|
List Of Delta 2 Launches
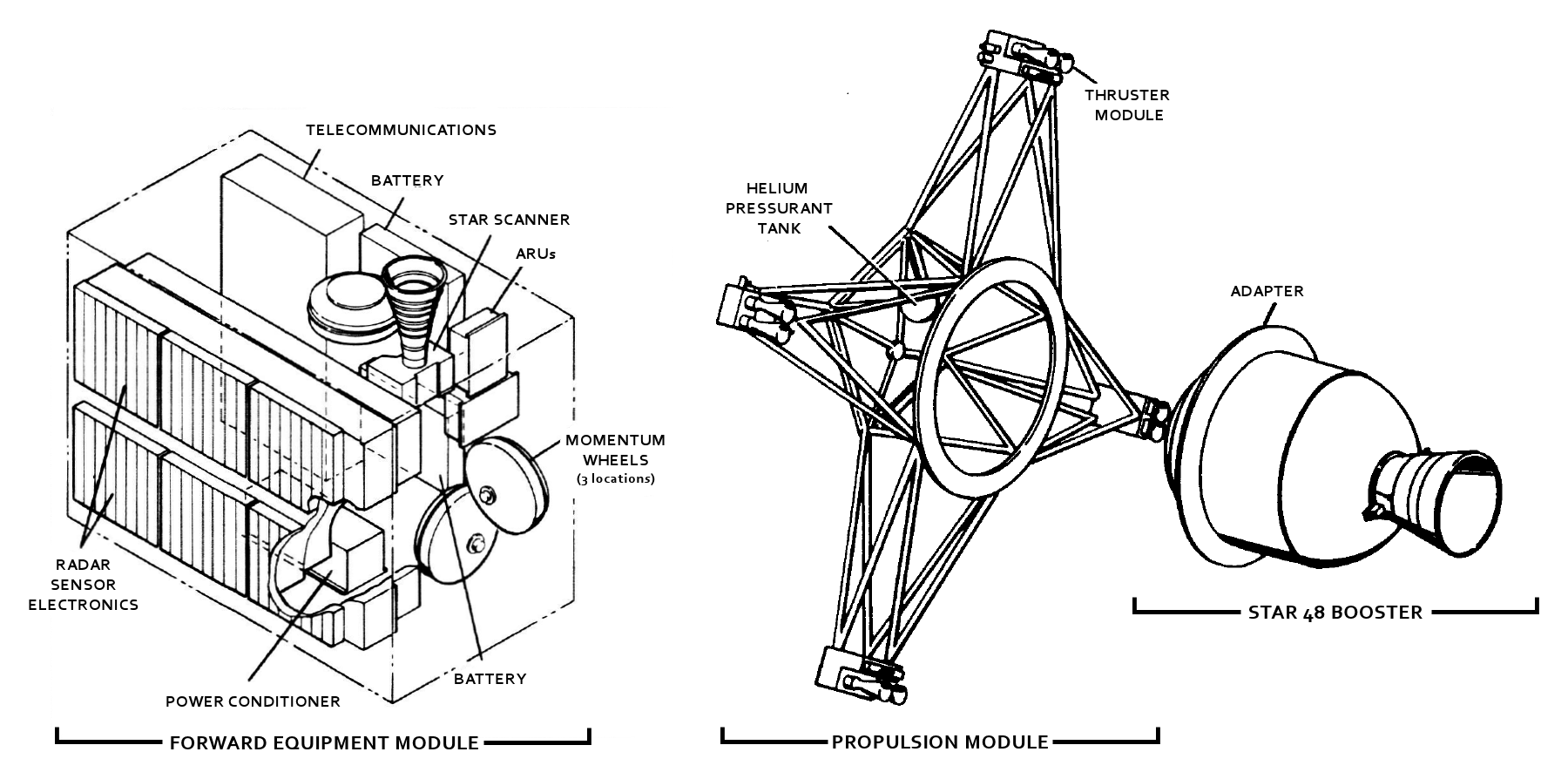
Delta II was an expendable launch system, originally designed and built by McDonnell Douglas. Delta II was part of the Delta rocket family and entered service in 1989. Delta II vehicles included the Delta 6000, and the two later Delta 7000 variants ("Lite" and "Heavy"). The rocket flew its final mission ICESat-2 on 15 September 2018, earning the launch vehicle a streak of 100 successful missions in a row, with the last failure being GPS IIR-1 in 1997. The Delta II series was developed after the 1986 ''Challenger'' accident and consisted of the Delta 6000-series and 7000-series, with two variants (Lite and Heavy) of the latter. The Delta 6000-series introduced the Extra Extended Long Tank first stage, which was 12 feet longer, and the Castor 4A boosters. Six SRBs ignited at takeoff and three ignited in the air. The Delta 7000-series introduced the RS-27A main engine, which was modified for efficiency at high altitude at some cost to low-altitude performance, and the lighter ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Launch Vehicle
A launch vehicle or carrier rocket is a rocket designed to carry a payload (spacecraft or satellites) from the Earth's surface to outer space. Most launch vehicles operate from a launch pad, launch pads, supported by a missile launch control center, launch control center and systems such as vehicle assembly and fueling. Launch vehicles are engineered with advanced aerodynamics and technologies, which contribute to large operating costs. An orbital spaceflight, orbital launch vehicle must lift its payload at least to the boundary of space, approximately and accelerate it to a horizontal velocity of at least . Suborbital spaceflight, Suborbital vehicles launch their payloads to lower velocity or are launched at elevation angles greater than horizontal. Practical orbital launch vehicles are multistage rockets which use chemical propellants such as Solid-propellant rocket, solid fuel, liquid hydrogen, kerosene, liquid oxygen, or Hypergolic propellants. Launch vehicles are cla ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Castor 4A
The Castor family of solid-fuel rocket stages and boosters built by Thiokol (now Northrop Grumman) and used on a variety of launch vehicles. They were initially developed as the second-stage motor of the Scout rocket. The design was based on the MGM-29 Sergeant, a surface-to-surface missile developed for the United States Army at the Jet Propulsion Laboratory. Versions Flown versions Castor 1 :The Castor 1 was first used for a successful suborbital launch of a Scout X-1 rocket on September 2, 1960. :It was long, in diameter, and had a burn time of 27 seconds. Castor 1 stages were also used as strap-on boosters for launch vehicles using Thor first stages, including the Delta-D. (A Delta-D was used in 1964 to launch Syncom-3, the first satellite placed in a geostationary orbit.) Castor 1 stages were used in 141 launch attempts of Scout and Delta rockets, only 2 of which were failures. They were also used on some thrust-assisted Thor-Agena launchers. The last launch usin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
McDonnell Douglas
McDonnell Douglas was a major American aerospace manufacturing corporation and defense contractor, formed by the merger of McDonnell Aircraft and the Douglas Aircraft Company in 1967. Between then and its own merger with Boeing in 1997, it produced well-known commercial and military aircraft, such as the DC-10 airliner, the F-15 Eagle air superiority fighter, the MD-80 airliner, and the F/A-18 Hornet multirole fighter. The corporation's headquarters were at St. Louis Lambert International Airport, near St. Louis, Missouri; its subsidiary, McDonnell Douglas Technical Services Company (MDTSC), was based elsewhere in St. Louis County, Missouri. At its peak in mid-1990, McDonnell Douglas employed 132,500 people. By the end of 1992, employment had dropped to approximately 87,400. History Background The company was formed from the firms of James Smith McDonnell and Donald Wills Douglas in 1967. Both men were of Scottish ancestry, were graduates of the Massachusetts Institute of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Expendable Launch System
An expendable launch system (or expendable launch vehicle/ELV) is a launch vehicle that can be launched only once, after which its components are either destroyed during reentry or discarded in space. ELVs typically consist of several rocket stages that are discarded sequentially as their fuel is exhausted and the vehicle gains altitude and speed. As of 2022, most satellites and human spacecraft are currently launched on ELVs. ELVs are simpler in design than reusable launch systems and therefore may have a lower production cost. Furthermore, an ELV can use its entire fuel supply to accelerate its payload, offering greater payloads. ELVs are proven technology in widespread use for many decades. ELVs are usable only once, and therefore have a significantly higher per-launch cost than modern (post-STS) reusable vehicles. Current operators Arianespace China ISRO JAXA Roscosmos United States Several governmental agencies of the United States purchase ELV launches. NASA is ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Star 48B
The Star 48 is the largest of a family of solid rocket motors used by many space propulsion and launch vehicle stages. It is used almost exclusively as an upper stage. It was developed primarily by Thiokol Propulsion and is now, after several mergers, manufactured by Northrop Grumman’s Space Systems division. A Star 48B stage is also one of the few man-made items sent on escape trajectories out of the Solar System, although it is derelict since its use. The Star 48B variant was the PAM-D upper stage used on the now retired Delta II rocket. The Star 48 has been used as an upper stage in three- and four-stage launch systems. Overview The "48" designation refers to the approximate diameter of the fuel casing in inches (122 cm); Thiokol had also manufactured other motors such as the Star 37 and Star 30. Internally, Thiokol's designation was TE-M-711 for early versions and TE-M-799 for later ones. Subtypes are given one or more letter suffixes af ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Payload Assist Module
The Payload Assist Module (PAM) is a modular upper stage designed and built by McDonnell Douglas (now Boeing), using Thiokol Star-series solid propellant rocket motors. The PAM was used with the Space Shuttle, Delta, and Titan launchers and carried satellites from low Earth orbit to a geostationary transfer orbit or an interplanetary course. The payload was spin stabilized by being mounted on a rotating plate. Originally developed for the Space Shuttle, different versions of the PAM were developed: * PAM-A (Atlas class), development terminated; originally to be used on both the Atlas and Space Shuttle * PAM-D (Delta class), uses a Star-48B rocket motor * PAM-DII (Delta class), uses a Star-63 rocket motor * PAM-S (Special) as a kick motor for the space probe ''Ulysses'' The PAM-D module, used as the third stage of the Delta II rocket, was the last version in use. As of 2018, no PAM is in active use on any rockets. 2001 re-entry incident On January 12, 2001, a PAM-D module re-e ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aerozine 50
__NOTOC__ Aerozine 50 is a 50:50 mix by weight of hydrazine and unsymmetrical dimethylhydrazine (UDMH), originally developed in the late 1950s by Aerojet General Corporation as a storable, high-energy, hypergolic fuel for the Titan II ICBM rocket engines. Aerozine continues in wide use as a rocket fuel, typically with dinitrogen tetroxide as the oxidizer, with which it is hypergolic. Aerozine 50 is more stable than hydrazine alone, and has a higher density and boiling point than UDMH alone. Pure hydrazine has a higher performance than Aerozine 50, but an unacceptable freezing point. By mixing pure hydrazine with UDMH, hydrazine's inconveniently high freezing point of 2 °C is lowered through freezing-point depression. In addition, UDMH is a more stable molecule; this reduces the chances of straight hydrazine decomposing unexpectedly, increasing safety and allowing the blend to be used as a coolant in regeneratively cooled engines. This type of fuel is mainly used for inte ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dinitrogen Tetroxide
Dinitrogen tetroxide, commonly referred to as nitrogen tetroxide (NTO), and occasionally (usually among ex-USSR/Russia rocket engineers) as amyl, is the chemical compound N2O4. It is a useful reagent in chemical synthesis. It forms an equilibrium mixture with nitrogen dioxide. Its molar mass is 92.011 g/mol. Dinitrogen tetroxide is a powerful oxidizer that is hypergolic (spontaneously reacts) upon contact with various forms of hydrazine, which has made the pair a common bipropellant for rockets. Structure and properties Dinitrogen tetroxide could be regarded as two nitro groups (-NO2) bonded together. It forms an equilibrium mixture with nitrogen dioxide. The molecule is planar with an N-N bond distance of 1.78Å and N-O distances of 1.19Å. The N-N distance corresponds to a weak bond, since it is significantly longer than the average N-N single bond length of 1.45Å. This exceptionally weak σ bond (amounting to overlapping of the ''sp''2 hybrid orbitals of the two NO2 units) ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
AJ-10
The AJ10 is a hypergolic rocket engine manufactured by Aerojet Rocketdyne (previously Aerojet). It has been used to propel the upper stages of several launch vehicles, including the Delta II and Titan III. Variants were and are used as the service propulsion engine for the Apollo command and service module, in the Space Shuttle Orbital Maneuvering System, and on NASA's Orion spacecraft. Variants It was first used in the Delta-A/Able second stage of the Vanguard rocket, in the AJ10-118 configuration. It was initially fueled by nitric acid and UDMH. An AJ10 engine was first fired in flight during the third Vanguard launch, on 17 March 1958, which successfully placed the Vanguard 1 satellite into orbit. The AJ10-101 engine was used on an uprated version of the Able stage, used on Atlas-Able and Thor-Able rockets. The first AJ10-101 flight, with a Thor-Able, occurred on 23 April 1958; however, the Thor failed before the upper Able stage fired. The second flight, which saw the fir ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Delta K
The Delta-K was an American rocket stage, developed by McDonnell Douglas and Aerojet. It was first used on 27 August 1989 as the second stage for the Delta 4000 series. It continued to serve as the second stage for subsequent variants of the Delta rocket. It was propelled by a single AJ10-118K rocket engine, fueled by Aerozine 50 and dinitrogen tetroxide,Delta K , ''Encyclopedia Astronautica'', date 30 Jan 1997, accessed 2011-02-01. which are . The Delta-K had a long heritage to the first Able stage used in |
RP-1
RP-1 (alternatively, Rocket Propellant-1 or Refined Petroleum-1) is a highly refined form of kerosene outwardly similar to jet fuel, used as rocket fuel. RP-1 provides a lower specific impulse than liquid hydrogen (LH2), but is cheaper, is stable at room temperature, and presents a lower explosion hazard. RP-1 is far denser than LH2, giving it a higher energy density (though its specific energy is lower). RP-1 also has a fraction of the toxicity and carcinogenic hazards of hydrazine, another room-temperature liquid fuel. Usage and history RP-1 is a fuel in the first-stage boosters of the Electron, Soyuz, Zenit, Delta I-III, Atlas, Falcon, Antares, and Tronador II rockets. It also powered the first stages of the Energia, Titan I, Saturn I and IB, and Saturn V. The Indian Space Research Organization (ISRO) is also developing an RP-1 fueled engine for its future rockets. Development During and immediately after World War II, alcohols (primarily ethanol, occasionally metha ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
RS-27A
The RS-27A is a liquid-fuel rocket engine developed in 1980s by Rocketdyne for use on the first stage of the Delta II and Delta III launch vehicles. It provides of thrust burning RP-1 and LOX in a gas-generator cycle. The engine is a modified version of its predecessor, the RS-27; its thrust nozzle has been extended to increase its area ratio from 8:1 to 12:1, which provides greater efficiency at altitude. The RS-27A main engine is neither restartable nor throttleable. In addition to its main engine, it includes two vernier engines to provide vehicle roll control during flight.. When used as the main booster propulsion system for the Delta II family of launch vehicles, has an operational duration of 265 seconds. The last RS-27A engine was used for the ICESat-2 ICESat-2 (Ice, Cloud, and land Elevation Satellite 2), part of NASA's Earth Observing System, is a satellite mission for measuring ice sheet elevation and sea ice thickness, as well as land topography, vegetation charact ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |