|
Lindsay-Shapley Ring
AM 0644-741, also known as the Lindsay-Shapley Ring, is an unbarred lenticular galaxy, and a ring galaxy, which is 300 million light-years away in the southern constellation Volans. Properties Formation The yellowish nucleus was once the center of a normal spiral galaxy, and the ring which currently surrounds the center is 150,000 light years in diameter. The ring is theorized to have formed by a collision with another galaxy, which triggered a gravitational disruption that caused dust in the galaxy to condense and form stars, which forced it to then expand away from the galaxy and create a ring. Physical characteristics The ring is a region of rampant star formation dominated by young, massive, hot blue stars. The pink regions along the ring are rarefied clouds of glowing hydrogen gas Hydrogen is the chemical element with the symbol H and atomic number 1. Hydrogen is the lightest element. At standard conditions hydrogen is a gas of diatomic molecules having the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hubble Space Telescope
The Hubble Space Telescope (often referred to as HST or Hubble) is a space telescope that was launched into low Earth orbit in 1990 and remains in operation. It was not the first space telescope, but it is one of the largest and most versatile, renowned both as a vital research tool and as a public relations boon for astronomy. The Hubble telescope is named after astronomer Edwin Hubble and is one of NASA's Great Observatories. The Space Telescope Science Institute (STScI) selects Hubble's targets and processes the resulting data, while the Goddard Space Flight Center (GSFC) controls the spacecraft. Hubble features a mirror, and its five main instruments observe in the ultraviolet, visible, and near-infrared regions of the electromagnetic spectrum. Hubble's orbit outside the distortion of Earth's atmosphere allows it to capture extremely high-resolution images with substantially lower background light than ground-based telescopes. It has recorded some of the most detaile ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
J2000
In astronomy, an epoch or reference epoch is a instant, moment in time used as a reference point for some time-varying astronomical quantity. It is useful for the celestial coordinates or orbital elements of a Astronomical object, celestial body, as they are subject to Perturbation (astronomy), perturbations and vary with time. These time-varying astronomical quantities might include, for example, the mean longitude or mean anomaly of a body, the node of its orbit relative to a reference plane, the direction of the apogee or Perihelion and aphelion, aphelion of its orbit, or the size of the major axis of its orbit. The main use of astronomical quantities specified in this way is to calculate other relevant parameters of motion, in order to predict future positions and velocities. The applied tools of the disciplines of celestial mechanics or its subfield orbital mechanics (for predicting orbital paths and positions for bodies in motion under the gravitational effects of other bodi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
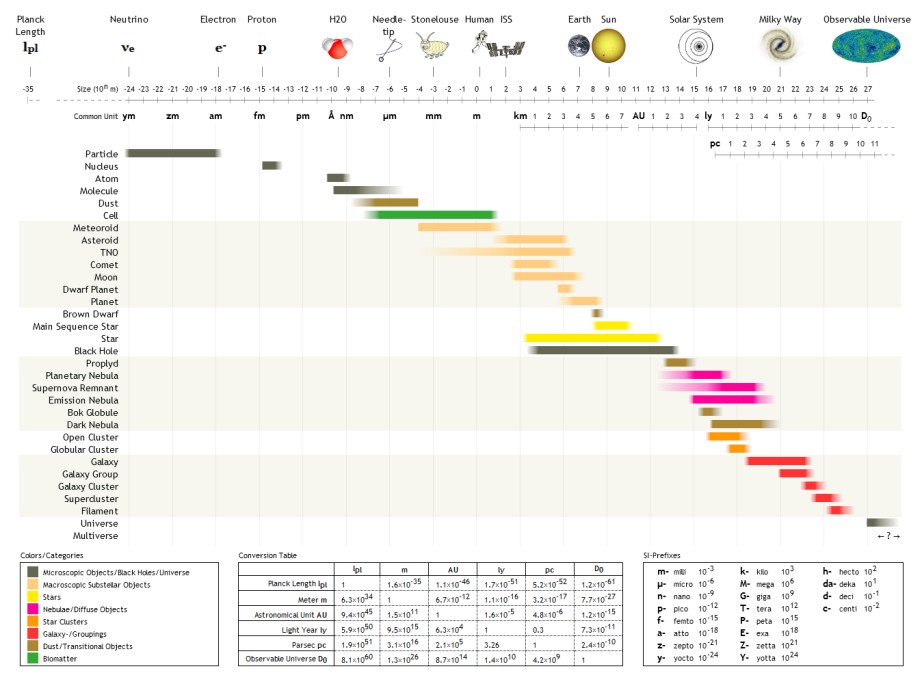
1 E24 M
The following are examples of order of magnitude, orders of magnitude for different lengths. __TOC__ Overview Detailed list To help compare different orders of magnitude, the following list describes various lengths between 1.6 \times 10^ metres and 10^metres. Subatomic scale Atomic to cellular scale Cellular to human scale Human to astronomical scale Astronomical scale Less than 1 zeptometre The ' (SI symbol: ') is a Units of measurement, unit of length in the metric system equal to . To help compare different orders of magnitude, this section lists lengths shorter than 10−21 metre, m (1 zm). *1.6 × 10−5 quectometres (1.6 × 10−35 metres) – the Planck length (Measures of distance shorter than this do not make physical sense, according to current theories of physics.) *1 qm – 1 quectometre, the smallest named subdivision of the metre in the SI base unit of length, one nonillionth of a metre *1 rm – 1 rontometre, a subdivision of the metre ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Light-year
A light-year, alternatively spelled light year, is a large unit of length used to express astronomical distances and is equivalent to about 9.46 trillion kilometers (), or 5.88 trillion miles ().One trillion here is taken to be 1012 (one million million, or billion in long scale). As defined by the International Astronomical Union (IAU), a light-year is the distance that light travels in a vacuum in one Julian year (365.25 days). Because it includes the time-measurement word "year", the term ''light-year'' is sometimes misinterpreted as a unit of time. The ''light-year'' is most often used when expressing distances to stars and other distances on a galactic scale, especially in non-specialist contexts and popular science publications. The unit most commonly used in professional astronomy is the parsec (symbol: pc, about 3.26 light-years) which derives from astrometry; it is the distance at which one astronomical unit subtends an angle of one second of arc. Defini ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Second
The second (symbol: s) is the unit of time in the International System of Units (SI), historically defined as of a day – this factor derived from the division of the day first into 24 hours, then to 60 minutes and finally to 60 seconds each (24 × 60 × 60 = 86400). The current and formal definition in the International System of Units ( SI) is more precise:The second ..is defined by taking the fixed numerical value of the caesium frequency, Δ''ν''Cs, the unperturbed ground-state hyperfine transition frequency of the caesium 133 atom, to be when expressed in the unit Hz, which is equal to s−1. This current definition was adopted in 1967 when it became feasible to define the second based on fundamental properties of nature with caesium clocks. Because the speed of Earth's rotation varies and is slowing ever so slightly, a leap second is added at irregular intervals to civil time to keep clocks in sync with Earth's rotation. Uses Analog clocks and watches often ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Volans
Volans is a constellation in the southern sky. It represents a flying fish; its name is a shortened form of its original name, Piscis Volans. Volans was one of twelve constellations created by Petrus Plancius from the observations of Pieter Dirkszoon Keyser and Frederick de Houtman and it first appeared on a 35-cm diameter celestial globe published in 1597 (or 1598) in Amsterdam by Plancius with Jodocus Hondius. The first depiction of this constellation in a celestial atlas was in Johann Bayer's ''Uranometria'' of 1603. History Volans is one of the 12 constellations that were introduced by the Dutch navigators Pieter Dirkszoon Keyser and Frederick de Houtman in the late 16th century. It was first depicted on Petrus Plancius’ globe in 1598. Plancius called the constellation ''Vliegendenvis'' (flying fish). In 1603, Johann Bayer included the constellation in his star atlas ''Uranometria'' under the name Piscis Volans, the flying fish. John Herschel proposed shrinking the name to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Unbarred Lenticular Galaxy
An unbarred spiral galaxyAstronomy Pictures(accessed 18 April 2010) is a type of spiral galaxy without a central bar, or one that is not a barred spiral galaxy. It is designated with an SA in the galaxy morphological classification scheme. Barless spiral galaxies are one of three general types of spiral galaxies under the ''de Vaucouleurs system'' classification system, the other two being intermediate spiral galaxy An intermediate spiral galaxy is a galaxy that is in between the classifications of a barred spiral galaxy and an unbarred spiral galaxy. It is designated as SAB in the galaxy morphological classification system devised by Gerard de Vaucouleu ... and barred spiral galaxy. Under the ''Hubble tuning fork'', it is one of two general types of spiral galaxy, the other being barred spirals. Grades Unbarred lenticular galaxy An unbarred lenticular galaxy is a lenticular version of an unbarred spiral galaxy. They have the Hubble type of SA0. An example ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ring Galaxy
A ring galaxy is a galaxy with a circle-like appearance. Hoag's Object, discovered by Art Hoag in 1950, is an example of a ring galaxy. The ring contains many massive, relatively young blue stars, which are extremely bright. The central region contains relatively little luminous matter. Some astronomers believe that ring galaxies are formed when a smaller galaxy passes through the center of a larger galaxy. Because most of a galaxy consists of empty space, this "collision" rarely results in any actual collisions between stars. However, the gravitational disruptions caused by such an event could cause a wave of star formation to move through the larger galaxy. Other astronomers think that rings are formed around some galaxies when external accretion takes place. Star formation would then take place in the accreted material because of the shocks and compressions of the accreted material. Formation theories Ring galaxies are theorized to be formed through various methods including, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gravitational
In physics, gravity () is a fundamental interaction which causes mutual attraction between all things with mass or energy. Gravity is, by far, the weakest of the four fundamental interactions, approximately 1038 times weaker than the strong interaction, 1036 times weaker than the electromagnetic force and 1029 times weaker than the weak interaction. As a result, it has no significant influence at the level of subatomic particles. However, gravity is the most significant interaction between objects at the macroscopic scale, and it determines the motion of planets, stars, galaxies, and even light. On Earth, gravity gives weight to physical objects, and the Moon's gravity is responsible for sublunar tides in the oceans (the corresponding antipodal tide is caused by the inertia of the Earth and Moon orbiting one another). Gravity also has many important biological functions, helping to guide the growth of plants through the process of gravitropism and influencing the circulatio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hydrogen
Hydrogen is the chemical element with the symbol H and atomic number 1. Hydrogen is the lightest element. At standard conditions hydrogen is a gas of diatomic molecules having the formula . It is colorless, odorless, tasteless, non-toxic, and highly combustible. Hydrogen is the most abundant chemical substance in the universe, constituting roughly 75% of all normal matter.However, most of the universe's mass is not in the form of baryons or chemical elements. See dark matter and dark energy. Stars such as the Sun are mainly composed of hydrogen in the plasma state. Most of the hydrogen on Earth exists in molecular forms such as water and organic compounds. For the most common isotope of hydrogen (symbol 1H) each atom has one proton, one electron, and no neutrons. In the early universe, the formation of protons, the nuclei of hydrogen, occurred during the first second after the Big Bang. The emergence of neutral hydrogen atoms throughout the universe occurred about 370,000 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
HubbleSite
The Space Telescope Science Institute (STScI) is the science operations center for the Hubble Space Telescope (HST), science operations and mission operations center for the James Webb Space Telescope (JWST), and science operations center for the Nancy Grace Roman Space Telescope. STScI was established in 1981 as a community-based science center that is operated for NASA by the Association of Universities for Research in Astronomy (AURA). STScI's offices are located on the Johns Hopkins University Homewood Campus and in the Rotunda building in Baltimore, Maryland. In addition to performing continuing science operations of HST and preparing for scientific exploration with JWST and Roman, STScI manages and operates the Mikulski Archive for Space Telescopes (MAST), which holds data from numerous active and legacy missions, including HST, JWST, Kepler, TESS, Gaia, and Pan-STARRS. Most of the funding for STScI activities comes from contracts with NASA's Goddard Space Flight Center bu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ring Galaxies
A ring galaxy is a galaxy with a circle-like appearance. Hoag's Object, discovered by Art Hoag in 1950, is an example of a ring galaxy. The ring contains many massive, relatively young blue stars, which are extremely bright. The central region contains relatively little luminous matter. Some astronomers believe that ring galaxies are formed when a smaller galaxy passes through the center of a larger galaxy. Because most of a galaxy consists of empty space, this "collision" rarely results in any actual collisions between stars. However, the gravitational disruptions caused by such an event could cause a wave of star formation to move through the larger galaxy. Other astronomers think that rings are formed around some galaxies when external accretion takes place. Star formation would then take place in the accreted material because of the shocks and compressions of the accreted material. Formation theories Ring galaxies are theorized to be formed through various methods includi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |