|
List Of Contact Lens Complications
{{short description, none This is a list of complications that may result from the use of contact lenses. Eyelid * Ptosis Conjunctiva * Giant papillary conjunctivitis * Superior limbic keratoconjunctivitis Cornea * Epithelium ** Corneal abrasion ** Corneal erosion ** Contact lens acute red eye (CLARE) ** Corneal epithelial infiltrates ** Keratitis ** Corneal ulcer * Corneal stroma ** Corneal neovascularisation ** Corneal oedema ** Corneal infiltrates * Corneal endothelium ** Endothelial polymegathism See also *Effects of long-term contact lens wear on the cornea Long-term contact lens use can lead to alterations in corneal thickness, stromal thickness, curvature, corneal sensitivity, cell density, and epithelial oxygen uptake, etc. Other changes may include the formation of epithelial vacuoles and microcy ... Contact lenses ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Contact Lens
Contact lenses, or simply contacts, are thin lenses placed directly on the surface of the eyes. Contact lenses are ocular prosthetic devices used by over 150 million people worldwide, and they can be worn to correct vision or for cosmetic or therapeutic reasons. In 2010, the worldwide market for contact lenses was estimated at $6.1 billion, while the US soft lens market was estimated at $2.1 billion.Nichols, Jason J., et a"ANNUAL REPORT: Contact Lenses 2010" January 2011. Multiple analysts estimated that the global market for contact lenses would reach $11.7 billion by 2015. , the average age of contact lens wearers globally was 31 years old, and two-thirds of wearers were female.Morgan, Philip B., et al"International Contact Lens Prescribing in 2010" ''Contact Lens Spectrum''. October 2011. People choose to wear contact lenses for many reasons. Aesthetics and cosmetics are main motivating factors for people who want to avoid wearing glasses or to change the appearance or c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ptosis (eyelid)
Ptosis, also known as blepharoptosis, is a drooping or falling of the upper eyelid. The drooping may be worse after being awake longer when the individual's muscles are tired. This condition is sometimes called "lazy eye", but that term normally refers to the condition amblyopia. If severe enough and left untreated, the drooping eyelid can cause other conditions, such as amblyopia or astigmatism. This is why it is especially important for this disorder to be treated in children at a young age, before it can interfere with vision development. The term is from Greek 'fall, falling'. Signs and symptoms Signs and symptoms typically seen in this condition include: * The eyelid(s) may appear to droop. * Droopy eyelids can give the face a false appearance of being fatigued, disinterested, or even sinister. * The eyelid may not protect the eye as effectively, allowing it to dry out. * Sagging upper eyelids can partially block the person's field of view. * Obstructed vision may cause ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Giant Papillary Conjunctivitis
Allergic conjunctivitis (AC) is inflammation of the conjunctiva (the membrane covering the white part of the eye) due to allergy. Although allergens differ among patients, the most common cause is hay fever. Symptoms consist of redness (mainly due to vasodilation of the peripheral small blood vessels), edema (swelling) of the conjunctiva, itching, and increased lacrimation (production of tears). If this is combined with rhinitis, the condition is termed allergic rhinoconjunctivitis (ARC). The symptoms are due to release of histamine and other active substances by mast cells, which stimulate dilation of blood vessels, irritate nerve endings, and increase secretion of tears. Treatment of allergic conjunctivitis is by avoiding the allergen (''e.g.'', avoiding grass in bloom during "hay fever season") and treatment with antihistamines, either topical (in the form of eye drops), or systemic (in the form of tablets). Antihistamines, medications that stabilize mast cells, and non ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Superior Limbic Keratoconjunctivitis
Superior limbic keratoconjunctivitis (SLK, Théodore's syndrome) is a disease of the eye characterized by episodes of recurrent inflammation of the superior cornea and limbus, as well as of the superior tarsal and bulbar conjunctiva. It was first described by F. H. Théodore in 1963. Symptoms and signs Patients present with red eye, burning, tearing, foreign body sensation and mild photophobia. Upon examination, the conjunctiva appears inflamed and thickened, especially at the limbus. Pathophysiology The development and pathophysiology of SLK is not well understood, but appears to involve microtrauma of keratoconjunctival surfaces. This mechanical hypothesis is supported by the increased lid apposition of exophthalmic thyroid patients, who are known to have an increased incidence of superior limbic keratoconjunctivitis. Diagnosis Treatment First-line treatments include topical corticosteroids and artificial tears. For non-responsive cases, potential treatments include top ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Epithelium
Epithelium or epithelial tissue is one of the four basic types of animal tissue, along with connective tissue, muscle tissue and nervous tissue. It is a thin, continuous, protective layer of compactly packed cells with a little intercellular matrix. Epithelial tissues line the outer surfaces of organs and blood vessels throughout the body, as well as the inner surfaces of cavities in many internal organs. An example is the epidermis, the outermost layer of the skin. There are three principal shapes of epithelial cell: squamous (scaly), columnar, and cuboidal. These can be arranged in a singular layer of cells as simple epithelium, either squamous, columnar, or cuboidal, or in layers of two or more cells deep as stratified (layered), or ''compound'', either squamous, columnar or cuboidal. In some tissues, a layer of columnar cells may appear to be stratified due to the placement of the nuclei. This sort of tissue is called pseudostratified. All glands are made up of epithe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
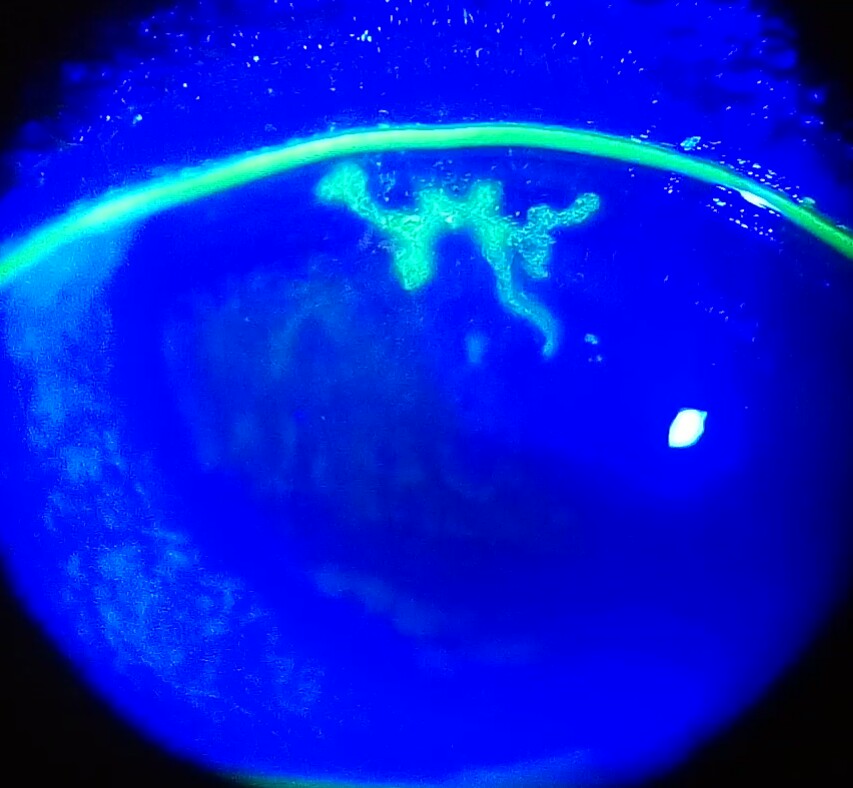
Corneal Abrasion
Corneal abrasion is a scratch to the surface of the cornea of the eye. Symptoms include pain, redness, light sensitivity, and a feeling like a foreign body is in the eye. Most people recover completely within three days. Most cases are due to minor trauma to the eye such as that which can occur with contact lens use or from fingernails. About 25% of cases occur at work. Diagnosis is often by slit lamp examination after fluorescein dye has been applied. More significant injuries like a corneal ulcer, globe rupture, recurrent erosion syndrome, and a foreign body within the eye should be ruled out. Prevention includes the use of eye protection. Treatment is typically with antibiotic ointment. In those who wear contact lenses a fluoroquinolone antibiotic is often recommended. Paracetamol (acetaminophen), NSAIDs, and eye drops such as cyclopentolate that paralyse the pupil can help with pain. Evidence does not support the usefulness of eye patching for those with simple abras ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Corneal Erosion
Recurrent corneal erosion is a disorder of the human eye, eyes characterized by the failure of the cornea's outermost layer of epithelial cells to attach to the underlying basement membrane (Bowman's layer). The condition is excruciatingly painful because the loss of these cells results in the exposure of sensitive corneal nerves. This condition can often leave patients with temporary blindness due to extreme light sensitivity (photophobia). Signs and symptoms Symptoms include recurring attacks of severe acute ocular pain, foreign-body sensation, photophobia (i.e. sensitivity to bright lights), and tearing often at the time of awakening or during sleep when the eyelids are rubbed or opened. Signs of the condition include corneal abrasion or localized roughening of the corneal epithelium, sometimes with map-like lines, epithelial dots or microcysts, or fingerprint patterns. An epithelial defect may be present, usually in the inferior interpalpebral zone. Cause Most cases of recurren ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
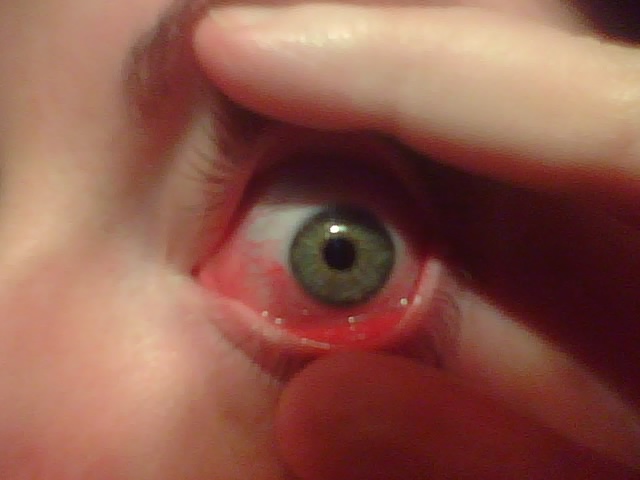
Contact Lens Acute Red Eye
Keratitis is a condition in which the eye's cornea, the clear dome on the front surface of the eye, becomes inflamed. The condition is often marked by moderate to intense pain and usually involves any of the following symptoms: pain, impaired eyesight, photophobia (light sensitivity), red eye and a 'gritty' sensation. Classification (by chronicity) Acute * Acute epithelial keratitis * Nummular keratitis * Interstitial keratitis * Disciform keratitis Chronic * Neurotrophic keratitis * Mucous plaque keratitis Classification (infective) Viral * Herpes simplex keratitis (dendritic keratitis). Viral infection of the cornea is often caused by the herpes simplex virus (HSV) which frequently leaves what is called a 'dendritic ulcer'. * Herpes zoster keratitis, associated with herpes zoster ophthalmicus, which is a form of shingles. Bacterial * Bacterial keratitis. Bacterial infection of the cornea can follow from an injury or from wearing contact lenses. The bacteria involve ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Corneal Epithelial Infiltrates
The cornea is the transparent front part of the eye that covers the iris, pupil, and anterior chamber. Along with the anterior chamber and lens, the cornea refracts light, accounting for approximately two-thirds of the eye's total optical power. In humans, the refractive power of the cornea is approximately 43 dioptres. The cornea can be reshaped by surgical procedures such as LASIK. While the cornea contributes most of the eye's focusing power, its focus is fixed. Accommodation (the refocusing of light to better view near objects) is accomplished by changing the geometry of the lens. Medical terms related to the cornea often start with the prefix "'' kerat-''" from the Greek word κέρας, ''horn''. Structure The cornea has unmyelinated nerve endings sensitive to touch, temperature and chemicals; a touch of the cornea causes an involuntary reflex to close the eyelid. Because transparency is of prime importance, the healthy cornea does not have or need blood vessel ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Keratitis
Keratitis is a condition in which the eye's cornea, the clear dome on the front surface of the eye, becomes inflamed. The condition is often marked by moderate to intense pain and usually involves any of the following symptoms: pain, impaired eyesight, photophobia (light sensitivity), red eye and a 'gritty' sensation. Classification (by chronicity) Acute * Acute epithelial keratitis * Nummular keratitis * Interstitial keratitis * Disciform keratitis Chronic * Neurotrophic keratitis * Mucous plaque keratitis Classification (infective) Viral * Herpes simplex keratitis (dendritic keratitis). Viral infection of the cornea is often caused by the herpes simplex virus (HSV) which frequently leaves what is called a 'dendritic ulcer'. * Herpes zoster keratitis, associated with herpes zoster ophthalmicus, which is a form of shingles. Bacterial * Bacterial keratitis. Bacterial infection of the cornea can follow from an injury or from wearing contact lenses. The bacteria involved ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Corneal Ulcer
Corneal ulcer is an inflammatory or, more seriously, infective condition of the cornea involving disruption of its epithelial layer with involvement of the corneal Stroma of cornea, stroma. It is a common condition in humans particularly in the tropics and the agrarian societies. In developing countries, children afflicted by Vitamin A deficiency are at high risk for corneal ulcer and may become blind in both eyes, which may persist lifelong. In ophthalmology, a corneal ulcer usually refers to having an infectious cause while the term corneal abrasion refers more to physical abrasions. Types Superficial and deep corneal ulcers Corneal ulcers are a common human eye disease. They are caused by trauma, particularly with vegetable matter, as well as chemical injury, contact lenses and infections. Other eye conditions can cause corneal ulcers, such as entropion, distichiasis, corneal dystrophy, and keratoconjunctivitis sicca (dry eye). Many micro-organisms cause infective corneal ulc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Corneal Stroma
The stroma of the cornea (or substantia propria) is a fibrous, tough, unyielding, perfectly transparent and the thickest layer of the cornea of the eye. It is between Bowman's membrane anteriorly, and Descemet's membrane posteriorly. At its centre, human corneal stroma is composed of about 200 flattened ''lamellæ'' (layers of collagen fibrils), superimposed one on another. They are each about 1.5-2.5 μm in thickness. The anterior lamellæ interweave more than posterior lamellæ. The fibrils of each lamella are parallel with one another, but at different angles to those of adjacent lamellæ. The lamellæ are produced by keratocytes (corneal connective tissue cells), which occupy about 10% of the substantia propria. Apart from the cells, the major non-aqueous constituents of the stroma are collagen fibrils and proteoglycans. The collagen fibrils are made of a mixture of type I and type V collagens. These molecules are tilted by about 15 degrees to the fibril axis, and becaus ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |