|
List Of Margraves Of Meißen
This article lists the margraves of Meissen, a march and territorial state on the eastern border of the Holy Roman Empire. History King Henry the Fowler, on his 928-29 campaign against the Slavic Glomacze tribes, had a fortress erected on a hill at Meissen (''Mišno'') on the Elbe river. Later named '' Albrechtsburg'', the castle about 965 became the seat of the Meissen margraves, installed by Emperor Otto I when the vast '' Marca Geronis'' ( Gero's march) was partitioned into five new margraviates, including Meissen, the Saxon Eastern March, and also the Northern March which eventually became the Margraviate of Brandenburg. During the tenth century, the Meissen margraves temporarily extended their territory into the Milceni lands up to the Kwisa (''Queis'') river and the border with the Silesian region of the Early Polish state. The eastern lands around Bautzen (''Budissin''), later known as Upper Lusatia, were ceded to the Polish duke Bolesław I the Brave acc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wappen Meißen
A coat of arms is a heraldic visual design on an escutcheon (i.e., shield), surcoat, or tabard (the latter two being outer garments). The coat of arms on an escutcheon forms the central element of the full heraldic achievement, which in its whole consists of a shield, supporters, a crest, and a motto. A coat of arms is traditionally unique to an individual person, family, state, organization, school or corporation. The term itself of 'coat of arms' describing in modern times just the heraldic design, originates from the description of the entire medieval chainmail 'surcoat' garment used in combat or preparation for the latter. Rolls of arms are collections of many coats of arms, and since the early Modern Age centuries, they have been a source of information for public showing and tracing the membership of a noble family, and therefore its genealogy across time. History Heraldic designs came into general use among European nobility in the 12th century. Systematic, heri ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
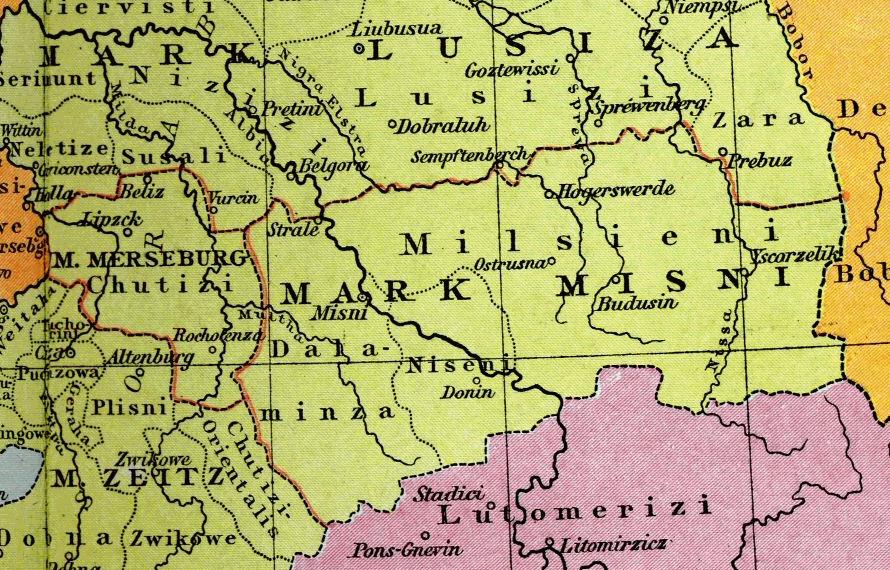
Milceni
The Milceni or Milzeni ( cs, Milčané; german: Milzener; pl, Milczanie) were a West Slavic tribe, who settled in the present-day Upper Lusatia region. They were first mentioned in the middle of the 9th century AD by the Bavarian Geographer, who wrote of 30 ''civitates'' which possibly had fortifications. They were gradually conquered by Germans during the 10th century. Modern descendants of the Milceni are the Sorbs of the Free State of Saxony, Germany.Institut für Sorabistik.About Sorbian Language". Accessed November 8, 2006. History The Milceni travelled to Upper Lusatia in the 7th century during the Migration Period.''Bautzen.de''History. Accessed November 8, 2006. The exact borders of their settlement area are disputed. It is generally accepted that their fielded land had fruitful loess soil and had dimensions of approximately 50 km from east to west and 20 km from north to south. The northern border was in swampy and partially infertile terrain, while the south ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
War Of The Thuringen Succession
The War of the Thuringian Succession (German: ''Thüringisch-hessischer Erbfolgekrieg'') (1247–1264) was a military conflict over a successor to the last Landgrave of Thuringia for control of the state of Thuringia (now in modern-day Germany). Cause of the conflict With the death of the childless Landgrave Henry Raspe in 1247, the Ludowingian line of Thuringian landgraves became extinct in the male line. His property included not only large parts of Thuringia, but also the Countship of Hesse had come into Ludowingian possession through the female line. In 1122, before his acquisition of the title of Landgrave, Count Louis I of Thuringia had married Hedwig of Gudensberg, the female heir of the Hessian comital family of the Gisonen. The Gisonen, whose lands were initially mainly in the upper Lahn area, had previously come into the significant inheritance of Count Werner in Lower Hesse. Then, through the marriage of Giso IV with Kunigunde of Bilstein, they had also acquired wides ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pleissnerland
