|
List Of Archaeological Sites In Israel And Palestine
This is a list of archaeological sites in Israel and Palestine. Introduction The geographical framework of the sites listed is based on the political boundaries rather than historical, archaeological boundaries. Sites in this list are located within the territory of the modern State of Israel, including Israeli-occupied territories that were fully annexed to Israel, namely East Jerusalem (part of the West Bank) and the Golan Heights (occupied from Syria). Under the Antiquities Law of the State of Israel of 1978, the archaeological activity in these territories is de facto administered by the Israel Antiquities Authority. The list also includes sites within the Palestinian territories (claimed by the State of Palestine). Archaeological activity in these territories is administered by the Staff Officer for Archaeology in Judea and Samaria of the Israel Defense Forces and the Palestinian Department of Antiquities of the Palestinian National Authority. The sites appear by the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Israel
Israel (; he, יִשְׂרָאֵל, ; ar, إِسْرَائِيل, ), officially the State of Israel ( he, מְדִינַת יִשְׂרָאֵל, label=none, translit=Medīnat Yīsrāʾēl; ), is a country in Western Asia. It is situated on the southeastern shore of the Mediterranean Sea and the northern shore of the Red Sea, and shares borders with Lebanon to the north, Syria to the northeast, Jordan to the east, and Egypt to the southwest. Israel also is bordered by the Palestinian territories of the West Bank and the Gaza Strip to the east and west, respectively. Tel Aviv is the economic and technological center of the country, while its seat of government is in its proclaimed capital of Jerusalem, although Israeli sovereignty over East Jerusalem is unrecognized internationally. The land held by present-day Israel witnessed some of the earliest human occupations outside Africa and was among the earliest known sites of agriculture. It was inhabited by the Canaanites ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
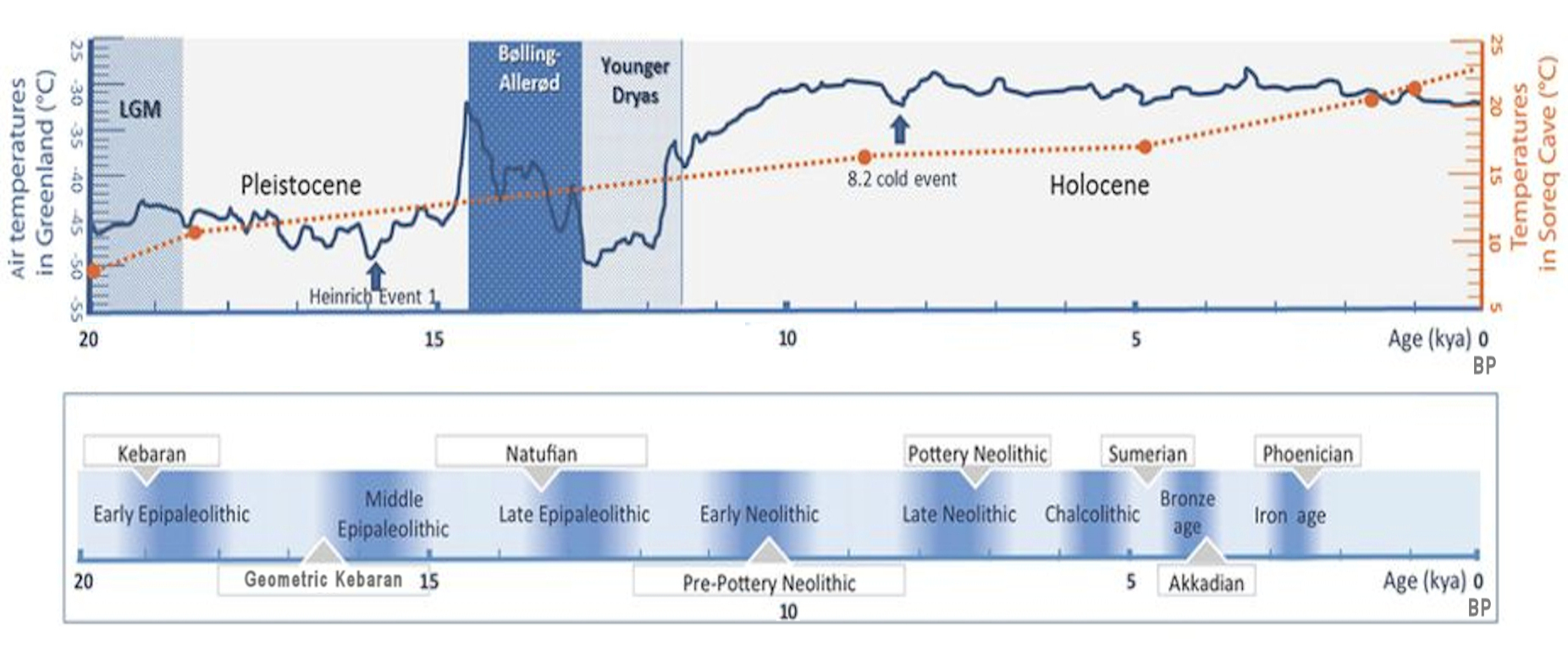
Epipalaeolithic Near East
The Epipalaeolithic Near East designates the Epipalaeolithic ("Final Old Stone Age", also known as Mesolithic) in the prehistory of the Near East. It is the period after the Upper Palaeolithic and before the Neolithic, between approximately 20,000 and 10,000 years Before Present (BP). The people of the Epipalaeolithic were nomadic hunter-gatherers who generally lived in small, seasonal camps rather than permanent villages. They made sophisticated stone tools using microliths—small, finely-produced blades that were hafted in wooden implements. These are the primary artifacts by which archaeologists recognise and classify Epipalaeolithic sites. The start of the Epipalaeolithic is defined by the appearance of microliths. Although this is an arbitrary boundary, the Epipalaeolithic does differ significantly from the preceding Upper Palaeolithic. Epipalaeolithic sites are more numerous, better preserved, and can be accurately radiocarbon dated. The period coincides with the gradual ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kingdom Of Jerusalem
The Kingdom of Jerusalem ( la, Regnum Hierosolymitanum; fro, Roiaume de Jherusalem), officially known as the Latin Kingdom of Jerusalem or the Frankish Kingdom of Palestine,Example (title of works): was a Crusader state that was established in the Levant immediately after the First Crusade. It lasted for almost two hundred years, from the accession of Godfrey of Bouillon in 1099 until the siege of Acre in 1291. Its history is divided into two periods with a brief interruption in its existence, beginning with its collapse after the siege of Jerusalem in 1187 and its restoration after the Third Crusade in 1192. The original Kingdom of Jerusalem lasted from 1099 to 1187 before being almost entirely overrun by the Ayyubid Sultanate under Saladin. Following the Third Crusade, it was re-established in Acre in 1192. The re-established state is commonly known as the "Second Kingdom of Jerusalem" or alternatively as the "Kingdom of Acre" after its new capital city. Acre remained t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fatimid Caliphate
The Fatimid Caliphate was an Isma'ilism, Ismaili Shia Islam, Shi'a caliphate extant from the tenth to the twelfth centuries AD. Spanning a large area of North Africa, it ranged from the Atlantic Ocean in the west to the Red Sea in the east. The Fatimid dynasty, Fatimids, a dynasty of Arab origin, trace their ancestry to Muhammad's daughter Fatimah, Fatima and her husband Ali, ‘Ali b. Abi Talib, the first Imamate in Shia doctrine, Shi‘a imam. The Fatimids were acknowledged as the rightful imams by different Isma'ilism, Isma‘ili communities, but also in many other Muslim lands, including Persia and the adjacent regions. Originating during the Abbasid Caliphate, the Fatimids conquered Tunisia and established the city of "Mahdia, al-Mahdiyya" ( ar, المهدية). The Ismaili dynasty ruled territories across the Mediterranean coast of Africa and ultimately made Egypt the center of the caliphate. At its height, the caliphate included – in addition to Egypt – varying ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Abbasid Caliphate
The Abbasid Caliphate ( or ; ar, الْخِلَافَةُ الْعَبَّاسِيَّة, ') was the third caliphate to succeed the Islamic prophet Muhammad. It was founded by a dynasty descended from Muhammad's uncle, Abbas ibn Abdul-Muttalib (566–653 CE), from whom the dynasty takes its name. They ruled as caliphs for most of the caliphate from their capital in Baghdad in modern-day Iraq, after having overthrown the Umayyad Caliphate in the Abbasid Revolution of 750 CE (132 AH). The Abbasid Caliphate first centered its government in Kufa, modern-day Iraq, but in 762 the caliph Al-Mansur founded the city of Baghdad, near the ancient Babylonian capital city of Babylon. Baghdad became the center of science, culture and invention in what became known as the Golden Age of Islam. This, in addition to housing several key academic institutions, including the House of Wisdom, as well as a multiethnic and multi-religious environment, garnered it a worldwide reputation as the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Umayyad Caliphate
The Umayyad Caliphate (661–750 CE; , ; ar, ٱلْخِلَافَة ٱلْأُمَوِيَّة, al-Khilāfah al-ʾUmawīyah) was the second of the four major caliphates established after the death of Muhammad. The caliphate was ruled by the Umayyad dynasty ( ar, ٱلْأُمَوِيُّون, ''al-ʾUmawīyūn'', or , ''Banū ʾUmayyah'', "Sons of Umayyah"). Uthman ibn Affan (r. 644–656), the third of the Rashidun caliphs, was also a member of the clan. The family established dynastic, hereditary rule with Muawiya ibn Abi Sufyan, long-time governor of Greater Syria, who became the sixth caliph after the end of the First Fitna in 661. After Mu'awiyah's death in 680, conflicts over the succession resulted in the Second Fitna, and power eventually fell into the hands of Marwan I from another branch of the clan. Greater Syria remained the Umayyads' main power base thereafter, with Damascus serving as their capital. The Umayyads continued the Muslim conquests, incorpo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rashidun Caliphate
The Rashidun Caliphate ( ar, اَلْخِلَافَةُ ٱلرَّاشِدَةُ, al-Khilāfah ar-Rāšidah) was the first caliphate to succeed the Islamic prophet Muhammad. It was ruled by the first four successive caliphs of Muhammad after his death in 632 CE (11 Hijri year, AH). During its existence, the empire was the most powerful economic, cultural, and military force in Western Asia, West Asia. The caliphate arose following Muhammad’s passing in June 632 and the subsequent debate over the Succession to Muhammad, succession to his leadership. Muhammad's childhood friend and close companion Abu Bakr (), of the Banu Taym clan, was elected the first caliph in Medina and he began the Early Muslim conquests, conquest of the Arabian Peninsula. His brief reign ended in August 634 when he died and was succeeded by Umar (), his appointed successor from the Banu Adi clan. Under Umar, the caliphate expanded at an unprecedented rate, ruling more than two-thirds of the Byzantine Empir ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Byzantine Empire
The Byzantine Empire, also referred to as the Eastern Roman Empire or Byzantium, was the continuation of the Roman Empire primarily in its eastern provinces during Late Antiquity and the Middle Ages, when its capital city was Constantinople. It survived the fragmentation and fall of the Western Roman Empire in the 5th century AD and continued to exist for an additional thousand years until the fall of Constantinople to the Ottoman Empire in 1453. During most of its existence, the empire remained the most powerful economic, cultural, and military force in Europe. The terms "Byzantine Empire" and "Eastern Roman Empire" were coined after the end of the realm; its citizens continued to refer to their empire as the Roman Empire, and to themselves as Romans—a term which Greeks continued to use for themselves into Ottoman times. Although the Roman state continued and its traditions were maintained, modern historians prefer to differentiate the Byzantine Empire from Ancient Rome ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Roman Empire
The Roman Empire ( la, Imperium Romanum ; grc-gre, Βασιλεία τῶν Ῥωμαίων, Basileía tôn Rhōmaíōn) was the post-Republican period of ancient Rome. As a polity, it included large territorial holdings around the Mediterranean Sea in Europe, North Africa, and Western Asia, and was ruled by emperors. From the accession of Caesar Augustus as the first Roman emperor to the military anarchy of the 3rd century, it was a Principate with Italia as the metropole of its provinces and the city of Rome as its sole capital. The Empire was later ruled by multiple emperors who shared control over the Western Roman Empire and the Eastern Roman Empire. The city of Rome remained the nominal capital of both parts until AD 476 when the imperial insignia were sent to Constantinople following the capture of the Western capital of Ravenna by the Germanic barbarians. The adoption of Christianity as the state church of the Roman Empire in AD 380 and the fall of the Western ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hellenistic Period
In Classical antiquity, the Hellenistic period covers the time in Mediterranean history after Classical Greece, between the death of Alexander the Great in 323 BC and the emergence of the Roman Empire, as signified by the Battle of Actium in 31 BC and the conquest of Ptolemaic Egypt the following year. The Ancient Greek word ''Hellas'' (, ''Hellás'') was gradually recognized as the name for Greece, from which the word ''Hellenistic'' was derived. "Hellenistic" is distinguished from "Hellenic" in that the latter refers to Greece itself, while the former encompasses all ancient territories under Greek influence, in particular the East after the conquests of Alexander the Great. After the Macedonian invasion of the Achaemenid Empire in 330 BC and its disintegration shortly after, the Hellenistic kingdoms were established throughout south-west Asia ( Seleucid Empire, Kingdom of Pergamon), north-east Africa ( Ptolemaic Kingdom) and South Asia ( Greco-Bactrian Kingdom, Indo-Greek ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Achaemenid Empire
The Achaemenid Empire or Achaemenian Empire (; peo, 𐎧𐏁𐏂, , ), also called the First Persian Empire, was an ancient Iranian empire founded by Cyrus the Great in 550 BC. Based in Western Asia, it was contemporarily the largest empire in history, spanning a total of from the Balkans and Egypt in the west to Central Asia and the Indus Valley in the east. Around the 7th century BC, the region of Persis in the southwestern portion of the Iranian plateau was settled by the Persians. From Persis, Cyrus rose and defeated the Median Empire as well as Lydia and the Neo-Babylonian Empire, marking the formal establishment of a new imperial polity under the Achaemenid dynasty. In the modern era, the Achaemenid Empire has been recognized for its imposition of a successful model of centralized, bureaucratic administration; its multicultural policy; building complex infrastructure, such as road systems and an organized postal system; the use of official languages across ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Iron Age
The Iron Age is the final epoch of the three-age division of the prehistory and protohistory of humanity. It was preceded by the Stone Age (Paleolithic, Mesolithic, Neolithic) and the Bronze Age (Chalcolithic). The concept has been mostly applied to Iron Age Europe and the Ancient Near East, but also, by analogy, to other parts of the Old World. The duration of the Iron Age varies depending on the region under consideration. It is defined by archaeological convention. The "Iron Age" begins locally when the production of iron or steel has advanced to the point where iron tools and weapons replace their bronze equivalents in common use. In the Ancient Near East, this transition took place in the wake of the Bronze Age collapse, in the 12th century BC. The technology soon spread throughout the Mediterranean Basin region and to South Asia (Iron Age in India) between the 12th and 11th century BC. Its further spread to Central Asia, Eastern Europe, and Central Europe is somewhat dela ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |

.jpg)




