|
Lips
The lips are the visible body part at the mouth of many animals, including humans. Lips are soft, movable, and serve as the opening for food intake and in the articulation of sound and speech. Human lips are a tactile sensory organ, and can be an erogenous zone when used in kissing and other acts of intimacy. Structure The upper and lower lips are referred to as the "Labium superius oris" and "Labium inferius oris", respectively. The juncture where the lips meet the surrounding skin of the mouth area is the vermilion border, and the typically reddish area within the borders is called the vermilion zone. The vermilion border of the upper lip is known as the cupid's bow. The fleshy protuberance located in the center of the upper lip is a tubercle known by various terms including the procheilon (also spelled ''prochilon''), the "tuberculum labii superioris", and the "labial tubercle". The vertical groove extending from the procheilon to the nasal septum is called the philtr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lower Lip
The lips are the visible body part at the mouth of many animals, including humans. Lips are soft, movable, and serve as the opening for food intake and in the articulation of sound and speech. Human lips are a tactile sensory organ, and can be an erogenous zone when used in kissing and other acts of intimacy. Structure The upper and lower lips are referred to as the "Labium superius oris" and "Labium inferius oris", respectively. The juncture where the lips meet the surrounding skin of the mouth area is the vermilion border, and the typically reddish area within the borders is called the vermilion zone. The vermilion border of the upper lip is known as the cupid's bow. The fleshy protuberance located in the center of the upper lip is a tubercle known by various terms including the procheilon (also spelled ''prochilon''), the "tuberculum labii superioris", and the "labial tubercle". The vertical groove extending from the procheilon to the nasal septum is called the philtr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
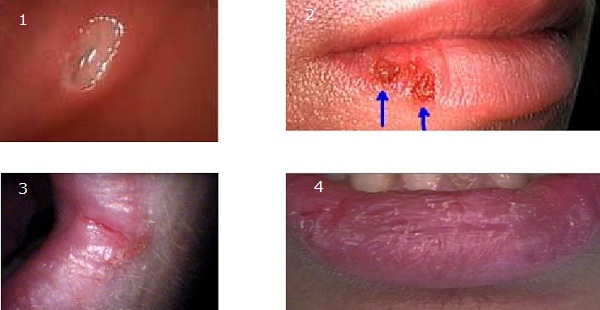
Chapped
Cheilitis is a medical condition characterized by inflammation of the lips. The inflammation may include the perioral skin (the skin around the mouth), the vermilion border, or the labial mucosa. The skin and the vermilion border are more commonly involved, as the mucosa is less affected by inflammatory and allergic reactions. ''Cheilitis'' is a general term, and there are many recognized types and different causes. According to its onset and course, cheilitis can be either acute or chronic. Most cheilitis is caused by exogenous factors such as dryness (chapping) and acute sun exposure. Allergic tests may identify allergens that cause cheilitis. Chapped lips Chapped lips (also known as cheilitis simplex or common cheilitis) is characterized by the cracking, fissuring, and peeling of the skin of the lips, and is one of the most common types of cheilitis. While both lips may be affected, the lower lip is the most common site. There may also be burning or the formation of large ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kiss
A kiss is the touch or pressing of one's lips against another person or an object. Cultural connotations of kissing vary widely. Depending on the culture and context, a kiss can express sentiments of love, passion, romance, sexual attraction, sexual activity, sexual arousal, affection, respect, greeting, friendship, peace, and good luck, among many others. In some situations, a kiss is a ritual, formal or symbolic gesture indicating devotion, respect, or a sacramental. The word came from Old English '' cyssan'' (" to kiss"), in turn from ''coss '' ("a kiss"). History Anthropologists disagree on whether kissing is an instinctual or learned behaviour. Those that believe kissing to be an instinctual behaviour, cite similar behaviours in other animals such as bonobos, which are known to kiss after fighting - possibly to restore peace. Others believe that it is a learned behaviour, having evolved from activities such as suckling or premastication in early human cultures passe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vermilion Border
The vermilion border (sometimes spelled vermillion border), also called margin or zone, is the normally sharp demarcation between the lip and the adjacent normal skin. It represents the change in the epidermis from highly keratinized external skin to less keratinized internal skin. It has no sebaceous glands, sweat glands, or facial hair. It has a prominence on the face, creating a focus for cosmetics (it is where lipstick is sometimes applied) and is also a location for several skin diseases. Its functional properties, however, remain unknown. Structure The lips are composed wholly of soft tissue. The skin of the face is thicker than the skin overlying the lips where blood vessels are closer to the surface. As a consequence, the margin of the lips shows a transition between the thicker and thinner skin, represented by the vermilion border. It therefore has the appearance of a sharp line between the coloured edge of the lip and adjoining skin. It has been described as a pale, whit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Orbicularis Oris
In human anatomy, the orbicularis oris muscle is a complex of muscles in the lips that encircles the mouth. It is a sphincter, or circular muscle, but it is actually composed of four independent quadrants that interlace and give only an appearance of circularity.Saladin, "Anatomy & Physiology: The Unity of Form and Function". 5th edition. McGraw Hill. Page 330 It is also one of the muscles used in the playing of all brass instruments and some woodwind instruments. This muscle closes the mouth and puckers the lips when it contracts. Structure The orbicularis oris is not a simple sphincter muscle like the orbicularis oculi; it consists of numerous strata of muscular fibers surrounding the orifice of the mouth, but having different direction. It consists partly of fibers derived from the other facial muscles which are inserted into the lips, and partly of fibers proper to the lips. Of the former, a considerable number are derived from the buccinator and form the deeper stratum of th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Erogenous Zone
An erogenous zone (from Greek , ''érōs'' "love"; and English ''-genous'' "producing", from Greek , ''-genḗs'' "born") is an area of the human body that has heightened sensitivity, the stimulation of which may generate a sexual response, such as relaxation, sexual fantasies, sexual arousal and orgasm. Erogenous zones are located all over the human body, but the sensitivity of each varies, and depends on concentrations of nerve endings that can provide pleasurable sensations when stimulated. The touching of another person's erogenous zone is regarded as an act of physical intimacy. Whether a person finds stimulation in these areas to be pleasurable or objectionable depends on a range of factors, including their level of arousal, the circumstances in which it takes place, the cultural context, the nature of the relationship between the partners, and the partners' personal histories. Erogenous zones may be classified by the type of sexual response that they generate. Many peo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Inferior Labial Artery
The inferior labial artery (inferior labial branch of facial artery) arises near the angle of the mouth as a branch of the facial artery; it passes upward and forward beneath the triangularis and, penetrating the orbicularis oris, runs in a tortuous course along the edge of the lower lip between this muscle and the mucous membrane. It supplies the labial glands, the mucous membrane, and the muscles of the lower lip; and anastomoses with the artery of the opposite side, and with the mental branch of the inferior alveolar artery The inferior alveolar artery (inferior dental artery) is an artery of the face. It is a branch of the first portion of the maxillary artery. Structure It descends with the inferior alveolar nerve to the mandibular foramen on the medial surface of .... Additional images File:Lateral head anatomy detail.jpg, Lateral head anatomy detail File:Head ap anatomy.jpg, Head anatomy anterior view File:Slide2bbb.JPG, Inferior labial artery References Externa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Superior Labial Artery
The superior labial artery (superior labial branch of facial artery) is larger and more egregious than the inferior labial artery. It follows a similar course along the edge of the upper lip, lying between the mucous membrane and the orbicularis oris, and anastomoses with the artery of the opposite side. It supplies the upper lip, and gives off in its course two or three vessels which ascend to the nose; a septal branch ramifies on the nasal septum as far as the point of the nose, and an alar branch supplies the ala of the nose. See also *Kiesselbach's plexus Kiesselbach's plexus is an anastomotic arterial network (plexus) of four or five arteries in the nose supplying the nasal septum. It lies in the anterior inferior part of the septum known as Little's area, Kiesselbach's area, or Kiesselbach's tri ... Additional images File:Lateral head anatomy detail.jpg, Lateral head anatomy detail File:Head ap anatomy.jpg, Head anatomy anterior view File:Slide1bbbb.JPG, Superior la ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Philtrum
The philtrum ( la, philtrum from Ancient Greek ''phíltron,'' lit. "love charm"), or medial cleft, is a vertical indentation in the middle area of the upper lip, common to therian mammals, extending in humans from the nasal septum to the tubercle of the upper lip. Together with a glandular rhinarium and slit-like nostrils, it is believed to constitute the primitive condition for at least therian mammals. Monotremes lack a philtrum, though this could be due to the specialised, beak-like jaws in living species. Function In most mammals, the philtrum is a narrow groove that may carry dissolved odorants from the rhinarium or nose pad to the vomeronasal organ via ducts inside the mouth. For humans and most primates, the philtrum survives only as a vestigial medial depression between the nose and upper lip. The human philtrum, bordered by ridges, is also known as the ''infranasal depression'', but has no apparent function. That may be because most higher primates rely more on vision ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sweat Gland
Sweat glands, also known as sudoriferous or sudoriparous glands, , are small tubular structures of the skin that produce sweat. Sweat glands are a type of exocrine gland, which are glands that produce and secrete substances onto an epithelial surface by way of a duct. There are two main types of sweat glands that differ in their structure, function, secretory product, mechanism of excretion, anatomic distribution, and distribution across species: * Eccrine sweat glands are distributed almost all over the human body, in varying densities, with the highest density in palms and soles, then on the head, but much less on the trunk and the extremities. Its water-based secretion represents a primary form of cooling in humans. * Apocrine sweat glands are mostly limited to the axillae (armpits) and perineal area in humans. They are not significant for cooling in humans, but are the sole effective sweat glands in hoofed animals, such as the camels, donkeys, horses, and cattle. Ceruminou ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mucous Membrane
A mucous membrane or mucosa is a membrane that lines various cavities in the body of an organism and covers the surface of internal organs. It consists of one or more layers of epithelial cells overlying a layer of loose connective tissue. It is mostly of endodermal origin and is continuous with the skin at body openings such as the eyes, eyelids, ears, inside the nose, inside the mouth, lips, the genital areas, the urethral opening and the anus. Some mucous membranes secrete mucus, a thick protective fluid. The function of the membrane is to stop pathogens and dirt from entering the body and to prevent bodily tissues from becoming dehydrated. Structure The mucosa is composed of one or more layers of epithelial cells that secrete mucus, and an underlying lamina propria of loose connective tissue. The type of cells and type of mucus secreted vary from organ to organ and each can differ along a given tract. Mucous membranes line the digestive, respiratory and reproductive trac ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Levator Labii Superioris
The levator labii superioris (pl. ''levatores labii superioris'', also called quadratus labii superioris, pl. ''quadrati labii superioris'') is a muscle of the human body used in facial expression. It is a broad sheet, the origin of which extends from the side of the nose to the zygomatic bone. Structure Its medial fibers form the ''angular head'' (also known as the levator labii superioris alaeque nasi muscle,) which arises by a pointed extremity from the upper part of the frontal process of the maxilla and passing obliquely downward and lateralward divides into two slips. One of these is inserted into the greater alar cartilage and skin of the nose; the other is prolonged into the lateral part of the upper lip, blending with the infraorbital head and with the orbicularis oris. The intermediate portion or ''infraorbital head'' arises from the lower margin of the orbit immediately above the infraorbital foramen, some of its fibers being attached to the maxilla, others to the zy ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |


.jpg)