Pleissnerland, Pleissenland or the Imperial Territory of Pleissenland (german: Reichsterritorium Pleißenland; la, Terra Plisensis) was a '' Reichsgut'' of the Holy Roman Empire, which meant that it was directly possessed by the respective elected King of the Romans or Emperor. It was named for the Pleiße River, and was located in what is now the border region between the German states of Thuringia and Saxony south of Leipzig, including the towns of Altenburg, Chemnitz, Zwickau and Leisnig. History The area east of the Sorbian March was conquered between 927 and 929 by King Henry I of Germany in the course of his campaign against the Polabian Slavs, it was incorporated as '' Gau Plisni'' into the Saxon ''Marca Geronis''. Upon the weakening of the Imperial authority during the 11th century Investiture Controversy, the estates gradually came under the rule of local comital dynasties, foremost the Burgraves of Nuremberg and the Margraves of Meissen. Emperor Lothair III (1133-1137) b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
House Of Wettin
The House of Wettin () is a dynasty of German kings, prince-electors, dukes, and counts that once ruled territories in the present-day German states of Saxony, Saxony-Anhalt and Thuringia. The dynasty is one of the oldest in Europe, and its origins can be traced back to the town of Wettin, Saxony-Anhalt. The Wettins gradually rose to power within the Holy Roman Empire. Members of the family became the rulers of several medieval states, starting with the Saxon Eastern March in 1030. Other states they gained were Meissen in 1089, Thuringia in 1263, and Saxony in 1423. These areas cover large parts of Central Germany as a cultural area of Germany. The family divided into two ruling branches in 1485 by the Treaty of Leipzig: the Ernestine and Albertine branches. The older Ernestine branch played a key role during the Protestant Reformation. Many ruling monarchs outside Germany were later tied to its cadet branch, the House of Saxe-Coburg and Gotha. The Albertine branch, while less ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Duchy Of Saxony
The Duchy of Saxony ( nds, Hartogdom Sassen, german: Herzogtum Sachsen) was originally the area settled by the Saxons in the late Early Middle Ages, when they were subdued by Charlemagne during the Saxon Wars from 772 and incorporated into the Carolingian Empire (Francia) by 804. Upon the 843 Treaty of Verdun, Saxony was one of the five German stem duchies of East Francia; Duke Henry the Fowler was elected German king in 919. Upon the deposition of the Welf duke Henry the Lion in 1180, the ducal title fell to the House of Ascania, while numerous territories split from Saxony, such as the Principality of Anhalt in 1218 and the Welf Duchy of Brunswick-Lüneburg in 1235. In 1296 the remaining lands were divided between the Ascanian dukes of Saxe-Lauenburg and Saxe-Wittenberg, the latter obtaining the title of Electors of Saxony by the Golden Bull of 1356. Geography The Saxon stem duchy covered the greater part of present-day Northern Germany, including the modern German states ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
English Feudal Barony
In the kingdom of England, a feudal barony or barony by tenure was the highest degree of feudal land tenure, namely ''per baroniam'' (Latin for "by barony"), under which the land-holder owed the service of being one of the king's barons. The duties owed by and the privileges granted to feudal barons are not exactly defined, but they involved the duty of providing soldiers to the royal feudal army on demand by the king, and the privilege of attendance at the king's feudal court, the precursor of parliament. If the estate-in-land held by barony contained a significant castle as its ''caput baroniae'' and if it was especially large – consisting of more than about 20 knight's fees (each loosely equivalent to a manor) – then it was termed an honour. The typical honour had properties scattered over several shires, intermingled with the properties of others. This was a specific policy of the Norman kings, to avoid establishing any one area under the control of a single lord. U ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Bohemian Monarchs
The Duchy of Bohemia was established in 870 and raised to the Kingdom of Bohemia in 1198. Several Bohemian monarchs ruled as non-hereditary kings beforehand, first gaining the title in 1085. From 1004 to 1806, Bohemia was part of the Holy Roman Empire, and its ruler was an elector. During 1526–1804 the Kingdom of Bohemia, together with the other lands of the Bohemian Crown, was ruled under a personal union as part of the Habsburg monarchy. From 1804 to 1918, Bohemia was part of the Austrian Empire, which itself was part of the dual monarchy of Austria-Hungary from 1867 to 1918. Following the dissolution of the monarchy, the Bohemian lands, now also referred to as Czech lands, became part of Czechoslovakia, and they have formed today's Czech Republic since 1993. Legendary rulers of Bohemia * praotec Čech (Pater Boemus) * Lech * Krok * Libuše, duchess * Přemysl the Ploughman, her husband * Nezamysl * Mnata * Vojen * Vnislav * Křesomysl * Neklan * Hostivít Princes ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Peace Of Bautzen
The Peace of Bautzen (; ; ) was a treaty concluded on 30 January 1018, between Holy Roman Emperor Henry II and Bolesław I of Poland which ended a series of Polish-German wars over the control of Lusatia and Upper Lusatia (''Milzenerland'' or ''Milsko'', the eastern part of the margraviate of Meissen (''Miśnia'')) as well as Bohemia, Moravia and Slovakia. Bolesław had enjoyed the close friendship of the emperor Otto III and after his death supported one of Otto's followers, Eckard I, Margrave of Meissen for the position of Holy Roman Emperor, against the claims of Henry II. After both emperor Otto III and Eckard's death in 1002, Bolesław conquered Eckard's domain of Meissen, as well as the march of Lusatia. Once Henry secured his position within Germany, an agreement was reached which left Bolesław with Lusatia and Upper Lusatia while the Polish duke in turn recognized Henry as Holy Roman Emperor. Fighting soon resumed, however, after an unsuccessful assassination attempt a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bolesław I The Brave
Bolesław I the Brave ; cs, Boleslav Chrabrý; la, Boleslaus I rex Poloniae (17 June 1025), less often known as Bolesław the Great, was Duke of Poland from 992 to 1025, and the first King of Poland in 1025. He was also Duke of Bohemia between 1003 and 1004 as Boleslaus IV. A member of the ancient Piast dynasty, Bolesław was a capable monarch and a strong mediator in Central European affairs. He continued to proselytise Western Christianity among his subjects and raised Poland to the rank of a kingdom, thus becoming the first Polish ruler to hold the title of ''rex'', Latin for king. The son of Mieszko I of Poland by his first wife Dobrawa of Bohemia, Bolesław ruled Lesser Poland already during the final years of Mieszko's reign. When the country became divided in 992, he banished his father's last consort, Oda of Haldensleben, purged his half-brothers along with their adherents and successfully reunified Poland by 995. As a devout Christian, Bolesław supported the mis ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Upper Lusatia
Upper Lusatia (german: Oberlausitz ; hsb, Hornja Łužica ; dsb, Górna Łužyca; szl, Gōrnŏ Łużyca; pl, Łużyce Górne or ''Milsko''; cz, Horní Lužice) is a historical region in Germany and Poland. Along with Lower Lusatia to the north, it makes up the region of Lusatia, named after the Slavic ''Lusici'' tribe. Both parts of Lusatia are home to the West Slavic minority group of the Sorbs. The major part of Upper Lusatia is part of the German federal state of Saxony, roughly comprising Bautzen district and Görlitz district. The northwestern extremity, around Ruhland and Tettau, is incorporated into the Oberspreewald-Lausitz district of the state of Brandenburg. The eastern part of Upper Lusatia is in Poland, east of the Neisse (''Nysa'') river, in Lower Silesian Voivodeship. A small strip of land in the north around Łęknica is incorporated into Lubusz Voivodeship, along with the Polish part of Lower Lusatia. The historic capital of Upper Lusatia is Bautzen/ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bautzen
Bautzen () or Budyšin () is a hill-top town in eastern Saxony, Germany, and the administrative centre of the district of Bautzen. It is located on the Spree river. In 2018 the town's population was 39,087. Until 1868, its German name was ''Budissin''. In 1945 the Battle of Bautzen was Hitler’s last victory against the Soviet Union during the Battle of Berlin . Bautzen is often regarded as the unofficial, but historical capital of Upper Lusatia. The town is also the most important cultural centre of the Sorbian minority, which constitutes about 10 percent of Bautzen's population. Asteroid '' 11580 Bautzen'' is named in honour of the city. Names Like other cities and places in Lusatia, Bautzen has several different names across languages. Its German name was also officially changed in 1868. As well as ''Bautzen'' (German) and ''Budyšin'' (Upper Sorbian), the town has had the following names: * German: ''Budissin'' (variants used from c. 11th century onwards; Saxon governme ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |