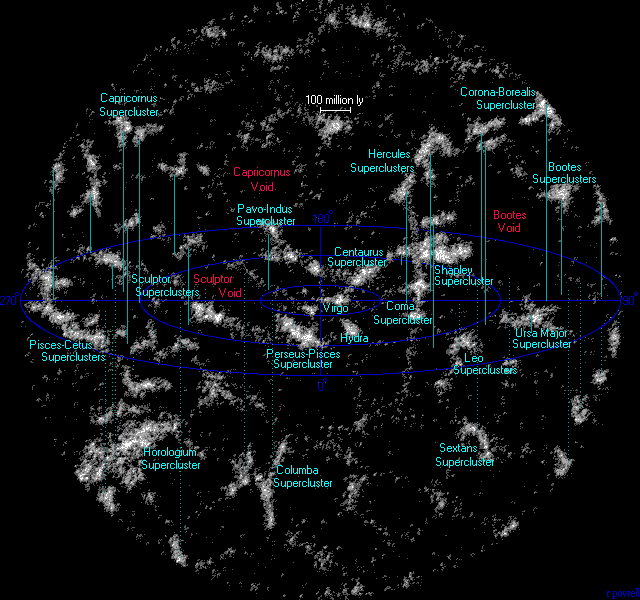
|
List Of Galaxy Superclusters
A supercluster is a large group of smaller galaxy clusters or galaxy groups; they are among the largest known structures in the universe. The Milky Way is part of the Local Group galaxy group (which contains more than 54 galaxies), which in turn is part of the Virgo Supercluster, which is part of the Laniakea Supercluster."Earth's new address: 'Solar System, Milky Way, Laniakea '''' The large size and low density of superclusters means that they, unlike clusters, expand with the |
Superclusters Atlasoftheuniverse
A supercluster is a large group of smaller galaxy clusters or galaxy groups; they are among the largest known structures in the universe. The Milky Way is part of the Local Group galaxy group (which contains more than 54 galaxies), which in turn is part of the Virgo Supercluster, which is part of the Laniakea Supercluster."Earth's new address: 'Solar System, Milky Way, Laniakea ''Nature (journal), Nature'' The large size and low density of superclusters means that they, unlike clusters, expand with the Hubble expansion. The number of superclusters in the observable universe is estimated to be 10 million. Existence [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Astrophysics And Space Science
''Astrophysics and Space Science'' is a bimonthly peer-reviewed scientific journal covering astronomy, astrophysics, and space science and astrophysical aspects of astrobiology. It was established in 1968 and is published by Springer Science+Business Media. From 2016 to 2020 the editors-in-chief were both Prof. Elias Brinks and Prof. Jeremy Mould. Since 2020 the sole editor-in-chief is Prof. Elias Brinks. Other editors-in-chief in the past have been Zdeněk Kopal (Univ. of Manchester) (1968-1993) and Michael A. Dopita (Australian National University) (1994-2015). Abstracting and indexing The journal is abstracted and indexed in the following databases: According to the ''Journal Citation Reports'', the journal has a 2020 impact factor The impact factor (IF) or journal impact factor (JIF) of an academic journal is a scientometric index calculated by Clarivate that reflects the yearly mean number of citations of articles published in the last two years in a given journal, a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fornax Cluster
The Fornax Cluster is a cluster of galaxies lying at a distance of 19 megaparsecs (62 million light-years). It has an estimated mass of solar masses, making it the second richest galaxy cluster within 100 million light-years, after the considerably larger Virgo Cluster. It may be associated with the nearby Eridanus Group. It lies primarily in the constellation Fornax, with its southern boundaries partially crossing into the constellation of Eridanus, and covers an area of sky about 6° across or about 28 sq degrees. The Fornax Cluster is a particularly valuable source of information about the evolution of such clusters due to its relatively close proximity to the Sun. It also shows the gravitational effects of a merger of a galaxy subgroup with the main galaxy group, which in turn lends clues about the associated galactic superstructure. At the centre of the cluster lies NGC 1399. Other cluster members include NGC 1316 (the group's brightest galaxy), NGC 1365, NGC 1427A, N ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Southern Supercluster
Southern may refer to: Businesses * China Southern Airlines, airline based in Guangzhou, China * Southern Airways, defunct US airline * Southern Air, air cargo transportation company based in Norwalk, Connecticut, US * Southern Airways Express, Memphis-based passenger air transportation company, serving eight cities in the US * Southern Company, US electricity corporation * Southern Music (now Peermusic), US record label * Southern Railway (other), various railways * Southern Records, independent British record label * Southern Studios, recording studio in London, England * Southern Television, defunct UK television company * Southern (Govia Thameslink Railway), brand used for some train services in Southern England Media * ''Southern Daily'' or ''Nanfang Daily'', the official Communist Party newspaper based in Guangdong, China * ''Southern Weekly'', a newspaper in Guangzhou, China * Heart Sussex, a radio station in Sussex, England, previously known as "Southern FM" * 88. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pavo–Indus Supercluster
The Pavo-Indus Supercluster is a neighboring supercluster located about away in the constellations of Pavo, Indus, and Telescopium. The supercluster contains three main clusters, Abell 3656, Abell 3698, and Abell 3742. Other groups and clusters in the supercluster include the NGC 6769 Group and Abell S805 (IC 4765 Group, Pavo II, DRCG 1842-63) and the massive Norma Cluster. In 2014 it was announced that the Pavo-Indus Supercluster is a lobe in a greater supercluster, Laniakea, that is centered on the Great Attractor. The Virgo Supercluster would also be part of this greater supercluster, thus becoming the local supercluster. Structure The Pavo-Indus Supercluster exhibits a wall or filamentary structure that extends to a total length of . The supercluster along with the Telescopium−Grus Cloud form parts of a wall bounding the Local Void and the Sculptor Void. Nearby superclusters Centaurus Supercluster In 1983, Winkler. et al suggested based on redshift maps of the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hydra–Centaurus Supercluster
The Hydra-Centaurus Supercluster (SCl 128), or the Hydra and Centaurus Superclusters, is a supercluster in two parts, the closest neighbour of Virgo Supercluster. Hydra-Centaurus The cluster includes four large galaxy clusters in the Centaurus part * Abell 3526 (Centaurus Cluster) * Abell 3565 * Abell 3574 * Abell 3581 and the proximate * Hydra Cluster (A1060) * Antlia Cluster (AS0636) Apart from the central clusters, which are 150 to 200 million light years away, several smaller clusters belong to the group. Within the proximity of this supercluster lies the Great Attractor, dominated by the Norma Cluster (Abell 3627). This massive cluster of galaxies exerts a large gravitational force, causing all matter within 50 Mpc to experience a bulk flow of 600 km/s toward the Norma Cluster Laniakea A 2014 announcement says that the Centaurus Supercluster (Hydra–Centaurus) is just a lobe in a greater supercluster, Laniakea, that is centered on the Great Attractor. That superc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Galaxy
A galaxy is a system of stars, stellar remnants, interstellar gas, dust, dark matter, bound together by gravity. The word is derived from the Greek ' (), literally 'milky', a reference to the Milky Way galaxy that contains the Solar System. Galaxies, averaging an estimated 100 million stars, range in size from dwarfs with less than a hundred million stars, to the largest galaxies known – supergiants with one hundred trillion stars, each orbiting its galaxy's center of mass. Most of the mass in a typical galaxy is in the form of dark matter, with only a few percent of that mass visible in the form of stars and nebulae. Supermassive black holes are a common feature at the centres of galaxies. Galaxies are categorized according to their visual morphology as elliptical, spiral, or irregular. Many are thought to have supermassive black holes at their centers. The Milky Way's central black hole, known as Sagittarius A*, has a mass four million times greater than the Sun. As o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Virgo Cluster
The Virgo Cluster is a large cluster of galaxies whose center is 53.8 ± 0.3 Mly (16.5 ± 0.1 Mpc) away in the constellation Virgo. Comprising approximately 1,300 (and possibly up to 2,000) member galaxies, the cluster forms the heart of the larger Virgo Supercluster, of which the Local Group (containing our Milky Way galaxy) is a member. The Local Group actually experiences the mass of the Virgo Supercluster as the Virgocentric flow. It is estimated that the Virgo Cluster's mass is 1.2 out to 8 degrees of the cluster's center or a radius of about 2.2 Mpc. Many of the brighter galaxies in this cluster, including the giant elliptical galaxy Messier 87, were discovered in the late 1770s and early 1780s and subsequently included in Charles Messier's catalogue of non-cometary fuzzy objects. Described by Messier as nebulae without stars, their true nature was not recognized until the 1920s. The cluster subtends a maximum arc of approximately 8 degrees centered in the constellation ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Megaparsec
The parsec (symbol: pc) is a unit of length used to measure the large distances to astronomical objects outside the Solar System, approximately equal to or (au), i.e. . The parsec unit is obtained by the use of parallax and trigonometry, and is defined as the distance at which 1 au subtends an angle of one arcsecond ( of a degree). This corresponds to astronomical units, i.e. 1\, \mathrm = 1/\tan \left( \ \mathrm \right)\, \mathrm. The nearest star, Proxima Centauri, is about from the Sun. Most stars visible to the naked eye are within a few hundred parsecs of the Sun, with the most distant at a few thousand. The word ''parsec'' is a portmanteau of "parallax of one second" and was coined by the British astronomer Herbert Hall Turner in 1913 to make calculations of astronomical distances from only raw observational data easy for astronomers. Partly for this reason, it is the unit preferred in astronomy and astrophysics, though the light-year remains prominent in popular ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Redshift
In physics, a redshift is an increase in the wavelength, and corresponding decrease in the frequency and photon energy, of electromagnetic radiation (such as light). The opposite change, a decrease in wavelength and simultaneous increase in frequency and energy, is known as a negative redshift, or blueshift. The terms derive from the colours red and blue which form the extremes of the visible light spectrum. In astronomy and cosmology, the three main causes of electromagnetic redshift are # The radiation travels between objects which are moving apart (" relativistic" redshift, an example of the relativistic Doppler effect) #The radiation travels towards an object in a weaker gravitational potential, i.e. towards an object in less strongly curved (flatter) spacetime (gravitational redshift) #The radiation travels through expanding space (cosmological redshift). The observation that all sufficiently distant light sources show redshift corresponding to their distance from Earth ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
The Astrophysical Journal
''The Astrophysical Journal'', often abbreviated ''ApJ'' (pronounced "ap jay") in references and speech, is a peer-reviewed Peer review is the evaluation of work by one or more people with similar competencies as the producers of the work (peers). It functions as a form of self-regulation by qualified members of a profession within the relevant field. Peer review ... scientific journal of astrophysics and astronomy, established in 1895 by American astronomers George Ellery Hale and James Edward Keeler. The journal discontinued its print edition and became an electronic-only journal in 2015. Since 1953 ''The Astrophysical Journal Supplement Series'' (''ApJS'') has been published in conjunction with ''The Astrophysical Journal'', with generally longer articles to supplement the material in the journal. It publishes six volumes per year, with two 280-page issues per volume. ''The Astrophysical Journal Letters'' (''ApJL''), established in 1967 by Subrahmanyan Chandrasekhar as ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sloan Great Wall
The Sloan Great Wall (SGW) is a cosmic structure formed by a giant wall of galaxies (a galaxy filament). Its discovery was announced from Princeton University on October 20, 2003, by J. Richard Gott III, Mario Jurić, and their colleagues, based on data from the Sloan Digital Sky Survey. Size The wall measures in length, located approximately one billion light-years away. In the sky, it is located within the region of the constellations Corvus, Hydra and Centaurus. It is approximately 1/60 of the diameter of the observable universe, making it the sixth largest known object after the large quasar groups Clowes-Campusano LQG, U1.11, Huge-LQG, the Giant GRB Ring and the galaxy filament Hercules–Corona Borealis Great Wall (Her-CrB GW), respectively. The Sloan Great Wall is between 1.8–2.7 times longer than the CfA2 Great Wall of galaxies (discovered by Margaret Geller and John Huchra of Harvard in 1989). It also contains several galactic supercluster A superclus ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |