|
List Of Integrals Of Exponential Functions
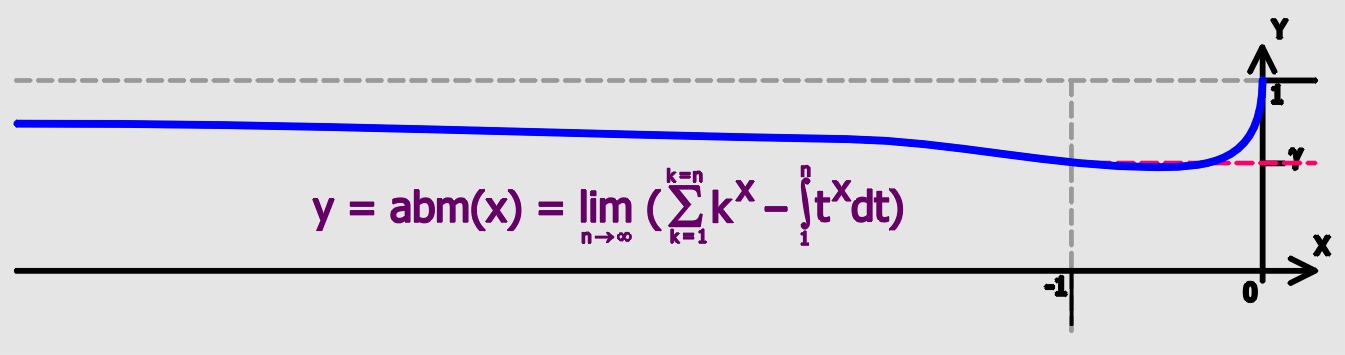
The following is a list of integrals of exponential functions. For a complete list of integral functions, please see the list of integrals. Indefinite integral Indefinite integrals are antiderivative functions. A constant (the constant of integration) may be added to the right hand side of any of these formulas, but has been suppressed here in the interest of brevity. Integrals of polynomials : \int xe^\,dx = e^\left(\frac\right) \text c \neq 0; : \int x^2 e^\,dx = e^\left(\frac-\frac+\frac\right) : \begin \int x^n e^\,dx &= \frac x^n e^ - \frac\int x^ e^ \,dx \\ &= \left( \frac \right)^n \frac \\ &= e^\sum_^n (-1)^i\fracx^ \\ &= e^\sum_^n (-1)^\fracx^i \end : \int\frac\,dx = \ln, x, +\sum_^\infty\frac : \int\frac\,dx = \frac\left(-\frac+c\int\frac\,dx\right) \qquad\textn\neq 1\text Integrals involving only exponential functions : \int f'(x)e^\,dx = e^ : \int e^\,dx = \frac e^ : \int a^\,dx = \frac a^\qquad\texta > 0,\ a \ne 1 Integrals involving the error functio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Integral
In mathematics, an integral assigns numbers to functions in a way that describes displacement, area, volume, and other concepts that arise by combining infinitesimal data. The process of finding integrals is called integration. Along with differentiation, integration is a fundamental, essential operation of calculus,Integral calculus is a very well established mathematical discipline for which there are many sources. See and , for example. and serves as a tool to solve problems in mathematics and physics involving the area of an arbitrary shape, the length of a curve, and the volume of a solid, among others. The integrals enumerated here are those termed definite integrals, which can be interpreted as the signed area of the region in the plane that is bounded by the graph of a given function between two points in the real line. Conventionally, areas above the horizontal axis of the plane are positive while areas below are negative. Integrals also refer to the concept of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Double Factorial
In mathematics, the double factorial or semifactorial of a number , denoted by , is the product of all the integers from 1 up to that have the same parity (odd or even) as . That is, :n!! = \prod_^ (n-2k) = n (n-2) (n-4) \cdots. For even , the double factorial is :n!! = \prod_^\frac (2k) = n(n-2)(n-4)\cdots 4\cdot 2 \,, and for odd it is :n!! = \prod_^\frac (2k-1) = n(n-2)(n-4)\cdots 3\cdot 1 \,. For example, . The zero double factorial as an empty product. The sequence of double factorials for even = starts as : 1, 2, 8, 48, 384, 3840, 46080, 645120,... The sequence of double factorials for odd = starts as : 1, 3, 15, 105, 945, 10395, 135135,... The term odd factorial is sometimes used for the double factorial of an odd number. History and usage In a 1902 paper, the physicist Arthur Schuster wrote: states that the double factorial was originally introduced in order to simplify the expression of certain trigonometric integrals that arise in the derivation of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
CRC Press
The CRC Press, LLC is an American publishing group that specializes in producing technical books. Many of their books relate to engineering, science and mathematics. Their scope also includes books on business, forensics and information technology. CRC Press is now a division of Taylor & Francis, itself a subsidiary of Informa. History The CRC Press was founded as the Chemical Rubber Company (CRC) in 1903 by brothers Arthur, Leo and Emanuel Friedman in Cleveland, Ohio, based on an earlier enterprise by Arthur, who had begun selling rubber laboratory aprons in 1900. The company gradually expanded to include sales of laboratory equipment to chemists. In 1913 the CRC offered a short (116-page) manual called the ''Rubber Handbook'' as an incentive for any purchase of a dozen aprons. Since then the ''Rubber Handbook'' has evolved into the CRC's flagship book, the ''CRC Handbook of Chemistry and Physics''. In 1964, Chemical Rubber decided to focus on its publishing ventures ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chapman And Hall
Chapman & Hall is an imprint owned by CRC Press, originally founded as a British publishing house in London in the first half of the 19th century by Edward Chapman and William Hall. Chapman & Hall were publishers for Charles Dickens (from 1840 until 1844 and again from 1858 until 1870), Thomas Carlyle, William Thackeray, Elizabeth Barrett Browning, Anthony Trollope, Eadweard Muybridge and Evelyn Waugh. History Upon Hall's death in 1847, Chapman's cousin Frederic Chapman began his progress through the ranks of the company and eventually becoming a partner in 1858 and sole proprietor on Edward Chapman's retirement from Chapman & Hall in 1866. In 1868 author Anthony Trollope bought a third of the company for his son, Henry Merivale Trollope. From 1902 to 1930 the company's managing director was Arthur Waugh. In the 1930s the company merged with Methuen, a merger which, in 1955, participated in forming the Associated Book Publishers. The latter was acquired by The Thomson ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gradshteyn And Ryzhik
''Gradshteyn and Ryzhik'' (''GR'') is the informal name of a comprehensive table of integrals originally compiled by the Russian mathematicians I. S. Gradshteyn and I. M. Ryzhik. Its full title today is ''Table of Integrals, Series, and Products''. Since its first publication in 1943, it was considerably expanded and it soon became a "classic" and highly regarded reference for mathematicians, scientists and engineers. After the deaths of the original authors, the work was maintained and further expanded by other editors. At some stage a German and English dual-language translation became available, followed by Polish, English-only and Japanese versions. After several further editions, the Russian and German-English versions went out of print and have not been updated after the fall of the Iron Curtain, but the English version is still being actively maintained and refined by new editors, and it has recently been retranslated back into Russian as well. Overview One of the valuab ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kronecker Delta
In mathematics, the Kronecker delta (named after Leopold Kronecker) is a function of two variables, usually just non-negative integers. The function is 1 if the variables are equal, and 0 otherwise: \delta_ = \begin 0 &\text i \neq j, \\ 1 &\text i=j. \end or with use of Iverson brackets: \delta_ = =j, where the Kronecker delta is a piecewise function of variables and . For example, , whereas . The Kronecker delta appears naturally in many areas of mathematics, physics and engineering, as a means of compactly expressing its definition above. In linear algebra, the identity matrix has entries equal to the Kronecker delta: I_ = \delta_ where and take the values , and the inner product of vectors can be written as \mathbf\cdot\mathbf = \sum_^n a_\delta_b_ = \sum_^n a_ b_. Here the Euclidean vectors are defined as -tuples: \mathbf = (a_1, a_2, \dots, a_n) and \mathbf= (b_1, b_2, ..., b_n) and the last step is obtained by using the values of the Kronecker ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Euler–Mascheroni Constant
Euler's constant (sometimes also called the Euler–Mascheroni constant) is a mathematical constant usually denoted by the lowercase Greek letter gamma (). It is defined as the limiting difference between the harmonic series and the natural logarithm, denoted here by \log: :\begin \gamma &= \lim_\left(-\log n + \sum_^n \frac1\right)\\ px&=\int_1^\infty\left(-\frac1x+\frac1\right)\,dx. \end Here, \lfloor x\rfloor represents the floor function. The numerical value of Euler's constant, to 50 decimal places, is: : History The constant first appeared in a 1734 paper by the Swiss mathematician Leonhard Euler, titled ''De Progressionibus harmonicis observationes'' (Eneström Index 43). Euler used the notations and for the constant. In 1790, Italian mathematician Lorenzo Mascheroni used the notations and for the constant. The notation appears nowhere in the writings of either Euler or Mascheroni, and was chosen at a later time perhaps because of the constant's connect ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Polylogarithm
In mathematics, the polylogarithm (also known as Jonquière's function, for Alfred Jonquière) is a special function of order and argument . Only for special values of does the polylogarithm reduce to an elementary function such as the natural logarithm or a rational function. In quantum statistics, the polylogarithm function appears as the closed form of integrals of the Fermi–Dirac distribution and the Bose–Einstein distribution, and is also known as the Fermi–Dirac integral or the Bose–Einstein integral. In quantum electrodynamics, polylogarithms of positive integer order arise in the calculation of processes represented by higher-order Feynman diagrams. The polylogarithm function is equivalent to the Hurwitz zeta function — either function can be expressed in terms of the other — and both functions are special cases of the Lerch transcendent. Polylogarithms should not be confused with polylogarithmic functions nor with the offset logarithmic integral ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Integral Of A Gaussian Function
In mathematics, a Gaussian function, often simply referred to as a Gaussian, is a function of the base form f(x) = \exp (-x^2) and with parametric extension f(x) = a \exp\left( -\frac \right) for arbitrary real constants , and non-zero . It is named after the mathematician Carl Friedrich Gauss. The graph of a Gaussian is a characteristic symmetric " bell curve" shape. The parameter is the height of the curve's peak, is the position of the center of the peak, and (the standard deviation, sometimes called the Gaussian RMS width) controls the width of the "bell". Gaussian functions are often used to represent the probability density function of a normally distributed random variable with expected value and variance . In this case, the Gaussian is of the form g(x) = \frac \exp\left( -\frac \frac \right). Gaussian functions are widely used in statistics to describe the normal distributions, in signal processing to define Gaussian filters, in image processing where two-dimens ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Exponential Function
The exponential function is a mathematical function denoted by f(x)=\exp(x) or e^x (where the argument is written as an exponent). Unless otherwise specified, the term generally refers to the positive-valued function of a real variable, although it can be extended to the complex numbers or generalized to other mathematical objects like matrices or Lie algebras. The exponential function originated from the notion of exponentiation (repeated multiplication), but modern definitions (there are several equivalent characterizations) allow it to be rigorously extended to all real arguments, including irrational numbers. Its ubiquitous occurrence in pure and applied mathematics led mathematician Walter Rudin to opine that the exponential function is "the most important function in mathematics". The exponential function satisfies the exponentiation identity e^ = e^x e^y \text x,y\in\mathbb, which, along with the definition e = \exp(1), shows that e^n=\underbrace_ for posi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |