|
Lingwu Museum
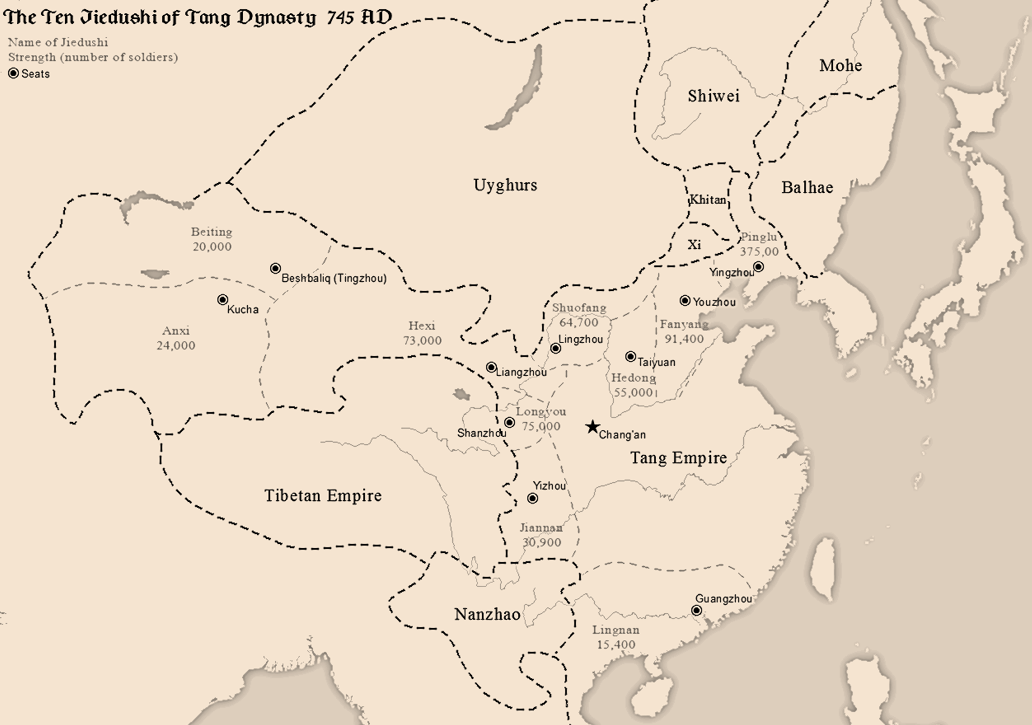
Lingwu (, Xiao'erjing: لِئٍوُ شِ) is a county-level city of Ningxia Hui Autonomous Region, Southwest China, it is under the administration of the prefecture-level city of Yinchuan. It is the most important industrial city of Ningxia. Lingwu spans an area of , and according to the 2010 Chinese census, Lingwu has a population of 261,677. Toponymy Lingwu was historically known as Lingzhou (, Xiao'erjing: لِئٍجِوْ). History During the Warring States period, the area was absorbed into the Qin dynasty under Beidi Commandery. The area was first incorporated into the Han dynasty in 191 BCE by Emperor Hui. In 437 CE, under the Northern Wei, the area was incorporated as . In 526 CE, Bogulu Town was renamed as Lingzhou. In 756 CE, during the Tang dynasty, Emperor Suzong fled to Lingzhou during the Anshi Rebellion, where he ascended the throne with the aid of loyal bureaucrats and military supporters, only notifying his father Xuanzong after the fact. Lingzho ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
County-level City
A county-level municipality (), county-level city or county city, formerly known as prefecture-controlled city (1949–1970: ; 1970–1983: ), is a Administrative divisions of China#County level (3rd), county-level administrative division of the China, People's Republic of China. County-level cities have judiciary, judicial but no legislature, legislative rights over their own local ordinance, local law and are usually governed by Administrative divisions of China#Prefectural level (2nd), prefecture-level divisions, but a few are governed directly by Administrative divisions of China#Provincial level (1st), province-level divisions. A county-level city is a "city" () and "county" () that have been merged into one unified jurisdiction. As such it is simultaneously a city, which is a municipal entity and a county which is an administrative division of a prefecture. Most county-level cities were created in the 1980s and 1990s by replacing denser populated Counties of Chin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Emperor Hui Of Han
Emperor Hui of Han (Liu Ying 劉盈; 210 BC – 26 September 188 BC) was the second emperor of the Chinese Han dynasty. He is also known as Han Huidi (Chinese: 漢惠帝 ''Hàn Huìdì''). He was the second son of Emperor Gaozu (Liu Bang, of the Liu family), the first Han emperor, and Empress Lü from the powerful Lü clan (House of Lü). Han Huidi is generally remembered as a somewhat weak character dominated and terrorized by his mother, Lü (Lu Hou, who became Empress Dowager after she encouraged her husband to command personally a war in which he died from an arrow wound). Huidi was personally kind and generous, but unable to escape the impact of Lu Hou's viciousness. However he did end the laws of Burning of books and burying of scholars. He tried to protect Ruyi, Prince Yin of Zhao, his younger half-brother, from being murdered by Empress Dowager Lü, but failed. After that, he indulged himself in drinking and sex, and died at a relatively young age. Emperor Hui's wife wa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Townships Of China
Townships (), formally township-level divisions (), are the basic level (fourth-level administrative units) of political divisions in China. They are similar to municipalities and communes in other countries and in turn may contain village committees and villages. In 1995 there were 29,502 townships and 17,532 towns (a total of 47,034 township-level divisions) in China. Much like other levels of government in mainland China, the township's governance is divided between the Communist Party Township Secretary, and the "county magistrate" (). The township party secretary, along with the township's party committee, determines policy. The magistrate is in charge of administering the daily affairs of government and executing policies as determined by the party committee. A township official is the lowest-level ranked official in the civil service hierarchy; in practice, however, the township party secretary and magistrate can amass high levels of personal power. A township government ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Towns Of China
When referring to political divisions of China, town is the standard English translation of the Chinese (traditional: ; ). The Constitution of the People's Republic of China classifies towns as third-level administrative units, along with for example townships (). A township is typically smaller in population and more remote than a town. Similarly to a higher-level administrative units, the borders of a town would typically include an urban core (a small town with the population on the order of 10,000 people), as well as rural area with some villages (, or ). Map representation A typical provincial map would merely show a town as a circle centered at its urban area and labeled with its name, while a more detailed one (e.g., a map of a single county-level division) would also show the borders dividing the county or county-level city into towns () and/or township () and subdistrict (街道) units. The town in which the county level government, and usually the division's mai ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Subdistricts Of China
A subdistrict ()' is one of the smaller administrative divisions of China. It is a form of township-level division which is typically part of a larger urban area, as opposed to a discrete town (zhèn, 镇) surrounded by rural areas, or a rural township (xiāng, 乡). In general, urban areas are divided into subdistricts and a subdistrict is sub-divided into several residential communities or neighbourhood A neighbourhood (British English, Irish English, Australian English and Canadian English) or neighborhood (American English; see spelling differences) is a geographically localised community within a larger city, town, suburb or rural are ...s as well as into villagers' groups (居民区/居住区, 小区/社区, 村民小组). The subdistrict's administrative agency is the subdistrict office ()"【街道办事处】 jiēdào bànshìchù 市辖区、不设区的市的人民政府派出机关。在上一级政府领导下,负责本辖区内的社区服务、经� ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Yellow River
The Yellow River or Huang He (Chinese: , Standard Beijing Mandarin, Mandarin: ''Huáng hé'' ) is the second-longest river in China, after the Yangtze River, and the List of rivers by length, sixth-longest river system in the world at the estimated length of . Originating in the Bayan Har Mountains in Qinghai province of Western China, it flows through nine provinces, and it empties into the Bohai Sea near the city of Dongying in Shandong province. The Yellow River basin has an east–west extent of about and a north–south extent of about . Its total drainage area is about . The Yellow River's basin was the Yellow River civilization, birthplace of ancient Chinese, and, by extension, Far East, Far Eastern civilization, and it was the most prosperous region in early Chinese history. There are frequent devastating natural disasters in China, floods and course changes produced by the continual elevation of the river bed, sometimes above the level of its surrounding farm fi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wuzhong, Ningxia
Wuzhong (, Xiao'erjing: وُجْو شِ) is a prefecture-level city in the Ningxia autonomous region of the People's Republic of China. It was known as Yinnan Prefecture (, Xiao'erjing: ءٍنًا دِٿِيُوِ) before it was upgraded to a prefecture-level city in 1998. In 2019, Wuzhong had a population of 1.4 million. Wuzhong is located in the Northwest of China, with the Yellow River flowing through the center of the city. Administrative divisions History During the early and mid-19th century, the territory of today's Wuzhong—as well as much of the northern Ningxia—became a stronghold of the Jahriyya Sufi order (''menhuan''), which was headquartered in the town of Jinjipu (a few km south of today's Wuzhong's main urban area). Under the leadership of the order's fourth and fifth ''shaykhs'', Ma Yide (the 1770s-1849) and Ma Hualong (d. 1871), it grew wealthy from the profits of caravan trade across Inner Mongolia, between Baotou, Huhhot and Beijing. Jinjipu became a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Counties Of China
Counties ( zh, t=縣, s=县, hp=Xiàn), formally county-level divisions, are found in the third level of the administrative hierarchy in Provinces and Autonomous regions and the second level in municipalities and Hainan, a level that is known as "county level" and also contains autonomous counties, county-level cities, banners, autonomous banners and City districts. There are 1,355 counties in Mainland China out of a total of 2,851 county-level divisions. The term ''xian'' is sometimes translated as "district" or "prefecture" when put in the context of Chinese history. History ''Xian'' have existed since the Warring States period and were set up nationwide by the Qin Dynasty. The number of counties in China proper gradually increased from dynasty to dynasty. As Qin Shi Huang reorganized the counties after his unification, there were about 1,000. Under the Eastern Han Dynasty, the number of counties increased to above 1,000. About 1400 existed when the Sui dynasty abolish ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Genghis Khan
''Chinggis Khaan'' ͡ʃʰiŋɡɪs xaːŋbr />Mongol script: ''Chinggis Qa(gh)an/ Chinggis Khagan'' , birth_name = Temüjin , successor = Tolui (as regent)Ögedei Khan , spouse = , issue = , house = Borjigin , dynasty = Genghisid , regnal name = Genghis Khan () , temple name = Taizu () , posthumous name = Emperor Fatian Qiyun Shengwu () , father = Yesügei , mother = Hoelun , religion = Tengrism , birth_date = , birth_place = Khentii Mountains, Khamag Mongol , death_date = (aged 64–65) , death_place = Xingqing, Western Xia , burial_place = Unknown(presumptively Ikh Khorig, Burkhan Khaldun, Khentii Province) Genghis Khan (born Temüjin; ; xng, Temüjin, script=Latn; ., name=Temujin – August 25, 1227) was the founder and first Great Khan (Emperor) of the Mongol Empire, which became the largest contiguous empire in history after his death. He came to power by uniting many of the nomadic tribes of t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Western Xia
The Western Xia or the Xi Xia (), officially the Great Xia (), also known as the Tangut Empire, and known as ''Mi-nyak''Stein (1972), pp. 70–71. to the Tanguts and Tibetans, was a Tangut-led Buddhist imperial dynasty of China that existed from 1038 to 1227. At its peak, the dynasty ruled over the modern-day northwestern Chinese provinces of Ningxia, Gansu, eastern Qinghai, northern Shaanxi, northeastern Xinjiang, and southwest Inner Mongolia, and southernmost Outer Mongolia, measuring about . Its capital was Xingqing (modern Yinchuan), until its destruction by the Mongols in 1227. Most of its written records and architecture were destroyed, so the founders and history of the empire remained obscure until 20th-century research in China and the West. The Western Xia occupied the area around the Hexi Corridor, a stretch of the Silk Road, the most important trade route between northern China and Central Asia. They made significant achievements in literature, art, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Emperor Xuanzong Of Tang
Emperor Xuanzong of Tang (; 8 September 685 – 3 May 762), personal name Li Longji, was the seventh emperor of the Tang dynasty in China, reigning from 712 to 756 CE. His reign of 44 years was the longest during the Tang dynasty. In the early half of his reign he was a diligent and astute ruler. Ably assisted by capable chancellors like Yao Chong, Song Jing and Zhang Yue, he was credited with bringing the Tang dynasty to a pinnacle of culture and power. Emperor Xuanzong, however, because of his interest in his two beloved concubines who were involved in governmental matters ( Consort Wu and later with her death; was succeeded by Yang Guifei) and was blamed for over-trusting Li Linfu, Yang Guozhong and An Lushan during his late reign, with Tang's golden age ending in the An Lushan Rebellion. Background Li Longji was born at the Tang dynasty eastern capital Luoyang in 685, during the first reign of his father Emperor Ruizong (Li Dan) – but at that time, Emperor Ruizong's mo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anshi Rebellion
The An Lushan Rebellion was an uprising against the Tang dynasty of China towards the mid-point of the dynasty (from 755 to 763), with an attempt to replace it with the Yan dynasty. The rebellion was originally led by An Lushan, a general officer of the Tang military system. The event involved military activity and direct deaths from battle, but also significant associated population loss from famine, and population dislocations. The event is also known, especially in Chinese historiography, either as the An–Shi Rebellion or as the An–Shi Disturbances (). The use of the term ''luàn'' ("chaos") indicates the extreme social instability and population loss which eventually resulted, far beyond the initial consequences of the rebellion. Traditionally, Chinese family names have begun with the family name first. In this case the family name of the initial rebel leader is An. The term ''Ān-Shǐ'' is used to recognize that the rebellion continued after An Lushan's death, with t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |




.jpg)