|
List Of Dutch Inventions And Innovations
The Netherlands and its people have made numerous contributions to the world's civilization in art, science, technology and engineering, economics and finance, cartography and geography, exploration and navigation, law and jurisprudence, thought and philosophy, medicine and agriculture. The following list is composed of objects, ideas, phenomena, processes, methods, techniques and styles that were discovered or invented by people from the Netherlands and Dutch-speaking people from the former Southern Netherlands (''Zuid-Nederlanders'' in Dutch). Until the fall of Antwerp (1585), the Dutch and Flemish were generally seen as one people. Inventions and innovations Arts and architecture Movements and styles = De Stijl (Neo-Plasticism) (1917) = The De Stijl school proposed simplicity and abstraction, both in architecture and painting, by using only straight horizontal and vertical lines and rectangular forms. Furthermore, their formal vocabulary was limited to the primary ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Piet Mondrian
Pieter Cornelis Mondriaan (), after 1906 known as Piet Mondrian (, also , ; 7 March 1872 – 1 February 1944), was a Dutch painter and art theoretician who is regarded as one of the greatest artists of the 20th century. He is known for being one of the pioneers of 20th-century abstract art, as he changed his artistic direction from figurative painting to an increasingly abstract style, until he reached a point where his artistic vocabulary was reduced to simple geometric elements. Mondrian's art was highly utopian and was concerned with a search for universal values and aesthetics. He proclaimed in 1914: "Art is higher than reality and has no direct relation to reality. To approach the spiritual in art, one will make as little use as possible of reality, because reality is opposed to the spiritual. We find ourselves in the presence of an abstract art. Art should be above reality, otherwise it would have no value for man." His art, however, always remained rooted in nature. H ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Frederiksborg Slot Hilleroed Denmark Outer Courtyard1 , signed at Frederiksborg Castle in 1720
{{Disambig, geo ...
Frederiksborg may refer to: * Frederiksborg Castle, in Hillerød, Denmark * Frederiksborg, former name of Hillerød, a municipality to the north of Copenhagen, Denmark * Frederiksborg County, former county on the island of Zealand in Denmark * Fort Frederiksborg, Danish and later English fort built in 1661 in contemporary Ghana * Frederiksborger, a kind of horse originating in Denmark * Frederiksborg Glacier, on the east coast of the Greenland ice sheet See also * Treaty of Frederiksborg The Treaty of Frederiksborg ( da, Frederiksborgfreden) was a treaty signed at Frederiksborg Castle, Zealand, on 3 July 1720Heitz (1995), p.244 (14 July 1720 according to the Gregorian calendar), ending the Great Northern War between Denmark-Norwa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Burgundian Netherlands
In the history of the Low Countries, the Burgundian Netherlands (french: Pays-Bas bourguignons, nl, Bourgondische Nederlanden, lb, Burgundeschen Nidderlanden, wa, Bas Payis borguignons) or the Burgundian Age is the period between 1384 and 1482, during which a growing part of the Low Countries was ruled by the Dukes of Burgundy. Within their Burgundian State, which itself belonged partly to the Holy Roman Empire and partly to the Kingdom of France, the dukes united these lowlands into a political union that went beyond a personal union as it gained central institutions for the first time (such as the States General). The period began with Duke Philip the Bold taking office as count of Flanders and Artois in 1384 and lasted until the death of Duchess Mary of Burgundy in 1482 after which the Burgundian State was dissolved, and the Low Countries came under the rule of the Habsburg monarchy by inheritance. In the 15th century, it was customary to refer to the Low Countries wh ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
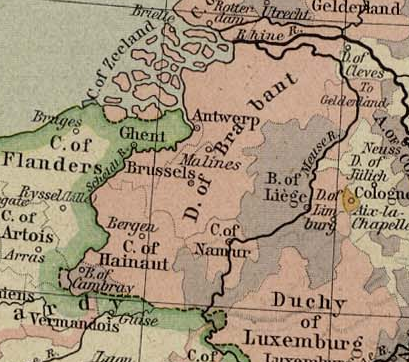
Duchy Of Brabant
The Duchy of Brabant was a State of the Holy Roman Empire established in 1183. It developed from the Landgraviate of Brabant and formed the heart of the historic Low Countries, part of the Burgundian Netherlands from 1430 and of the Habsburg Netherlands from 1482, until it was partitioned after the Dutch revolt. Present-day North Brabant (''Noord-Brabant'') was ceded to the Generality Lands of the Dutch Republic according to the 1648 Peace of Westphalia, while the reduced duchy remained part of the Habsburg Netherlands until it was conquered by French Revolutionary forces in 1794, which was recognized by treaty in 1797. Today all the duchy's former territories, apart from exclaves, are in Belgium except for the Dutch province of North Brabant. Geography The Duchy of Brabant (adjective: ''Brabantian'' or '' Brabantine'') was historically divided into four parts, each with its own capital. The four capitals were Leuven, Brussels, Antwerp and 's-Hertogenbosch. Before 's-Hertogenb ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mechelen
Mechelen (; french: Malines ; traditional English name: MechlinMechelen has been known in English as ''Mechlin'', from where the adjective ''Mechlinian'' is derived. This name may still be used, especially in a traditional or historical context. The city's French name ' had also been used in English in the past (in the 19th and 20th century) however this has largely been abandoned. Meanwhile, the Dutch derived ' began to be used in English increasingly from late 20th century onwards, even while ''Mechlin'' remained still in use (for example a ''Mechlinian'' is an inhabitant of this city or someone seen as born-and-raised there; the term is also the name of the city dialect; as an adjective ''Mechlinian'' may refer to the city or to its dialect.) is a city and municipality in the province of Antwerp in the Flemish Region of Belgium. The municipality comprises the city of Mechelen proper, some quarters at its outskirts, the hamlets of (adjacent) and (a few kilometers away), as ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Saint Rumbold's Cathedral
St. Rumbold's Cathedral ( nl, Sint-Romboutskathedraal, french: Cathédrale Saint-Rombaut) is the Roman Catholic metropolitan archiepiscopal cathedral in Mechelen, Belgium, dedicated to Saint Rumbold, Christian missionary and martyr who had founded an abbey nearby. His remains are rumoured to be buried inside the cathedral. State-of-the-art examination of the relics honoured as Saint Rumbold's and kept in a shrine in the retro-choir, showed a life span of about 40 years and a death date between 580 and 655, while tradition had claimed 775 AD.The abbey founded by St. Rumbold in the 6th, 7th or 8th century and a 9th century St. Rumbold's abbey church subordinate to the bishops of Liège are assumed to have been located in the ''Holm'', higher grounds a little outside the later city walls of Mechelen. A 9th century St. Rumbold's Chapel in the city centre stood till 1580, was rebuilt in 1597 and demolished in 1798. After Prince-Bishop Notger's founding of the St. Rumbold's Chapter ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
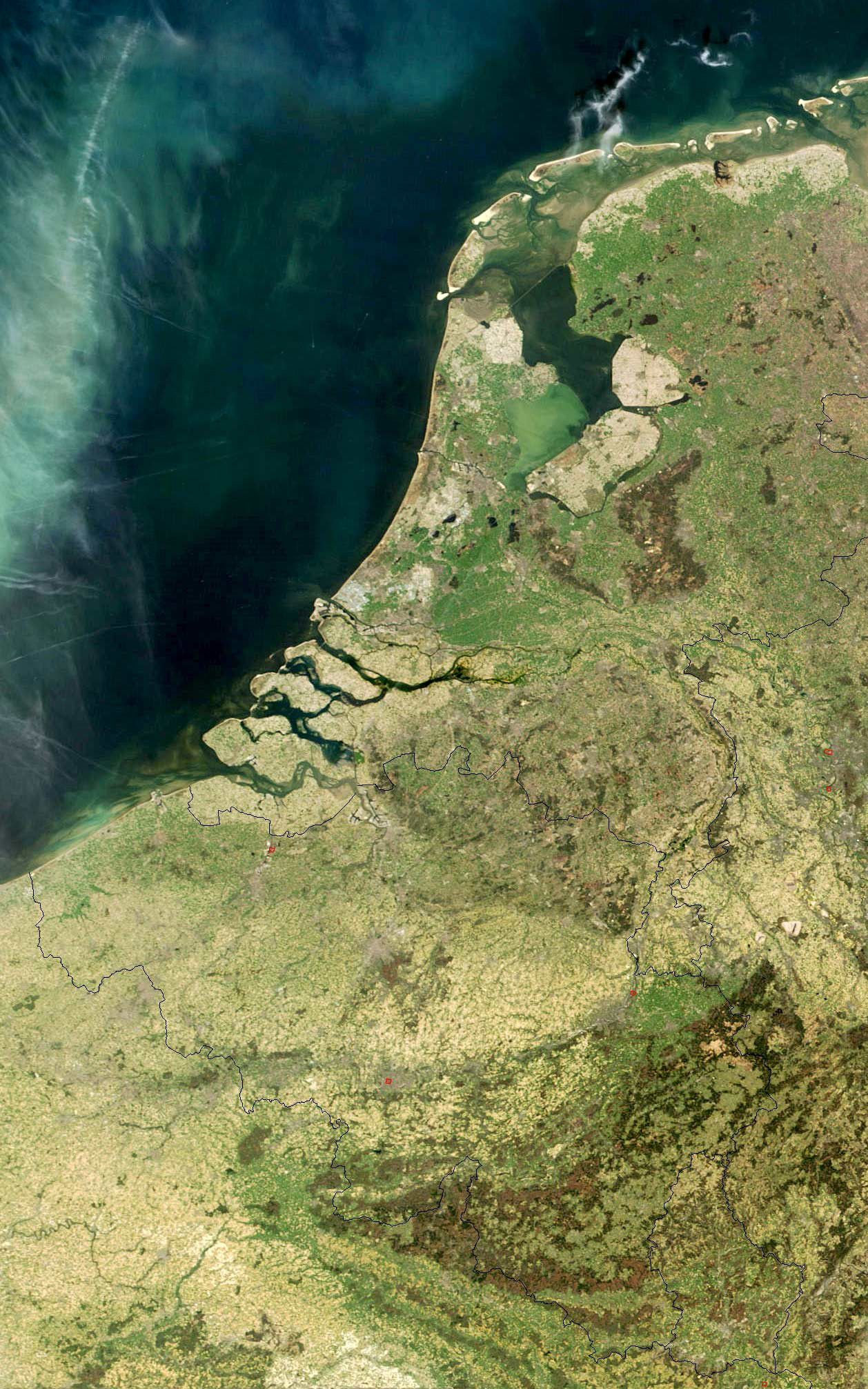
Low Countries
The term Low Countries, also known as the Low Lands ( nl, de Lage Landen, french: les Pays-Bas, lb, déi Niddereg Lännereien) and historically called the Netherlands ( nl, de Nederlanden), Flanders, or Belgica, is a coastal lowland region in Northwestern Europe forming the lower basin of the Rhine–Meuse–Scheldt delta and consisting of three countries: Belgium, the Netherlands and Luxembourg. Geographically and historically, the area also includes parts of France and Germany such as the French Flanders and the German regions of East Frisia and Cleves. During the Middle Ages, the Low Countries were divided into numerous semi-independent principalities. Historically, the regions without access to the sea linked themselves politically and economically to those with access to form various unions of ports and hinterland, stretching inland as far as parts of the German Rhineland. Because of this, nowadays not only physically low-altitude areas, but also some hilly or elevated regi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gothic Architecture
Gothic architecture (or pointed architecture) is an architectural style that was prevalent in Europe from the late 12th to the 16th century, during the High and Late Middle Ages, surviving into the 17th and 18th centuries in some areas. It evolved from Romanesque architecture and was succeeded by Renaissance architecture. It originated in the Île-de-France and Picardy regions of northern France. The style at the time was sometimes known as ''opus Francigenum'' (lit. French work); the term ''Gothic'' was first applied contemptuously during the later Renaissance, by those ambitious to revive the architecture of classical antiquity. The defining design element of Gothic architecture is the pointed or ogival arch. The use of the pointed arch in turn led to the development of the pointed rib vault and flying buttresses, combined with elaborate tracery and stained glass windows. At the Abbey of Saint-Denis, near Paris, the choir was reconstructed between 1140 and 1144, draw ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Brabantian Gothic
Brabantine Gothic, occasionally called Brabantian Gothic, is a significant variant of Gothic architecture that is typical for the Low Countries. It surfaced in the first half of the 14th century at St. Rumbold's Cathedral in the City of Mechelen.The earliest Brabantine Gothic style elements were built soon after 1333 when the Prince-Bishopric of Liège, Prince-Bishop of Liège passed his Feudalism, feudal claim on Mechelen, in particular through its cathedral chapter, to Louis II, Count of Flanders, who married the Margaret of Brabant, Countess of Flanders, heiress of Brabant and in 1355 took the title of Duke of Brabant. Reputed architects such as Jean d'Oisy, Jacob van Thienen, Everaert Spoorwater, (This architect is also known as Evert van der Weyden.) Matheus de Layens, and the Keldermans family, Keldermans and De Waghemakere families disseminated the style and techniques to cities and towns of the Duchy of Brabant and beyond.About Gothic architecture in the Low Countries, th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Brabantine Gothic
Brabantine Gothic, occasionally called Brabantian Gothic, is a significant variant of Gothic architecture that is typical for the Low Countries. It surfaced in the first half of the 14th century at St. Rumbold's Cathedral in the City of Mechelen.The earliest Brabantine Gothic style elements were built soon after 1333 when the Prince-Bishop of Liège passed his feudal claim on Mechelen, in particular through its cathedral chapter, to Louis II, Count of Flanders, who married the heiress of Brabant and in 1355 took the title of Duke of Brabant. Reputed architects such as Jean d'Oisy, Jacob van Thienen, Everaert Spoorwater, (This architect is also known as Evert van der Weyden.) Matheus de Layens, and the Keldermans and De Waghemakere families disseminated the style and techniques to cities and towns of the Duchy of Brabant and beyond.About Gothic architecture in the Low Countries, the Dutch-language term ''kustgotiek'' ('Coastal Gothic') occurs. Apparently, that literature d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Robert Van 't Hoff
Robert van 't Hoff (November 5, 1887 – April 25, 1979), born Robbert van 't Hoff, was a Dutch architect and furniture designer. His ''Villa Henny'', designed in 1914, was one of the earliest modernist houses and one of the first to be built out of reinforced concrete. From 1917 he was an influential member of the ''De Stijl'' movement. Although he was born to a comfortable middle-class background, married a wealthy heiress, and for a while was able to subsidise the publication of the ''De Stijl'' journal, van 't Hoff was a member of the Communist Party of the Netherlands in the years following World War I. Following the failure of Pieter Jelles Troelstra's call for a socialist revolution in the Netherlands in 1919, van 't Hoff split from ''De Stijls founder Theo van Doesburg and withdrew from artistic activity, declaring himself an "ex-architect" in 1922, and spending much of the rest of his life promoting experimental anarchist communities. Life Early life and education V ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |




.jpg)

