|
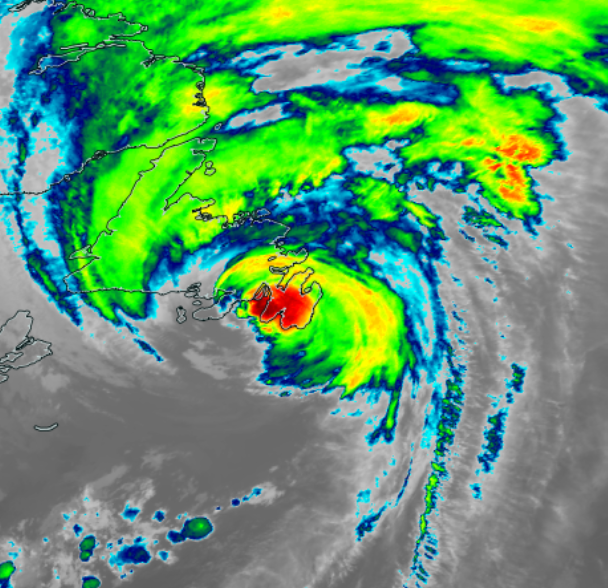
List Of Canada Hurricanes
The list of hurricanes in Canada refers to any tropical cyclone originating in the Atlantic or Pacific Ocean affecting the country of Canada. Canada is usually only hit with weak storms, due to the generally cool waters immediately offshore. However, some hurricanes can strike the area full force as the warm Gulf Stream extends fairly close to Atlantic Canada. Due to the cool waters for a great distance from the Pacific coast of Canada, there has never been a storm of any intensity to directly affect the Pacific coast. On occasion tropical systems can transition into, or be absorbed by, non-tropical systems that strongly affect western Canada, most notably by the remnants of Typhoon Freda that were absorbed by the Columbus Day Storm of 1962. According to the Canadian Hurricane Centre, Hurricane Ella of 1978 is the strongest tropical cyclone in Canadian waters, passing approximately 335 miles (540 km) south of Halifax, Nova Scotia as a Category 4 hurricane. Despi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1900 Galveston Hurricane
The 1900 Galveston hurricane, also known as the Great Galveston hurricane and the Galveston Flood, and known regionally as the Great Storm of 1900 or the 1900 Storm, is the deadliest natural disaster in United States history and the third-deadliest Atlantic hurricane, only behind the Great Hurricane of 1780 and Hurricane Mitch overall. The hurricane left between 6,000 and 12,000 fatalities in the United States; the number most cited in official reports is 8,000. Most of these deaths occurred in and near Galveston, Texas, after the storm surge inundated the coastline and the island city with 8 to 12 ft (2.4 to 3.7 m) of water. In addition to the number killed, the storm destroyed about 7,000 buildings of all uses in Galveston, which included 3,636 demolished homes; every dwelling in the city suffered some degree of damage. The hurricane left approximately 10,000 people in the city homeless, out of a total population of fewer than 38,000. The dis ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1873 Atlantic Hurricane Season
The 1873 Atlantic hurricane season was quiet, with only two tropical storms and three hurricanes, two of which were major hurricanes (Category 3+), being recorded. However, in the absence of modern satellite and other remote-sensing technologies, only storms that affected populated land areas or encountered ships at sea were recorded, so the actual total could be higher. An undercount bias of zero to six tropical cyclones per year between 1851 and 1885 and zero to four per year between 1886 and 1910 has been estimated. Of the known cyclones, large alterations were made to the tracks of Hurricane Two and Hurricane Five in 1995 by Jose Fernandez-Partagas and Henry Diaz, who also proposed smaller changes to the known track of Hurricane Three.Partagas, J.F. and H.F. Diaz, 1995b "A Reconstruction of Historical Tropical Cyclone Frequency in the Atlantic from Documentary and other Historical Sources : 1851–1880 Part II: 1871–1880" Climate Diagnostics Center, NOAA, Boulder, CO All of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
New Brunswick
New Brunswick (french: Nouveau-Brunswick, , locally ) is one of the thirteen provinces and territories of Canada. It is one of the three Maritime provinces and one of the four Atlantic provinces. It is the only province with both English and French as its official languages. New Brunswick is bordered by Quebec to the north, Nova Scotia to the east, the Gulf of Saint Lawrence to the northeast, the Bay of Fundy to the southeast, and the U.S. state of Maine to the west. New Brunswick is about 83% forested and its northern half is occupied by the Appalachians. The province's climate is continental with snowy winters and temperate summers. New Brunswick has a surface area of and 775,610 inhabitants (2021 census). Atypically for Canada, only about half of the population lives in urban areas. New Brunswick's largest cities are Moncton and Saint John, while its capital is Fredericton. In 1969, New Brunswick passed the Official Languages Act which began recognizing French as an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bay Of Fundy
The Bay of Fundy (french: Baie de Fundy) is a bay between the Canadian provinces of New Brunswick and Nova Scotia, with a small portion touching the U.S. state of Maine. It is an arm of the Gulf of Maine. Its extremely high tidal range is the highest in the world. The name is likely a corruption of the French word , meaning 'split'. Hydrology Tides The tidal range in the Bay of Fundy is about ; the average tidal range worldwide is only . Some tides are higher than others, depending on the position of the moon, the sun, and atmospheric conditions. Tides are semidiurnal, meaning they have two highs and two lows each day, with about six hours and 13 minutes between each high and low tide. Because of tidal resonance in the funnel-shaped bay, the tides that flow through the channel are very powerful. In one 12-hour tidal cycle, about 100 billion tons (110 billion short tons) of water flows in and out of the bay, which is twice as much as the combined total flow of all the rive ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1869 Saxby Gale
The Saxby Gale was a tropical cyclone which struck eastern Canada's Bay of Fundy region on the night of October 4–5, 1869. The storm was named for Lieutenant Stephen Martin Saxby, a naval instructor who, based on his astronomical studies, had predicted extremely high tides in the North Atlantic Ocean on October 1, 1869, which would produce storm surges in the event of a storm. Effects The hurricane caused extensive destruction to port facilities and communities along the Bay of Fundy coast in both New Brunswick and Nova Scotia as well as Maine, particularly Calais, St. Andrews, St. George, Saint John, Moncton, Sackville, Amherst, Windsor and Truro. Much of the devastation was attributed to a two-metre storm surge created by the storm which coincided with a perigean spring tide; the Bay of Fundy having one of the highest tidal ranges in the world. The Saxby Gale storm surge produced a water level which gave Burntcoat Head, Nova Scotia, the honor of having the highe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nova Scotia
Nova Scotia ( ; ; ) is one of the thirteen provinces and territories of Canada. It is one of the three Maritime provinces and one of the four Atlantic provinces. Nova Scotia is Latin for "New Scotland". Most of the population are native English-speakers, and the province's population is 969,383 according to the 2021 Census. It is the most populous of Canada's Atlantic provinces. It is the country's second-most densely populated province and second-smallest province by area, both after Prince Edward Island. Its area of includes Cape Breton Island and 3,800 other coastal islands. The Nova Scotia peninsula is connected to the rest of North America by the Isthmus of Chignecto, on which the province's land border with New Brunswick is located. The province borders the Bay of Fundy and Gulf of Maine to the west and the Atlantic Ocean to the south and east, and is separated from Prince Edward Island and the island of Newfoundland by the Northumberland and Cabot straits, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1804 Snow Hurricane
The 1804 New England hurricane (also known as the Storm of October 1804) was the first tropical cyclone in recorded history known to have produced snowfall. An unusual late-season storm in 1804, it yielded vast amounts of snow, rain, and powerful winds across the northeastern United States. Prior to its approach towards the East Coast of the United States, it passed through the Caribbean Sea on October 4, and later emerged near Georgetown, South Carolina. By early on October 9, a trough near the Virginia Capes turned the disturbance toward New England. Soon thereafter, the hurricane's abundant moisture clashed with an influx of cold Canadian air, leading to the deepening of the resulting pressure gradient and provoking inland intensification. While situated over Massachusetts, it attained its peak intensity of 110 mph (175 km/h), undergoing an extratropical transition. Even as it drifted towards the Canadian maritimes, consequently gradually weakening, pre ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1775 Newfoundland Hurricane
The 1775 Newfoundland hurricane, also known as the Independence Hurricane, was a hurricane that struck the Thirteen Colonies and the Colony of Newfoundland in August and September, 1775, at the outset of the American War of Independence. It is believed to have killed at least 4,000 people, making it one of the deadliest Atlantic hurricanes of all time. There is disagreement among historians and meteorologists whether the events were one storm or two distinct storms. Impact North Carolina and Virginia On August 27, 1775, a hurricane hit the Outer Banks of North Carolina. It turned northeastward and left the state on September 2, bringing heavy wind and rain to southeastern Virginia. A letter from New Bern, North Carolina, recounted, ''"We had a violent hurricane...which has done a vast deal of damage here, at the Bar, and at Matamuskeet, near 150 lives being lost at the Bar, and 15 in one neighborhood at Matamuskeet."'' The September 9, 1775, edition of The Virginia Gazette repor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Colony Of Newfoundland
Newfoundland Colony was an English and, later, British colony established in 1610 on the island of Newfoundland off the Atlantic coast of Canada, in what is now the province of Newfoundland and Labrador. That followed decades of sporadic English settlement on the island, which was at first seasonal, rather than permanent. It was made a Crown colony in 1824 and a Dominion in 1907. Its economy collapsed during the Great Depression of the 1930s, and Newfoundland relinquished its dominion status, effectively becoming once again a colony governed by appointees from the Colonial Office in Whitehall in London. In 1949, the colony voted to join Canada as the Province of Newfoundland. History Indigenous people like the Beothuk (known as the ''Skræling'' in Greenlandic Norse), and Innu were the first inhabitants of Newfoundland and Labrador. During the late 15th century, European explorers like João Fernandes Lavrador, Gaspar Corte-Real, John Cabot, Jacques Cartier and others b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
NOAA
The National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (abbreviated as NOAA ) is an United States scientific and regulatory agency within the United States Department of Commerce that forecasts weather, monitors oceanic and atmospheric conditions, charts the seas, conducts deep sea exploration, and manages fishing and protection of marine mammals and endangered species in the U.S. exclusive economic zone. Purpose and function NOAA's specific roles include: * ''Supplying Environmental Information Products''. NOAA supplies to its customers and partners information pertaining to the state of the oceans and the atmosphere, such as weather warnings and forecasts via the National Weather Service. NOAA's information services extend as well to climate, ecosystems, and commerce. * ''Providing Environmental Stewardship Services''. NOAA is a steward of U.S. coastal and marine environments. In coordination with federal, state, local, tribal and international authorities, NOAA manages the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dominion Of Newfoundland
Newfoundland was a British dominion in eastern North America, today the modern Canadian province of Newfoundland and Labrador. It was established on 26 September 1907, and confirmed by the Balfour Declaration of 1926 and the Statute of Westminster of 1931. It included the island of Newfoundland, and Labrador on the continental mainland. Newfoundland was one of the original dominions within the meaning of the Balfour Declaration and accordingly enjoyed a constitutional status equivalent to the other dominions of the time. In 1934, Newfoundland became the only dominion to give up its self-governing status, which ended 79 years of self-government. The abolition of self-government came about because of a crisis in Newfoundland's public finances in 1932. Newfoundland had accumulated a significant amount of debt by building a railway across the island, which was completed in the 1890s, and by raising its own regiment during World War I. In November 1932, the government warned th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |



.jpg)
