|
List Of DOS System Files
MS-DOS / PC DOS and some related disk operating systems use the files mentioned here. System Files: *IO.SYS (or IBMBIO.COM): This contains the system initialization code and builtin device drivers. *MSDOS.SYS (or IBMDOS.COM): This contains the DOS kernel. Command-line interpreter (Shell): *COMMAND.COM: This is the command interpreter. User configuration files: *AUTOEXEC.BAT: This is run by the default shell (usually COMMAND.COM) to execute commands at startup. *CONFIG.SYS: This contains statements to configure DOS and load device drivers. Standard DOS utility programs: *APPEND: Set a search path for data files. * ASSIGN: Redirect requests for disk operations on one drive to a different drive. * ATTRIB: Set or display file attributes. *BACKUP / RESTORE: simple backup and restore utilities. *CHKDSK: Check disk for file system integrity. *COMP: File compare utility. * DEBUG: Simple command line debugger. *DELTREE: Delete a directory tree. *DISKCOMP: Compare floppy disks. *DISKCO ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
MS-DOS
MS-DOS ( ; acronym for Microsoft Disk Operating System, also known as Microsoft DOS) is an operating system for x86-based personal computers mostly developed by Microsoft. Collectively, MS-DOS, its rebranding as IBM PC DOS, and a few operating systems attempting to be compatible with MS-DOS, are sometimes referred to as "DOS" (which is also the generic acronym for disk operating system). MS-DOS was the main operating system for IBM PC compatibles during the 1980s, from which point it was gradually superseded by operating systems offering a graphical user interface (GUI), in various generations of the graphical Microsoft Windows operating system. IBM licensed and re-released it in 1981 as PC DOS 1.0 for use in its PCs. Although MS-DOS and PC DOS were initially developed in parallel by Microsoft and IBM, the two products diverged after twelve years, in 1993, with recognizable differences in compatibility, syntax, and capabilities. Beginning in 1988 with DR-DO ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Diskcomp
In computing, diskcomp is a command used for comparing the complete contents of a floppy disk to another one. Overview The command is used on DOS, Digital Research FlexOS, IBM/Toshiba 4690 OS, SISNE plus, IBM OS/2 and Microsoft Windows. It is available in MS-DOS versions 3.2 and later and IBM PC DOS releases 1 and later. Digital Research DR DOS 6.0 and Datalight ROM-DOS also include an implementation of the command. The FreeDOS version was developed by Michal Meller. The diskcomp command does not work with hard disk drives, CDs, network drives, Zip drives, or USB flash drives, etc. It also does not allow comparison from 3.5 inch drive to 5.25 inch drives, and vice versa. The source and target drive must be the same size. Examples Compare floppy disks in drive A: and drive B: diskcomp a: b: If the computer has only one floppy disk drive (in this case drive A:), it is still possible to compare two disks: diskcomp a: a: The diskcomp command will prompt to insert each disk, a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
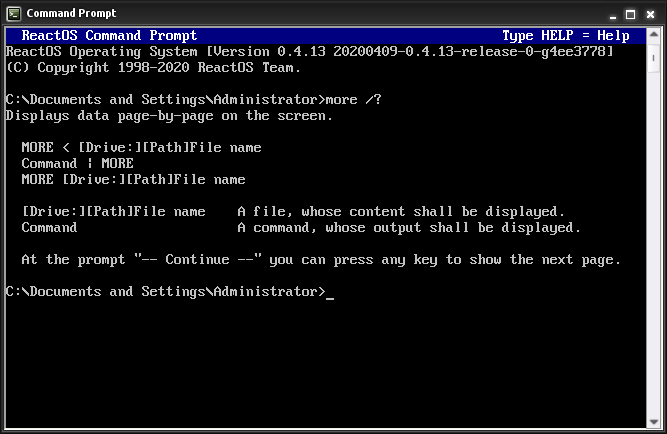
More (command)
In computing, more is a command to view (but not modify) the contents of a text file one screen at a time. It is available on Unix and Unix-like systems, DOS, Digital Research FlexOS, IBM/Toshiba 4690 OS, IBM OS/2, Microsoft Windows and ReactOS. Programs of this sort are called ''pagers''. more is a very basic pager, originally allowing only forward navigation through a file, though newer implementations do allow for limited backward movement. History The more command was originally written by Daniel Halbert, a graduate student at the University of California, Berkeley, in 1978. It was later expanded on by Eric Shienbrood, Geoff Peck (added underlining, single spacing) and John Foderaro (added -c, more environment variable history). It was first included in 3.0 BSD, and has since become a standard program in all Unix systems. less, a similar command with the extended capability of allowing both forward and backward navigation through the file, was written by Mark Nudelman betwe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mode (command)
This article presents a list of commands used by DOS operating systems, especially as used on x86-based IBM PC compatibles (PCs). Other DOS operating systems are not part of the scope of this list. In DOS, many standard system commands were provided for common tasks such as listing files on a disk or moving files. Some commands were built into the command interpreter, others existed as external commands on disk. Over the several generations of DOS, commands were added for the additional functions of the operating system. In the current Microsoft Windows operating system, a text-mode command prompt window, cmd.exe, can still be used. Command processing The command interpreter for DOS runs when no application programs are running. When an application exits, if the transient portion of the command interpreter in memory was overwritten, DOS will reload it from disk. Some commands are internal—built into COMMAND.COM; others are external commands stored on disk. When the user ty ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mem (command)
