|
List Of Invasive Fungi
Some fungi are considered invasive species in certain parts of the world: *''Amanita muscaria'' *''Amanita phalloides'' *'' Batrachochytrium dendrobatidis'' *'' Batrachochytrium salamandrivorans'' *'' Carpenterella'' *'' Cryphonectria parasitica'' – causes chestnut blight *'' Cucumispora dikerogammari'' *''Geosmithia morbida'' which, in partnership with the walnut twig beetle ''Pityophthorus juglandis'', causes thousand cankers disease *'' Heterobasidion irregulare'' *''Hymenoscyphus fraxineus'' *''Puccinia horiana'' – causes Chrysanthemum white rust *'' Puccinia psidii'' *'' Pucciniastrum americanum'' *'' Ophiognomonia clavigignenti-juglandacearum'' *certain ''Ophiostoma'' species which cause Dutch elm disease **''Ophiostoma ulmi'' **''Ophiostoma himal-ulmi'' **''Ophiostoma novo-ulmi'' *'' Pseudogymnoascus destructans'' *''Uredo rangelii'' References {{Reflist fungi A fungus ( : fungi or funguses) is any member of the group of eukaryotic organisms that includes mi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chestnut Blight On Tree In Adams County Ohio
The chestnuts are the deciduous trees and shrubs in the genus ''Castanea'', in the beech family Fagaceae. They are native to temperate climate, temperate regions of the Northern Hemisphere. The name also refers to the edible nut (fruit), nuts they produce. The unrelated horse chestnuts (genus ''Aesculus'') are not true chestnuts, but are named for producing nuts of similar appearance that are mildly poisonous to humans. True chestnuts should also not be confused with Eleocharis dulcis, water chestnuts, which are tubers of an aquatic herbaceous plant in the sedge family Cyperaceae. Other species commonly mistaken for chestnut trees are the chestnut oak (''Quercus prinus'') and the American beech (''Fagus grandifolia''),Chestnut Tree in chestnuttree.net. both of which are also in the Fagaceae family. Brazil nuts, called "Br ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hymenoscyphus Fraxineus
''Hymenoscyphus fraxineus'' () is an ascomycete fungus that causes ash dieback, a chronic fungal disease of ash trees in Europe characterised by leaf loss and crown dieback in infected trees. The fungus was first scientifically described in 2006 under the name ''Chalara fraxinea''. Four years later it was discovered that ''Chalara fraxinea'' is the asexual (anamorphic) stage of a fungus that was subsequently named ''Hymenoscyphus pseudoalbidus'' and then renamed as ''Hymenoscyphus fraxineus''. Trees reported dying in Poland in 1992 are now believed to have been infected with this pathogen. It is now widespread in Europe, with up to 85% mortality rates recorded in plantations and 69% in woodlands. It is closely related to a native fungus '' Hymenoscyphus albidus'', which is harmless to European ash trees. According to a 2016 report published in the Journal of Ecology a combination of ''H. fraxineus'' and emerald ash borer attacks could wipe out European ash trees. Genetics The f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
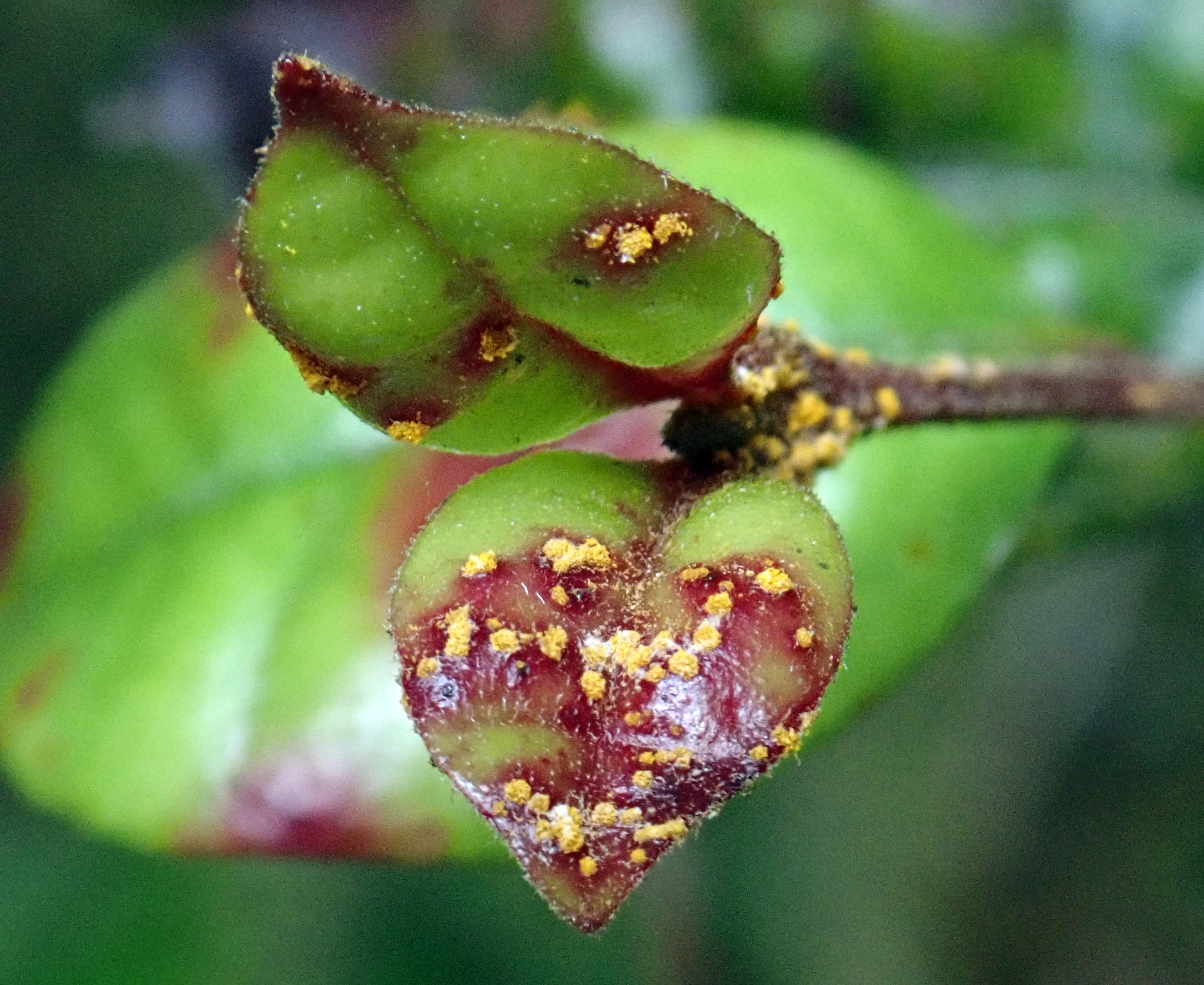
Uredo Rangelii
''Austropuccinia psidii'', commonly known as myrtle rust, guava rust, or ʻōhiʻa rust; is a rust (a type of plant pathogen) native to South America that affects plants in the family Myrtaceae. It is a member of the fungal complex called the guava rust (''Puccinia psidii'') group. The spores have a distinctive yellow to orange colour, occasionally encircled by a purple ring. They are found on lesions on new growth including shoots, leaves, buds and fruits. Leaves become twisted and may die. Infections in highly susceptible species may result in the death of the host plant. As of late 2013, it is infecting around 179 species in New South Wales and Queensland, from 41 genera (around 46% of genera in the Myrtaceae) in Australia. Importance ''Austropuccinia psidii'', a myrtle rust or a rust fungus, has a large host range for infection making it difficult for disease control and prevention, but it has been seen to have biological uses for it. In Florida, the pathogen has been ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pseudogymnoascus Destructans
''Pseudogymnoascus destructans'' (formerly known as ''Geomyces destructans'') is a psychrophilic (cold-loving) fungus that causes white-nose syndrome (WNS), a fatal disease that has devastated bat populations in parts of the United States and Canada. Unlike species of ''Geomyces'', ''P. destructans'' forms asymmetrically curved conidia. ''Pseudogymnoascus destructans'' grows very slowly on artificial media and cannot grow at temperatures above 20 °C. It can grow around 4 °C to 20 °C, which encompasses the temperatures found in winter bat hibernacula. Phylogenic evaluation has revealed this organism should be reclassified under the family ''Pseudeurotiaceae'', changing its name to ''Pseudogymnoascus destructans''. History In 2008, Blehert ''et al.'' described the fungus associated with white-nose syndrome as a member of the genus ''Geomyces''. In 2009, Gargas ''et al.'' were the first to describe the fungus as a unique species; the specific name they chose, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ophiostoma Novo-ulmi
''Ophiostoma'' is a genus of fungi within the family Ophiostomataceae. It was circumscribed in 1919 by mycologists Hans Sydow and Paul Sydow. Species *''Ophiostoma adjuncti'' *'' Ophiostoma ainoae'' *'' Ophiostoma allantosporum'' *'' Ophiostoma angusticollis'' *'' Ophiostoma araucariae'' *'' Ophiostoma bacillisporum'' *'' Ophiostoma bicolor'' *''Ophiostoma bragantinum'' *'' Ophiostoma brevicolle'' *''Ophiostoma brunneociliatum'' *''Ophiostoma brunneum'' *'' Ophiostoma cantabriense'' *''Ophiostoma canum'' *''Ophiostoma carpenteri''Hausner, G., et al. 2003Three new species of ''Ophiostoma'' and notes on ''Cornuvesica falcate''.''Canadian Journal of Botany'' 81(1) 40–48. *''Ophiostoma clavatum'' *''Ophiostoma colliferum'' *''Ophiostoma coronatum'' *''Ophiostoma cuculatum'' *''Ophiostoma distortum'' *''Ophiostoma epigloeum'' *''Ophiostoma flexuosum'' *''Ophiostoma grande'' *''Ophiostoma himal-ulmi'' *''Ophiostoma longicollum'' *''Ophiostoma manitobense'' *'' Ophiostoma megalobrun ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ophiostoma Himal-ulmi
''Ophiostoma himal-ulmi'' is a species of fungus in the family Ophiostomataceae. It is one of the causative agents of Dutch elm disease. It was first isolated around breeding galleries of scolytid beetles in the bark of ''Ulmus wallichiana'' (the Himalayan elm). This, together with the fact that it is endemic to the Himalayas, is the reason it is named ''himal-ulmi'' (‘of the Himalayan elm’; means ‘of the elm’). It is outcrossing and heterothallic, with two sexual compatibility types: A and B, occurring in a near 1:1 ratio in nature. It also exhibits a distinctive colony type, an ability to produce synnemata on malt extract agar, production of perithecia with long necks, a very high level of cerato-ulmin toxin production in liquid shake cultures, and moderate to strong vascular wilt pathogenicity on ''Ulmus procera The field elm (''Ulmus minor'') cultivar 'Atinia' , commonly known as the English elm, formerly common elm and horse may, Republished 1978 by EP Publ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ophiostoma Ulmi
''Ophiostoma ulmi'' is a species of fungus in the family Ophiostomataceae. It is one of the causative agents of Dutch elm disease. It was first described under the name ''Graphium ulmi'', and later transferred to the genus ''Ophiostoma''. Dutch elm disease originated in Europe in the early 1900s. Elm trees were once an ecologically valuable tree that dominated mixed broadleaf forests, floodplains, and low areas near rivers and streams. They were planted in urban settings because of their aesthetic appeal and their ability to provide shade due to their V like shape. An outbreak of Dutch elm disease in the 1920s and again in the 1970s was responsible for the death of more than 40 million American elm trees. ''Ophiostoma ulmi'' was the first known cause of Dutch elm disease . Since its discovery in 1910, new forms of the fungus, specifically ''Ophiostoma novo-ulmi,'' have emerged and appear to be more resistant to control measures and more aggressive in their infection. Host rang ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dutch Elm Disease
Dutch elm disease (DED) is caused by a member of the sac fungi (Ascomycota) affecting elm trees, and is spread by elm bark beetles. Although believed to be originally native to Asia, the disease was accidentally introduced into Americas, America, Europe, and New Zealand. In these regions it has devastated native populations of elms that did not have resistance to the disease. The name "Dutch elm disease" refers to its identification in 1921 and later in the Netherlands by Dutch phytopathologists Marie Beatrice Schol-Schwarz, Bea Schwarz and Christine Buisman, who both worked with professor Johanna Westerdijk. The disease affects species in the genera ''Ulmus'' and ''Zelkova''; therefore it is not specific to the Ulmus × hollandica, Dutch elm hybrid. Overview Dutch elm disease (DED) is caused by ascomycete microfungi. [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ophiostoma
''Ophiostoma'' is a genus of fungi within the family Ophiostomataceae. It was circumscribed in 1919 by mycologists Hans Sydow and Paul Sydow. Species *''Ophiostoma adjuncti'' *'' Ophiostoma ainoae'' *'' Ophiostoma allantosporum'' *'' Ophiostoma angusticollis'' *'' Ophiostoma araucariae'' *'' Ophiostoma bacillisporum'' *'' Ophiostoma bicolor'' *''Ophiostoma bragantinum'' *'' Ophiostoma brevicolle'' *''Ophiostoma brunneociliatum'' *''Ophiostoma brunneum'' *'' Ophiostoma cantabriense'' *''Ophiostoma canum'' *''Ophiostoma carpenteri''Hausner, G., et al. 2003Three new species of ''Ophiostoma'' and notes on ''Cornuvesica falcate''.''Canadian Journal of Botany'' 81(1) 40–48. *''Ophiostoma clavatum'' *''Ophiostoma colliferum'' *''Ophiostoma coronatum'' *''Ophiostoma cuculatum'' *''Ophiostoma distortum'' *''Ophiostoma epigloeum'' *''Ophiostoma flexuosum'' *''Ophiostoma grande'' *''Ophiostoma himal-ulmi'' *''Ophiostoma longicollum'' *''Ophiostoma manitobense'' *'' Ophiostoma megalobrun ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ophiognomonia Clavigignenti-juglandacearum
''Ophiognomonia clavigignenti-juglandacearum'' is a mitosporic fungus that causes the lethal disease of butternut trees (''Juglans cinerea''), butternut canker. It is also known to parasitize other members of the genus '' Juglans'' on occasion, and very rarely other related trees including hickories. The fungus is found throughout North America, occurring on up to 91% of butternut trees, and may be threatening the viability of butternut as a species. Distribution Butternut, the primary host of ''S. clavigignenti-juglandacearum'', is found in mixed hardwood forests throughout central North America, from New Brunswick to North Carolina. The pathogen was identified as an invasive species in 1967. It was first discovered in Wisconsin, but has since spread to other states and into Canada, making the Butternut an endangered species in Ontario. Its native origin is unknown, but possibly in Asia given the resistance of Asian walnuts to the disease. The United States Forest Se ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pucciniastrum Americanum
''Pucciniastrum americanum'' is a plant pathogen infecting caneberries. References Fungal plant pathogens and diseases Small fruit diseases Pucciniales Fungi described in 1908 Fungus species {{fungus-plant-disease-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Puccinia Psidii
''Austropuccinia psidii'', commonly known as myrtle rust, guava rust, or ʻōhiʻa rust; is a rust (a type of plant pathogen) native to South America that affects plants in the family Myrtaceae. It is a member of the fungal complex called the guava rust (''Puccinia psidii'') group. The spores have a distinctive yellow to orange colour, occasionally encircled by a purple ring. They are found on lesions on new growth including shoots, leaves, buds and fruits. Leaves become twisted and may die. Infections in highly susceptible species may result in the death of the host plant. As of late 2013, it is infecting around 179 species in New South Wales and Queensland, from 41 genera (around 46% of genera in the Myrtaceae) in Australia. Importance ''Austropuccinia psidii'', a myrtle rust or a rust fungus, has a large host range for infection making it difficult for disease control and prevention, but it has been seen to have biological uses for it. In Florida, the pathogen has been con ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |