|
List Of Extinct Animals Of Europe
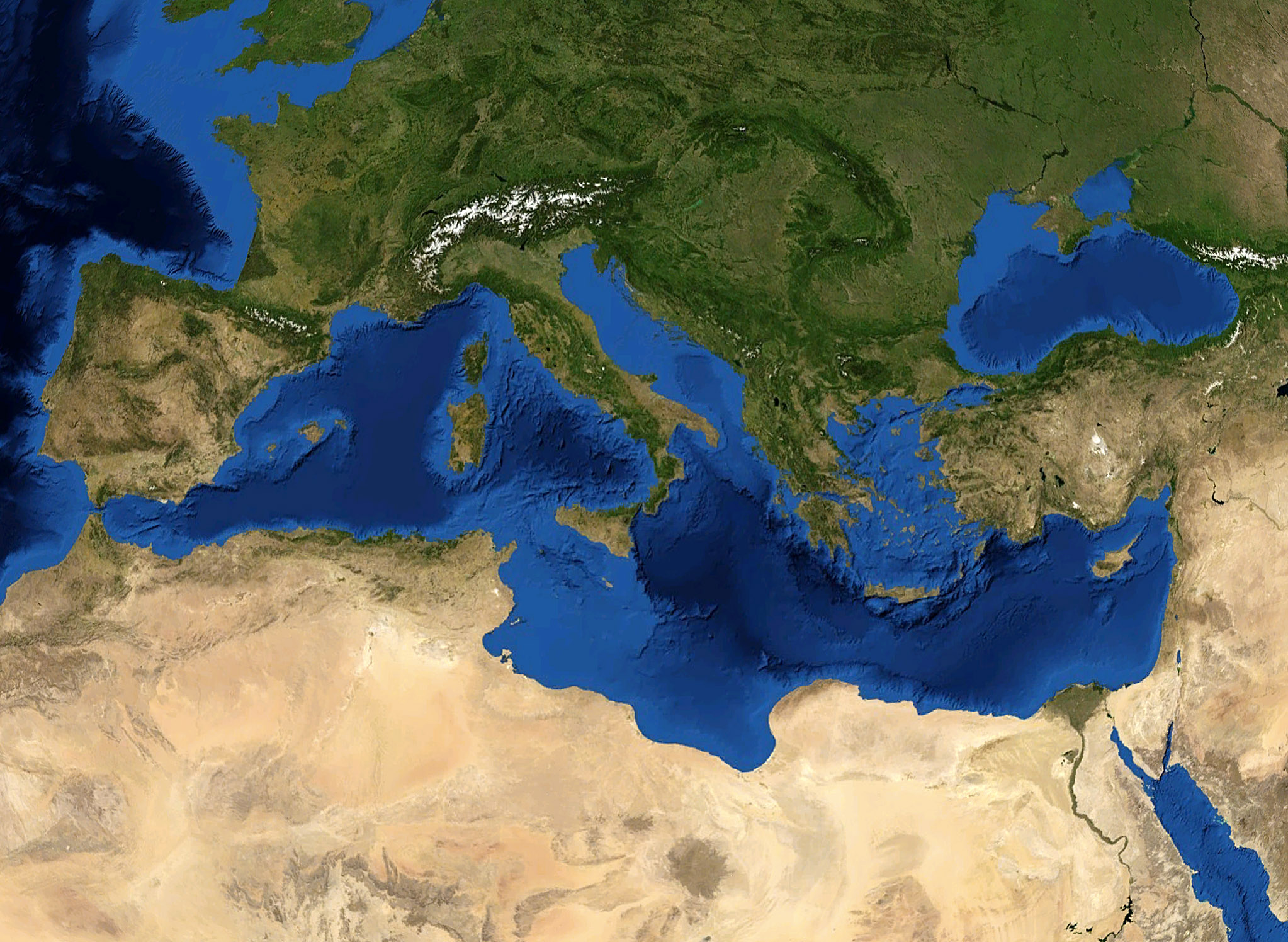
This list of European animals extinct in the Holocene features animals known to have become extinct in the last 12,000 years on the European continent and its surrounding islands. Dependent territories of European countries in other continents, like Greenland, are not included, as they should be found in their pertaining list. The Açores are included but not other Macaronesian islands, which are in the List of African animals extinct in the Holocene. Likewise, all large islands in the Mediterranean Sea are included except for Cyprus, which is in the List of Asian animals extinct in the Holocene. Many extinction dates are unknown due to a lack of relevant information. Mammals Undated Prehistoric Recent Local Birds Reptiles Fish Insects Sea anemones Molluscs See also * Limousin horse, extinct * List of extinct animals of Catalonia * List of extinct animals of Caucasus * List of extinct animals of the British Isles * Li ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Europe Orthographic Caucasus Urals Boundary
Europe is a large peninsula conventionally considered a continent in its own right because of its great physical size and the weight of its history and traditions. Europe is also considered a subcontinent of Eurasia and it is located entirely in the Northern Hemisphere and mostly in the Eastern Hemisphere. Comprising the westernmost peninsulas of Eurasia, it shares the continental landmass of Afro-Eurasia with both Africa and Asia. It is bordered by the Arctic Ocean to the north, the Atlantic Ocean to the west, the Mediterranean Sea to the south and Asia to the east. Europe is commonly considered to be separated from Asia by the watershed of the Ural Mountains, the Ural River, the Caspian Sea, the Greater Caucasus, the Black Sea and the waterways of the Turkish Straits. "Europe" (pp. 68–69); "Asia" (pp. 90–91): "A commonly accepted division between Asia and Europe ... is formed by the Ural Mountains, Ural River, Caspian Sea, Caucasus Mountains, and the Black Sea ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Steppe Bison
The steppe bisonSeveral literatures address the species as ''primeval bison''. or steppe wisent (''Bison'' ''priscus'') – Yukon Beringia Interpretive Centre. Beringia.com. Retrieved on 2013-05-31. is an extinct species of that was once found on the where its range included , , [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
European Wild Ass
The European wild ass (''Equus hemionus hydruntinus'') or hydruntine is an extinct equine from the Middle Pleistocene to Late Holocene of Western Eurasia. It appeared first in the fossil record around 350–300,000 years before present. In the late Pleistocene it was widespread throughout much of western Eurasia from the Middle East to Europe, especially along the Mediterranean, with fossil reports from Sicily, Turkey, Spain, France and Portugal. In the east the range apparently stretched at least to the Volga and to Iran. In the north it reached almost to the North Sea in Germany and the British Isles. Its range fragmented after the Last Glacial Maximum, surviving into the Holocene, its range gradually contracted further, persisting in small regions of southern Europe into the Bronze Age, and in Iran and the Caucasus into the Iron Age, around 500 BC. It has been suggested that the Iberian Zebro, extinct in the wild from the 16th century, could correspond to the ''Equus hydruntinu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cynotherium Sardous Restoration
The Sardinian dhole (''Cynotherium sardous'') is an extinct island, insular Canidae, canid which was endemic to what is now the Mediterranean Sea, Mediterranean islands of Sardinia (Italy) and Corsica (France), which were joined for much of the Pleistocene. It went extinct when humans began to settle on the island. Its scientific name means "dog-beast of Sardinia", the genus name from the and and the Specific name (zoology), specific name from the , alt. form of . The oldest fossils of the ''Cynotherium'' lineage on Sardinia, belonging to the species ''Cynotherium malatestai'' likely ancestral to ''C. sardous'' date to the Early-Middle Pleistocene transition, corresponding to faunal turnover between the older ''Nesogoral'' Faunal Complex and the younger ''Microtus'' (''Tyrrhenicola henseli, Tyrrhenicola'') faunal complex. The genomic analysis of a 21,000 year-old Sardinian dhole specimen indicates that the Sardinian dhole lineage and the Dhole, Asian dhole lineage diverged fr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Oxford University Press
Oxford University Press (OUP) is the university press of the University of Oxford. It is the largest university press in the world, and its printing history dates back to the 1480s. Having been officially granted the legal right to print books by decree in 1586, it is the second oldest university press after Cambridge University Press. It is a department of the University of Oxford and is governed by a group of 15 academics known as the Delegates of the Press, who are appointed by the vice-chancellor of the University of Oxford. The Delegates of the Press are led by the Secretary to the Delegates, who serves as OUP's chief executive and as its major representative on other university bodies. Oxford University Press has had a similar governance structure since the 17th century. The press is located on Walton Street, Oxford, opposite Somerville College, in the inner suburb of Jericho. For the last 500 years, OUP has primarily focused on the publication of pedagogical texts and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sardinian Dhole
The Sardinian dhole (''Cynotherium sardous'') is an extinct insular canid which was endemic to what is now the Mediterranean islands of Sardinia (Italy) and Corsica (France), which were joined for much of the Pleistocene. It went extinct when humans began to settle on the island. Its scientific name means "dog-beast of Sardinia", the genus name from the and and the specific name from the , alt. form of . The oldest fossils of the ''Cynotherium'' lineage on Sardinia, belonging to the species ''Cynotherium malatestai'' likely ancestral to ''C. sardous'' date to the Early-Middle Pleistocene transition, corresponding to faunal turnover between the older '' Nesogoral'' Faunal Complex and the younger ''Microtus'' ('' Tyrrhenicola'') faunal complex. The genomic analysis of a 21,000 year-old Sardinian dhole specimen indicates that the Sardinian dhole lineage and the Asian dhole lineage diverged from each other 885,000 years ago. Gene flow continued between the two lineages until b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cuon Alpinus Cova Negra
The dhole (''Cuon alpinus''; ) is a Canidae, canid native to Central Asia, Central, South Asia, South, East Asia, East and Southeast Asia. Other English names for the species include Asian wild dog, Asiatic wild dog, Indian wild dog, whistling dog, red dog, red wolf, and mountain wolf. It is genetically close to species within the genus ''Canis'', but distinct in several anatomical aspects: its skull is convex rather than concave in profile, it lacks a third lower molar (tooth), molar and the upper molars sport only a single Cusp (dentistry), cusp as opposed to between two and four. During the Pleistocene, the dhole ranged throughout Asia, Europe and North America but became restricted to its historical range 12,000–18,000 years ago. The dhole is a highly social animal, living in large clans without rigid dominance hierarchies and containing multiple breeding females. Such clans usually consist of about 12 individuals, but groups of over 40 are known. It is a diurna ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Southern Europe
Southern Europe is the southern regions of Europe, region of Europe. It is also known as Mediterranean Europe, as its geography is essentially marked by the Mediterranean Sea. Definitions of Southern Europe include some or all of these countries and regions: Albania, Andorra, Bosnia and Herzegovina, Bulgaria, Croatia, Cyprus, East Thrace, Gibraltar, Greece, Italy, Kosovo, Malta, Moldova, Monaco, Montenegro, North Macedonia, Portugal, Romania, San Marino, Serbia, Slovenia, Southern France, Spain, and Vatican City (the Holy See). Southern Europe is focused on the three peninsulas located in the extreme south of the European continent. These are the Iberian Peninsula, the Italian Peninsula, Apennine Peninsula, and the Balkans, Balkan Peninsula. These three peninsulas are separated from the rest of Europe by towering mountain ranges, respectively by the Pyrenees, the Alps and the Balkan Mountains. The location of these peninsulas in the heart of the Mediterranean Sea, as well as the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Central Europe
Central Europe is an area of Europe between Western Europe and Eastern Europe, based on a common historical, social and cultural identity. The Thirty Years' War (1618–1648) between Catholicism and Protestantism significantly shaped the area's history. The concept of "Central Europe" appeared in the 19th century. Central Europe comprised most of the territories of the Holy Roman Empire and those of the two neighboring kingdoms of Poland and Hungary. Hungary and parts of Poland were later part of the Habsburg monarchy, which also significantly shaped the history of Central Europe. Unlike their Western European (Portugal, Spain et al.) and Eastern European (Russia) counterparts, the Central European nations never had any notable colonies (either overseas or adjacent) due to their inland location and other factors. It has often been argued that one of the contributing causes of both World War I and World War II was Germany's lack of original overseas colonies. After World War ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
European Dhole
The European dhole (''Cuon alpinus europaeus'') was a paleosubspecies of the dhole, which ranged throughout much of Western and Central Europe during the Middle and Late Pleistocene. Like the modern Asiatic populations, it was a more progressive form than other prehistoric members of the genus ''Cuon'', having transformed its lower molar tooth into a single cusped slicer. It was virtually indistinguishable from its modern counterpart, save for its greater size, which closely approached that of the gray wolf.Kurtén, Björn (1968), ''Pleistocene mammals of Europe'', Weidenfeld and Nicolson, pp. 111-114 Lineage ''Cuon alpinus priscus'' Thenius 1954 was the first member of genus ''Cuon'' to be identified in Europe during the Middle Pleistocene. This was followed by ''Cuon alpinus fossilis'' Nehring 1890, then ''Cuon alpinus europaeus'' Bourguignat 1868 during the Middle and Late Pleistocene. The descent is thought to be ''C. a. priscus→C. a. fossilis→C. a. europaeus''. In compar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Coelodonta Antiquitatis By Benjamin Langlois
''Coelodonta'' (, from the Greek κοιλία, ''koilía'' and οδούς, ''odoús'', "hollow tooth", in reference to the deep grooves of their molars) is an extinct genus of rhinoceros that lived in Eurasia between 3.7 million years to 10,000 years before the present, in the Pliocene and the Pleistocene epochs. It is best known from the type species, the woolly rhinoceros (''Coelodonta antiquitatis''), which ranged throughout northern Eurasia during the Pleistocene. The earliest known species, ''Coelodonta thibetana,'' lived in Tibet during the Pliocene, with the genus spreading to the rest of Eurasia during the Pleistocene. Species Species recognised as members of ''Coelodonta'', according to Deng ''et al''. (2011), include: * ''Coelodonta thibetana'' (Deng et al. 2011): The most primitive species of the genus, inhabited the Tibetan Plateau during the Pliocene. * ''Coelodonta nihowanensis'' (Chow, 1978): A primitive species from northern China, it lived in the earliest Ple ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Woolly Rhinoceros
The woolly rhinoceros (''Coelodonta antiquitatis'') is an extinct species of rhinoceros that was common throughout Europe and Asia during the Pleistocene epoch and survived until the end of the last glacial period. The woolly rhinoceros was a member of the Pleistocene megafauna. The woolly rhinoceros was covered with long, thick hair that allowed it to survive in the extremely cold, harsh mammoth steppe. It had a massive hump reaching from its shoulder and fed mainly on herbaceous plants that grew in the steppe. Mummified carcasses preserved in permafrost and many bone remains of woolly rhinoceroses have been found. Images of woolly rhinoceroses are found among cave paintings in Europe and Asia. Taxonomy Woolly rhinoceros remains have been known long before the species was described, and were the basis for some mythical creatures. Native peoples of Siberia believed their horns were the claws of giant birds. A rhinoceros skull was found in Kl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |


.jpg)