This article presents a list of commands used by DOS operating systems, especially as used on x86-based IBM PC compatibles (PCs). Other DOS operating systems are not part of the scope of this list. In DOS, many standard system commands were provided for common tasks such as listing files on a disk or moving files. Some commands were built into the command interpreter, others existed as external commands on disk. Over the several generations of DOS, commands were added for the additional functions of the operating system. In the current Microsoft Windows operating system, a text-mode command prompt window, cmd.exe, can still be used. Command processing The command interpreter for DOS runs when no application programs are running. When an application exits, if the transient portion of the command interpreter in memory was overwritten, DOS will reload it from disk. Some commands are internal—built into COMMAND.COM; others are external commands stored on disk. When the user type ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Label (command)
In computing, label is a command included with some operating systems (e.g., DOS, IBM OS/2, Microsoft Windows and ReactOS). It is used to create, change, or delete a volume label on a logical drive, such as a hard disk partition or a floppy disk. Used without parameters, label changes the current volume label or deletes the existing label. History The command was originally designed to label floppy disks as a reminder of which one is in the machine. However, it can also be applied to other types of drive such as mapped drives. It is available in MS-DOS versions 3.1 and later and IBM PC DOS releases 3 and later. It is an external command. MS-DOS 4.0x and earlier used label.com as the external file. MS-DOS 5.0 and Windows use label.exe as the external file. DR DOS 6.0 includes an implementation of the command. The FreeDOS version was developed by Joe Cosentino and is licensed under the GPL. In modern versions of Microsoft Windows, changing the disk label requires elevated p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
JOIN (DOS Command)
This article presents a list of commands used by DOS operating systems, especially as used on x86-based IBM PC compatibles (PCs). Other DOS operating systems are not part of the scope of this list. In DOS, many standard system commands were provided for common tasks such as listing files on a disk or moving files. Some commands were built into the command interpreter, others existed as external commands on disk. Over the several generations of DOS, commands were added for the additional functions of the operating system. In the current Microsoft Windows operating system, a text-mode command prompt window, cmd.exe, can still be used. Command processing The command interpreter for DOS runs when no application programs are running. When an application exits, if the transient portion of the command interpreter in memory was overwritten, DOS will reload it from disk. Some commands are internal—built into COMMAND.COM; others are external commands stored on disk. When the user ty ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Find (Windows)
In computing, find is a command in the command-line interpreters ( shells) of a number of operating systems. It is used to search for a specific text string in a file or files. The command sends the specified lines to the standard output device. Overview The find command is a filter to find lines in the input data stream that contain or don't contain a specified string and send these to the output data stream. It does not support wildcard characters. The command is available in DOS, Digital Research FlexOS, IBM/Toshiba 4690 OS, IBM OS/2, Microsoft Windows, and ReactOS. On MS-DOS, the command is available in versions 2 and later. DR DOS 6.0 and Datalight ROM-DOS include an implementation of the command. The FreeDOS version was developed by Jim Hall and is licensed under the GPL. The Unix command find performs an entirely different function, analogous to forfiles on Windows. The rough equivalent to the Windows find is the Unix grep. Syntax FIND V C N I"string" drive:path] ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fdisk
In computing, the fdisk command-line utility provides disk-partitioning functions, preparatory to defining file systems. fdisk features in the DOS, DR FlexOS, IBM OS/2, and Microsoft Windows operating systems, and in certain ports of FreeBSD, NetBSD, OpenBSD, DragonFly BSD and macOS for compatibility reasons. In versions of the Windows NT operating-system line from Windows 2000 onwards, is replaced by a more advanced tool called diskpart. Similar utilities exist for Unix-like systems, for example, BSD disklabel. Implementations IBM PC DOS IBM introduced , Fixed Disk Setup Program version 1.00, with the March 1983 release of the IBM PC/XT, the first PC to store data on a hard disk, and the IBM Personal Computer DOS version 2.0. Version 1 could be used to create one FAT12 DOS partition, delete it, change the active partition, or display partition data. writes the master boot record, which supported up to four partitions. The other three were intended for other op ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
File Compare
In computing, fc (File Compare) is a command-line program in DOS, IBM OS/2 and Microsoft Windows operating systems, that compares multiple files and outputs the differences between them. It is similar to the Unix commands comm, cmp and diff. History The fc command has been included in Microsoft operating systems since MS-DOS 2.11 (e.g. on the 1984/85 DEC Rainbow release) and is included in all versions of Microsoft Windows. fc has also been included in IBM OS/2 Version 2.0. DR DOS 6.0 includes an implementation of the command. The command is also available in FreeDOS. This implementation is licensed under the GPLv2+. Functionality fc can compare text files as well as binary files. The latest versions can compare ASCII or Unicode text. The result of comparisons are output to the standard output. The output of fc is intended primarily to be human readable and may be difficult to use in other programs. See also * Data comparison * comp (command) * List of DOS commands This ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |