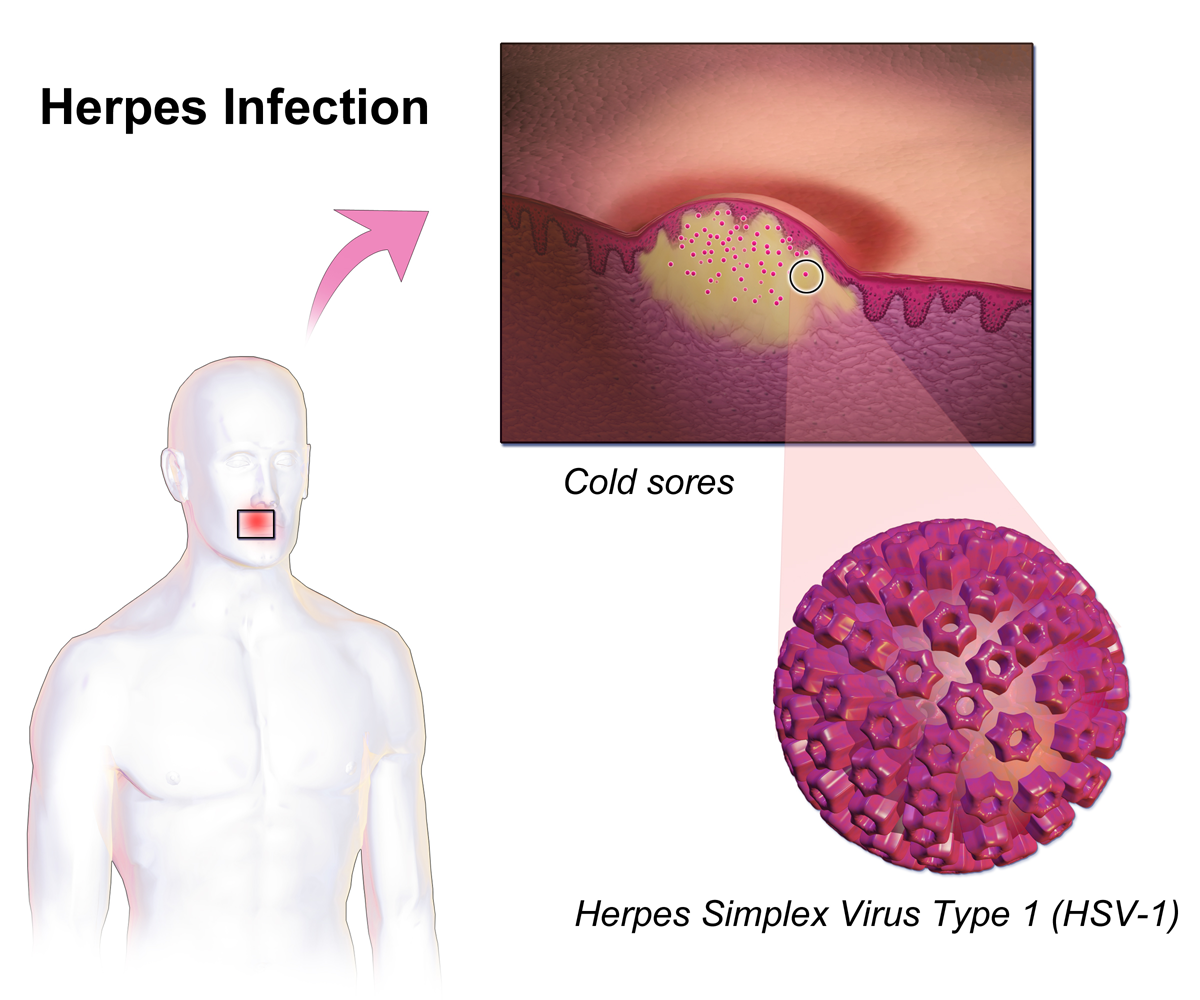
Herpes Zoster Oticus
Herpes simplex is a viral infection caused by the herpes simplex virus. Infections are categorized based on the part of the body infected. Oral herpes involves the face or mouth. It may result in small blisters in groups often called cold sores or fever blisters or may just cause a sore throat. Genital herpes, often simply known as herpes, involves the genitalia. It may have minimal symptoms or form blisters that break open and result in small ulcers. These typically heal over two to four weeks. Tingling or shooting pains may occur before the blisters appear. Herpes cycles between periods of active disease followed by periods without symptoms. The first episode is often more severe and may be associated with fever, muscle pains, swollen lymph nodes and headaches. Over time, episodes of active disease decrease in frequency and severity. Herpetic whitlow typically involves the fingers or thumb. Herpes simplex keratitis involves the eye. Herpesviral encephalitis involv ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tinnitus
Tinnitus is the perception of sound when no corresponding external sound is present. Nearly everyone experiences a faint "normal tinnitus" in a completely quiet room; but it is of concern only if it is bothersome, interferes with normal hearing, or is associated with other problems. While often described as a ringing, it may also sound like a clicking, buzzing, hissing or roaring. It may be soft or loud, low- or high- pitched, and may seem to come from one or both ears or from the head itself. In some people, it may interfere with concentration, and in some cases is associated with anxiety and depression. Tinnitus is usually associated with a degree of hearing loss and decreased comprehension of speech in noisy environments. It is common, affecting about 10–15% of people. Most, however, tolerate it well, and it is a significant problem in only 1–2% of all people. It can trigger a fight-or-flight response, as the brain may perceive it as dangerous and important. The word ' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hyperacusis
Hyperacusis is the increased sensitivity to sound and a low tolerance for environmental noise. Definitions of hyperacusis can vary significantly; it can refer to normal noises being perceived as: loud, annoying, painful, fear-inducing, or a combination of those, and is often categorized into four subtypes: loudness, pain, annoyance, and fear. It can be a highly debilitating hearing disorder. Hyperacusis is often coincident with tinnitus. The latter is more common and there are important differences between their involved mechanisms. Little is known about the prevalence of hyperacusis, in part due to the degree of variation in the term's definition. Reported prevalence in children and adolescents ranges from 3% to 17%. Signs and symptoms In hyperacusis, the symptoms are ear pain, annoyance, distortions, and general intolerance to many sounds that most people are unaffected by. Crying spells or panic attacks may result from the experience of hyperacusis. It may affect only one or ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hearing Loss, Unilateral
Unilateral hearing loss (UHL) is a type of hearing impairment where there is normal hearing in one ear and impaired hearing in the other ear. Signs and symptoms Patients with unilateral hearing loss have difficulty: * Hearing conversation on their impaired side * Localizing sound * Understanding speech in the presence of background noise * In interpersonal interaction in social settings * Focusing on individual sound sources in large, open environments * Heavy impairment of the auditory Figure–ground perception In quiet conditions, speech discrimination is no worse than normal hearing in those with partial deafness; however, in noisy environments speech discrimination is almost always severe. The prevalence is 3–8.3% of the population. Individuals who are diagnosed with Single Sided Deafness have difficulties with sound localization and speech in noise discrimination. Children with SSD are more likely to experience developmental delays- school, speech, behavioral problems. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hearing Loss, Sudden
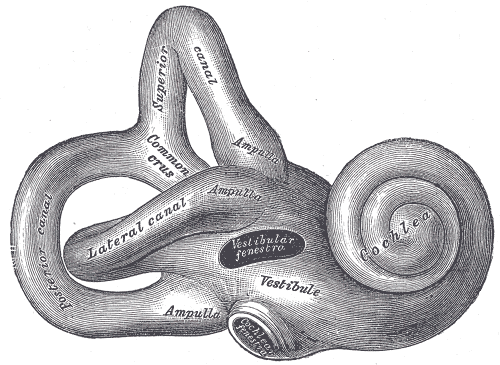
Hearing, or auditory perception, is the ability to perceive sounds through an organ, such as an ear, by detecting vibrations as periodic changes in the pressure of a surrounding medium. The academic field concerned with hearing is auditory science. Sound may be heard through solid, liquid, or gaseous matter. It is one of the traditional five senses. Partial or total inability to hear is called hearing loss. In humans and other vertebrates, hearing is performed primarily by the auditory system: mechanical waves, known as vibrations, are detected by the ear and transduced into nerve impulses that are perceived by the brain (primarily in the temporal lobe). Like touch, audition requires sensitivity to the movement of molecules in the world outside the organism. Both hearing and touch are types of mechanosensation. Hearing mechanism There are three main components of the human auditory system: the outer ear, the middle ear, and the inner ear. Outer ear The o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Usher Syndromes
Usher syndrome, also known as Hallgren syndrome, Usher–Hallgren syndrome, retinitis pigmentosa–dysacusis syndrome or dystrophia retinae dysacusis syndrome, is a rare genetic disorder caused by a mutation in any one of at least 11 genes resulting in a combination of hearing loss and visual impairment. It is a major cause of deafblindness and is at present incurable. Usher syndrome is classed into three subtypes (I, II and III) according to the genes responsible and the onset of deafness. All three subtypes are caused by mutations in genes involved in the function of the inner ear and retina. These mutations are inherited in an autosomal recessive pattern. The occurrence of Usher syndrome varies across the world and across the different syndrome types, with rates as high as 1 in 12,500 in Germany to as low as 1 in 28,000 in Norway. Type I is most common in Ashkenazi Jewish and Acadian populations, and type III is rarely found outside Ashkenazi Jewish and Finnish populat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Presbycusis
Presbycusis (also spelled presbyacusis, from Greek πρέσβυς ''presbys'' "old" + ἄκουσις ''akousis'' "hearing"), or age-related hearing loss, is the cumulative effect of aging on hearing. It is a progressive and irreversible bilateral symmetrical age-related sensorineural hearing loss resulting from degeneration of the cochlea or associated structures of the inner ear or auditory nerves. The hearing loss is most marked at higher frequencies. Hearing loss that accumulates with age but is caused by factors other than normal aging ( nosocusis and sociocusis) is not presbycusis, although differentiating the individual effects of distinct causes of hearing loss can be difficult. The cause of presbycusis is a combination of genetics, cumulative environmental exposures and pathophysiological changes related to aging. At present there are no preventive measures known; treatment is by hearing aid or surgical implant. Presbycusis is the most common cause of hearing loss, affec ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hearing Loss, Noise-induced
Noise-induced hearing loss (NIHL) is a hearing impairment resulting from exposure to loud sound. People may have a loss of perception of a narrow range of frequencies or impaired perception of sound including sensitivity to sound or ringing in the ears. When exposure to hazards such as noise occur at work and is associated with hearing loss, it is referred to as occupational hearing loss. Hearing may deteriorate gradually from chronic and repeated noise exposure (such as to loud music or background noise) or suddenly from exposure to impulse noise, which is a short high intensity noise (such as a gunshot or airhorn). In both types, loud sound overstimulates delicate hearing cells, leading to the permanent injury or death of the cells. Once lost this way, hearing cannot be restored in humans. There are a variety of prevention strategies available to avoid or reduce hearing loss. Lowering the volume of sound at its source, limiting the time of exposure and physical protect ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hearing Loss, Central
Hearing, or auditory perception, is the ability to perceive sounds through an organ, such as an ear, by detecting vibrations as periodic changes in the pressure of a surrounding medium. The academic field concerned with hearing is auditory science. Sound may be heard through solid, liquid, or gaseous matter. It is one of the traditional five senses. Partial or total inability to hear is called hearing loss. In humans and other vertebrates, hearing is performed primarily by the auditory system: mechanical waves, known as vibrations, are detected by the ear and transduced into nerve impulses that are perceived by the brain (primarily in the temporal lobe). Like touch, audition requires sensitivity to the movement of molecules in the world outside the organism. Both hearing and touch are types of mechanosensation. Hearing mechanism There are three main components of the human auditory system: the outer ear, the middle ear, and the inner ear. Outer ear The o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hearing Loss, Sensorineural
Sensorineural hearing loss (SNHL) is a type of hearing loss in which the root cause lies in the inner ear or sensory organ ( cochlea and associated structures) or the vestibulocochlear nerve (cranial nerve VIII). SNHL accounts for about 90% of reported hearing loss . SNHL is usually permanent and can be mild, moderate, severe, profound, or total. Various other descriptors can be used depending on the shape of the audiogram, such as high frequency, low frequency, U-shaped, notched, peaked, or flat. ''Sensory'' hearing loss often occurs as a consequence of damaged or deficient cochlear hair cells. Hair cells may be abnormal at birth or damaged during the lifetime of an individual. There are both external causes of damage, including infection, and ototoxic drugs, as well as intrinsic causes, including genetic mutations. A common cause or exacerbating factor in SNHL is prolonged exposure to environmental noise, or noise-induced hearing loss. Exposure to a single very loud nois ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |